(Press-News.org) When diagnosed with a blood clot or atrial fibrillation, patients are often prescribed anticoagulants, or blood thinners, to prevent a future clot.
In a study of the three most commonly prescribed blood thinners, the oral anticoagulant rivaroxaban, known by the brand name Xarelto, was associated with a significantly higher risk of bleeding complications than apixaban (brand name Eliquis) and warfarin for patients with blood clots or atrial fibrillation.
The findings, reported at the 2023 American Society of Hematology’s Annual Meeting & Exposition, covered over 10 years of patient data from the Michigan Anticoagulation Quality Improvement Initiative registry. The multi-center initiative is sponsored by Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan.
“We found the highest rates of bleeding among patients who took rivaroxaban, followed by warfarin and then apixaban,” said Jordan K. Schaefer, M.D., first author and clinical associate professor of hematology at University of Michigan Medical School.
“We followed patients for over two years on average and were able to compare apixaban to rivaroxaban, something that has not yet been done in a randomized clinical trial. While the findings should be confirmed with randomized studies, they may have implications for providers as they select anticoagulants for their patients.”
Through their analysis, researchers found that if 100 patients were followed over 1 year, rivaroxaban resulted in nearly 40 bleeding events compared to around 25 for warfarin. Bleeding events were similar between apixaban and warfarin, but the latter medication was associated with more major bleeds.
The rate of blood clots was higher with apixaban compared to warfarin, but researchers say it seemed largely driven by other thrombotic events, which included events like heart attacks.
Of the three medications, apixaban was associated with a lower mortality rate than rivaroxaban and warfarin.
“These three medications are the most commonly prescribed anticoagulants for thrombosis and atrial fibrillation, and it is important that we continue to investigate the possible effect they carry as we attempt to best serve our patients,” said Geoffrey Barnes, M.D., M.Sc., senior author and associate professor of cardiology-internal medicine at U-M Medical School.
Additional authors include Josh Errickson, Ph.D., Xiaowen Kong, Naina Chipalkatti, M.D., Brian Haymart, R.N., Suman L. Wood, M.D., MSCE, and James Froehlich, M.D., M.P.H., all of University of Michigan, Mona A. Ali, PharmD., Corewell Health William Beaumont University Hospital, Scott Kaatz, D.O., M.Sc., Gregory D. Krol, M.D., both of Henry Ford Health.
Schaefer reports a consulting relationship with Pfizer. Barnes reports a consulting relationship with Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Bayer, AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Anthos, Abbott Vascular and Boston Scientific.
The opinions, beliefs and viewpoints expressed by the authors do not necessarily reflect those of Blue Cross Blue Shield of any of its employees.
END
Popular blood thinner associated with higher risk of bleeding complications
Researchers examined three of the most commonly prescribed blood thinners for patients with blood clots or atrial fibrillation
2023-12-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study shows tree nuts as snacks reduces metabolic syndrome risk in Millenials
2023-12-14
DAVIS, CA, December 14, 2023 – A recent study published online in the journal, Nutrients[1], suggests daily tree nut consumption reduces the risk of metabolic syndrome (MetSx) by improving waist circumference, lipid biomarkers, and/or insulin levels, without requiring calorie restriction, in young adults.
In a randomized, parallel arm, dietary intervention study design, researchers at Vanderbilt University Medical Center enrolled 84 men and women, ages 22-36, most of whom were either overweight or obese (BMI 24.5 to 34.9 kg/m2) and had at least one MetSx risk factor ...
Pattern of alcohol intake more accurate indicator of liver disease risk than overall consumption
2023-12-14
Those who binge drink and have a certain genetic makeup are six times more likely to develop alcohol-related cirrhosis, according to new research from UCL, the Royal Free Hospital, the University of Oxford and the University of Cambridge.
The study, published in Nature Communications, is the first to assess how an individual’s pattern of drinking, their genetic profile (via a polygenic risk score) and whether or not they have type-2 diabetes affects their risk of developing alcohol-related cirrhosis (ARC).
The observation that pattern of drinking is more important than volume, coupled with the increased risk when genetic makeup and type-2 diabetes are also present, ...
Spinal cord stimulation reduces pain, improves balance in people with lower limb amputation
2023-12-14
PITTSBURGH, Dec. 14, 2023 – Spinal cord stimulation can elicit sensation in the missing foot and alleviate phantom limb pain in people with lower limb amputations, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine rehabilitation scientists report today.
