Novel study finds aspirin-free regimen benefits patients with LVAD
2023-11-29
(Press-News.org) The ARIES-HM3 Randomized Clinical Trial assessed the safety and efficacy of excluding aspirin from the antithrombotic regimen in patients with advanced heart failure who have undergone implantation of a fully magnetically levitated left ventricular assist device (LVAD).
“We can now safely say that not giving aspirin is not only safe from a thromboembolic risk profile but results in improved adverse event rate by a significant reduction in non-surgical bleeding which is a well-known complication related to LVAD therapy,” said Mirnela Byku, M.D., Ph.D., MBA, co-author of the study and director of the UNC Durable Mechanical Circulatory Device Program at the UNC School of Medicine. “Improving not only longevity but also reducing morbidity and improving quality of life is a big focus in the field of MCS.”
Until this study, there had been no consensus in the field about use of or dose of aspirin in the LVAD population. The paper was published in JAMA.
The international clinical trial followed a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled design and involved 628 patients across 51 centers in 9 countries. The patients were divided into two groups: one receiving aspirin (100mg/d) and the other receiving a placebo in addition to vitamin K antagonist (VKA) therapy.
A focus was to determine if the likelihood a patient experiences major nonsurgical hemocompatibility-related adverse events (such as stroke, pump thrombosis, major bleeding, or arterial peripheral thromboembolism) within 12 months differed between the two groups.
The results showed not giving aspirin to patients with advanced heart failure, treated with a fully magnetically levitated LVAD who are receiving VKAs, did not make their survival worse. Furthermore, aspirin avoidance was associated with a significant reduction (34%) in major nonsurgical bleeding events.
About UNC School of Medicine
The UNC School of Medicine (SOM) is the state’s largest medical school, graduating more than 180 new physicians each year. It is consistently ranked among the top medical schools in the US, including 5th overall for primary care by US News & World Report, and 6th for research among public universities. More than half of the school’s 1,700 faculty members served as principal investigators on active research awards in 2021. Two UNC SOM faculty members have earned Nobel Prize awards.
# # # #
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-11-29
The frilled dog winkle may sound like a complex knot for a tie, but this local sea snail holds clues to our warmer future, including a dire outlook for species that can’t move, adapt, or acclimate as fast as their environment heats up.
Strait of Georgia hotspot
To figure out how location affects vulnerability to a changing climate, UBC zoology researchers Drs. Fiona Beaty and Chris Harley collected marine snails from the Strait of Georgia, a potential hot spot of climate risk, and the Central Coast, where waters are cooler and warming more slowly.
They monitored snails ...
2023-11-29
The San Joaquin Valley in California has experienced vast variability in climate extremes, with droughts and floods that were more severe and lasted longer than what has been seen in the modern record, according to a new study of 600 years of tree rings from the valley.
The researchers used the tree rings to reconstruct plausible daily records of weather and streamflow scenarios during the 600-year period.
This new approach, combining paleo information with synthetic weather generation, may help policymakers and scientists better understand – and anticipate ...
2023-11-29
We tend to think of large cities as melting pots – places where people from all sorts of backgrounds can mingle and interact. But according to new research, people in big cities tend to primarily interact with other individuals in the same socioeconomic bracket, whereas people in small cities and rural areas are much more likely to have diverse interactions.
Using cellphone data, a collaboration of researchers led by Stanford University determined that most people in big cities have very few opportunities for even brief interactions with those outside their own socioeconomic status. ...
2023-11-29
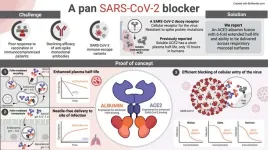
When the COVID-19 pandemic first started, no effective anti-viral drugs were available to fight the disease. However, in record time, so-called monoclonal antibodies were developed as a lifesaving treatment. Now, 3 years later, none of the approved antibodies work effectively against the new SARS-CoV-2 virus variants due to mutations that alter their spike protein.
While vaccines protect against severe disease, there is still an urgent need for effective virus-blocking agents for therapeutic or prophylactic use. This is particularly relevant for patients ...
2023-11-29
Despite a similar statutory tax rate for multinational corporations (MNCs) across many countries, the effective tax rate that MNCs actually pay differs greatly — as low as 1% of gross income in Luxembourg and as high as 67% in Norway. That’s one conclusion of a study published this week in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Javier Garcia-Bernardo of Utrecht University, the Netherlands, Petr Janský of Charles University, Czechia, and Thomas Tørsløv of Danmarks Nationalbank, Denmark. The study comes on the ...
2023-11-29
Ancient animals were walking around on bird-like feet over 210 million years ago, according to a study published November 29, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Miengah Abrahams and Emese M. Bordy of the University of Cape Town, South Africa.
Numerous fossil sites in southern Africa preserve distinctive three-toed footprints that have been named Trisauropodiscus. For many years, researchers have debated what animals might have left these tracks, as well as precisely how many different species (technically called ichnospecies) of Trisauropodiscus there are.
In this study, the researchers reassessed the ...
2023-11-29
Exercise may reduce postpartum depression, with moderate intensity exercises three to four times a week being especially effective, per meta-analysis
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0287650
Article Title: Effectiveness of aerobic exercise in the prevention and treatment of postpartum depression: Meta-analysis and network meta-analysis
Author Countries: China
Funding: This work was financially supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities in China (Grant no. CUG150607). The funders did not play a role ...
2023-11-29
Bacterial vaginosis is a common condition in which the natural microbiome of the vagina falls out of balance, sometimes leading to complications in sexual and reproductive health. But exactly how these bacterial populations disrupt vaginal health has remained unclear.
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine have now found that in bacterial vaginosis, certain bacterial species dismantle protective molecules on the surface of the cells lining the vagina, dysregulating key processes that mediate cell turnover, death and response to surrounding bacteria.
The findings, published November 29, 2023 in Science Translational Medicine, may help explain why bacterial ...
2023-11-29
The record storm surge in October 2023 caused severe damage to the German Baltic coast. Effective adaptation scenarios to rising sea levels are therefore becoming increasingly urgent. In two recent studies, researchers at Kiel University have modelled both the flooding extent along the Baltic Sea coastal areas and, for the first time, two possible upgrades for current dike lines in high resolution. They modelled various storm surge and sea level rise scenarios. Their results show that, based on the current dike line, neither an increase ...
2023-11-29
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- Some viruses move between species. For example, SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, can spill over from humans to mink, an agricultural species, and then spill back from mink to humans. Spill back is a concern because SARS-CoV-2 can mutate in the mink and come back to humans in a more virulent form. Both spill over and spill back of SARS-CoV-2 have been reported on mink farms in the United States and Europe.
To address these issues, a research team at the University of California, Riverside, has ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Novel study finds aspirin-free regimen benefits patients with LVAD