(Press-News.org) As more medications move toward federal approval for Alzheimer’s disease, a new study led by researchers at UC San Francisco and Kaiser Permanente Washington has found that personalized health and lifestyle changes can delay or even prevent memory loss for higher-risk older adults.
The two-year study compared cognitive scores, risk factors and quality of life among 172 participants, of whom half had received personalized coaching to improve their health and lifestyle in areas believed to raise the risk of Alzheimer’s, such as uncontrolled diabetes and physical inactivity. These participants were found to experience a modest boost in cognitive testing, amounting to a 74% improvement over the non-intervention group.
Improvements were also noted between the two groups in measurements of risk factors and quality of life, translating approximately to 145% and 8%, respectively, the researchers reported. The study publishes Nov. 27, 2023, in JAMA IM.
Older adults highly motivated to make changes
The study, known as SMARRT, for systematic multi-domain Alzheimer’s risk reduction trial, follows previous work from other researchers that has yielded contradictory results on the effects of health and lifestyle interventions. This study differed, though, in providing personal coaching that was customized to each participant.
“This is the first personalized intervention, focusing on multiple areas of cognition, in which risk factor targets are based on a participant’s risk profile, preferences and priorities, which we think may be more effective than a one-size-fits-all approach,” said first author and lead investigator Kristine Yaffe, MD, vice chair of research in psychiatry and professor in the UCSF departments of neurology, psychiatry, and epidemiology and biostatistics. “Not only did we find a significant reduction in risk factors, this is one of only a few trials that has shown a benefit in cognition that likely translates to lower dementia risk.
“In an earlier survey of 600 older adults, we found that most were concerned about Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias. They wanted to know their personal risk factors and were highly motivated to make lifestyle changes to lower dementia risk,” said Yaffe, referring to her collaboration with co-lead investigator and co-author Eric B. Larson, MD, MPH, former vice president for research and health care intervention at Kaiser Permanente Washington.
Participants in the current study, as well as the earlier survey, were enrolled in Kaiser Permanente Washington and were between 70 and 89 years old. They had at least two of eight risk factors for dementia: physical inactivity, uncontrolled hypertension, uncontrolled diabetes, poor sleep, use of prescription medications associated with risk of cognitive decline, high depressive symptoms, social isolation and current smoking status.
The intervention participants met with a nurse and health coach and selected specific risk factors they wanted to address. They received coaching sessions every few months to review their goals, which ranged from tracking hypertension to walking a certain number of steps per day or signing up for a class. The meetings started in person and switched to phone calls during the pandemic.
Non-intervention participants were similar in age, risk factors and cognitive scores and received educational material, mailed every three months, on dementia risk reduction.
Pandemic did not offset study’s positive effects
“We were pleasantly surprised that the positive results of the trial were not offset by the impact of the pandemic,” said Larson, who is currently professor of medicine at University of Washington. “We know that isolation from social distancing took a heavy toll on cognition, social lives, and mental and physical health in some older adults. But participants in the intervention group fared better cognitively and had fewer risk factors after the trial, during the pandemic, than they did before.”
Unlike anti-amyloid medications, risk-reduction programs are not costly, nor do they have strict eligibility criteria or require extensive monitoring for side-effects, said Yaffe, who is also affiliated with the San Francisco VA Health Care System and the UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences.
“Hopefully in the future, treatment of Alzheimer’s and related dementias will be like cardiovascular disease management, with a combination of risk-reduction and specific drugs targeted for disease mechanisms,” she said.
Co-Authors: Eric Vittinghoff, PhD, and Deborah E. Barnes, PhD, MPH, of UCSF; Carrie B. Peltz, PhD, of the San Francisco VA Health Care System; and Sascha Dublin, MD, PhD, Lynn Fleckenstein, MA, Dori Rosenberg, PhD, MPH, and Benjamin H. Balderson, PhD, of Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute, Seattle.
Funding Support: National Institute on Aging (1R01AG057508)
Disclosures: Please see the paper.
About UCSF: The University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) is exclusively focused on the health sciences and is dedicated to promoting health worldwide through advanced biomedical research, graduate-level education in the life sciences and health professions, and excellence in patient care. UCSF Health, which serves as UCSF's primary academic medical center, includes top-ranked specialty hospitals and other clinical programs, and has affiliations throughout the Bay Area. UCSF School of Medicine also has a regional campus in Fresno. Learn more at https://ucsf.edu, or see our Fact Sheet.
###
Follow UCSF
ucsf.edu | Facebook.com/ucsf | YouTube.com/ucsf
END
Can health, lifestyle changes protect elders from Alzheimer's?