Pressure sensors on the insole of a prosthetic foot triggered electrical pulses that were then delivered to a participants’ spinal cord. Researchers found that this sensory feedback also improved balance and gait stability. The proof-of-concept study was done in collaboration with Carnegie Mellon ...
Eating meals early could reduce cardiovascular risk
2023-12-14
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death in the world according to the Global Burden of Disease study, with 18.6 million annual deaths in 2019, of which around 7.9 are attributable to diet. This means that diet plays a major role in the development and progression of these diseases. The modern lifestyle of Western societies has led to specific eating habits such as eating dinner late or skipping breakfast. In addition to light, the daily cycle of food intake (meals, snacks, etc.) alternating with periods of fasting synchronizes the peripheral clocks, or circadian rhythms, of the body’s various organs, thus ...
What do Gifted dogs have in common?
2023-12-14
All dog owners think that their pup is special. Science now has documented that some rare dogs are…even more special! They have a talent for learning hundreds of names of dog toys. Due to the extreme rarity of this phenomenon, until recently, very little was known about these dogs, as most of the studies that documented this ability included only a small sample of one or two dogs. In a new study published in the Journal Scientific Reports, researchers from the Family Dog Project (ELTE Eötvös Loránd University, Budapest) shed new light on the characteristics of these exceptional dogs.
In ...
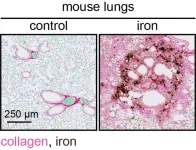
Iron accumulation: a new insight into fibrotic diseases
2023-12-14
Researchers at IRB Barcelona reveal the pivotal role of iron accumulation in the development of fibrotic diseases and propose that iron detection via MRI can serve to diagnose fibrosis.
Fibrotic diseases account for 45% of all mortality in developed countries.
Published in Nature Metabolism, the study points to new therapeutic opportunities that target iron.
Barcelona, 14 December 2023 – Fibrosis is associated with various chronic and life-threatening conditions, including pulmonary fibrosis, liver cirrhosis, kidney disease, and cardiovascular diseases, ...
Facial symmetry doesn’t explain “beer goggles”
2023-12-14
If you thought blurry eyes were to blame for the “beer goggles” phenomenon, think again.
Scientists from the University of Portsmouth have tested the popular theory that people are more likely to find someone attractive while drunk, because their faces appear more symmetrical.
The term “beer goggles” has been used for decades to describe when a person finds themselves sexually attracted to someone while intoxicated, but not sober.
One possible explanation for the effect is that alcohol impairs the drinker’s ability to detect facial asymmetry, ...
New study eyes nutrition-rich chia seed for potential to improve human health
2023-12-14
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Oregon State University scientists have sequenced the chia genome and in doing so provided a blueprint for future research that capitalizes on the nutritional and human health benefits of the plant.
In the just-published paper, the researchers identified chia genes associated with improving nutrition and sought after properties for pharmaceuticals that could be used to treat everything from cancer to high blood pressure. The seeds of the chia plant have received widespread attention in recent years because of the nutritional punch they pack.
Others have sequenced the chia genome, but this paper provides a more detailed look at the molecular ...
Were Neanderthals morning people ?
2023-12-14
A new paper in Genome Biology and Evolution, published by Oxford University Press, finds that genetic material from Neanderthal ancestors may have contributed to the propensity of some people today to be “early risers,” the sort of people who are more comfortable getting up and going to bed earlier.
All anatomically modern humans trace their origin to Africa around 300 thousand years ago, where environmental factors shaped many of their biological features. Approximately seventy-thousand years ago, the ancestors ...
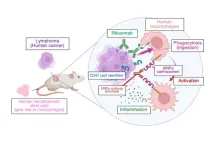
Mice with humanized immune systems to test cancer immunotherapies
2023-12-14
Mice with human immune cells are a new way of testing anti-cancer drugs targeting the immune system in pre-clinical studies. Using their new model, the Kobe University research team successfully tested a new therapeutic approach that blindfolds immune cells to the body’s self-recognition system and so makes them attack tumor cells.
Cancer cells display structures on their surface that identify them as part of the self and thus prevent them from being ingested by macrophages, a type of immune cell. Cancer immunotherapy aims at disrupting these recognition systems. Previous studies showed that a substance that blinds macrophages to one of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Popular blood thinner associated with higher risk of bleeding complicationsResearchers examined three of the most commonly prescribed blood thinners for patients with blood clots or atrial fibrillation