2023-11-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Millions of kids in U.S. have inadequate health care coverage
2023-11-28
November 28, 2023-- Inadequate health coverage is a particular problem for commercially insured children, according to a new study released by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. The research shows that coverage gaps are affecting publicly insured children as well. Until now, prior research had focused on documenting rates and trends in insurance consistency for children covered by all insurance types. The findings are published in JAMA Health Forum.
“While uninsurance among children has generally been declining in the U.S., our results highlight the need for a renewed focus on making sure that children’s ...
NIH awards $2.6 million to Wayne State to develop new filtration platform for insulin administration
2023-11-28
DETROIT – A Wayne State University College of Engineering professor has received a $2.65 million award from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases of the National Institutes of Health to develop a novel filtration platform to improve an advanced drug delivery device to optimize diabetes insulin treatments.
Subcutaneous insulin administration (SIA) technology has improved significantly over the past two decades, but SIA technology failure and underlying tissue damage caused by insulin phenolic preservatives ...
Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees approves plans to transform healthcare, improve experience for staff and patients, redesign Rochester campus
2023-11-28
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Mayo Clinic’s Board of Trustees has approved Bold. Forward. Unbound. in Rochester, a multiyear strategic initiative that advances Mayo Clinic’s Bold. Forward. strategy to Cure, Connect and Transform healthcare for the benefit of patients everywhere. It reimagines Mayo Clinic’s downtown Rochester campus and introduces new facilities with a combination of innovative care concepts and digital technologies that will give Mayo Clinic the ability to scale transformation ...
Threats against public health workers doubled during the COVID-19 pandemic
2023-11-28
While doctors and nurses were hailed as the frontline heroes of the COVID-19 pandemic, their counterparts in public health were experiencing threats. During the pandemic, threats against public health workers reached an all-time high. After the vaccine was released, those threats increased and changed in nature, according to a longitudinal study conducted during the first year of the pandemic by Jennifer Horney, founder of the University of Delaware Epidemiology Program in the College of Health Sciences.
The results, recently published in an open-access commentary in Public Health in Practice, show a strong need for expanded legal protections ...
Reducing inequitable health outcomes requires reducing residential segregation
2023-11-28
The U.S. must reduce racial residential segregation if it is to reduce racial disparities in health outcomes, according to a recently published study by researchers at Tufts University School of Medicine. The research on 220 metropolitan areas nationwide between 1980 and 2020 found strong links between trends in racial residential segregation and racial disparities in early death rates from a variety of causes.
The study is the first known to examine the association between changes in racial segregation over time ...
Manard named recipient of 2023 JAAS Emerging Investigator Lectureship
2023-11-28
Manard named recipient of 2023 JAAS Emerging Investigator Lectureship
Benjamin Manard, an analytical chemist in the Chemical Sciences Division of the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, has been selected for the 2023 Emerging Investigator Lectureship from the Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry. JAAS is a publication of the Royal Society of Chemistry that shares innovative research on the fundamental theory and application of spectrometric techniques. Manard is the first winner of this award from a Department of Energy ...
Alcohol consumption may have positive and negative effects on cardiovascular disease risk
2023-11-28
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
November 28, 2023
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
Lisa LaPoint, lisa.lapoint@tufts.edu
##
While past research has indicated that moderate alcohol consumption can lower one’s risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD), more recent studies suggest that moderate levels of drinking may be hazardous to heart health. ...
Anti-aging effects of 1,5-anhydro-D-fructose on brain diseases via AMPK activation
2023-11-28
A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 21, entitled, “1,5-anhydro-D-fructose induces anti-aging effects on aging-associated brain diseases by increasing 5’-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase activity via the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ co-activator-1α/brain-derived neurotrophic factor pathway.”
5’-Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a metabolic sensor that serves as a cellular housekeeper; it also controls energy homeostasis and stress resistance. Thus, correct regulation ...
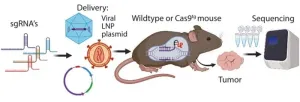
The double-edge sword of CRISPR application for in vivo studies
2023-11-28
“The Achilles’ heel of CRISPR application is the delivery of sgRNA/Cas9 to the desired tissues.”
BUFFALO, NY- November 28, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on November 27, 2023, entitled, “The double-edge sword of CRISPR application for in vivo studies.”
In this new paper, researcher Martin K. Thomsen from Aarhus University begins his editorial by discussing a hallmark paper that was published a decade ago by Platt et al. on the in vivo ...
UTA research examines how to stay on task
2023-11-28
Our ability to pay attention to tasks—a key component of our everyday lives—is heavily influenced by factors like motivation, arousal and alertness. Maintaining focus can be especially challenging when the task is boring or repetitive.
“In many activities, it is difficult to maintain a high level of focus over time. Our research asks why this is the case,” said Matthew K. Robison, assistant professor of psychology at The University of Texas at Arlington.
He and colleagues at the University ...