(Press-News.org) Ecological restoration may save coral atoll islands from the rising seas of climate change, according to an international team of scientists, conservationists, and an indigenous leader.
While global carbon emission reduction is imperative, local measures could be the key to the islands outpacing sea levels, they argue today in the journal Trends in Ecology & Evolution.
“Far from being doomed, in their natural state most coral atoll islands could adapt to sea level rise”, says Dr Sebastian Steibl from the University of Auckland in New Zealand, lead author of the study. “This paper is a global call to identify and quantify the best measures for restoring atoll island growth.”
The world’s 320 tropical coral atolls are made up of thousands of islands and are a treasure trove of biodiversity, homes to millions of turtles and seabirds. These islands are naturally growing up to 1 cm a year by accreting sediment – enough to outpace most predictions of sea level rise.
Ecologically restoring this natural process holds the key to climate change resilience for the islands, says the team of scientists, who are already trialling restoration methods on atolls such as Tetiaroa and Palmyra in the eastern Pacific Ocean and Aldabra in the western Indian Ocean.
While densely populated islands such as in the Maldives will still need human-engineered solutions most coral atoll islands are sparsely inhabited and excellent candidates for restoration, the scientists say.
“Restoration of atoll island ecosystems is a proven conservation action that can significantly improve the health of the surrounding coral reef habitat”, says island resilience scientist and co-author Dr Alex Wegmann from The Nature Conservancy in California.
The climate damage fund announced at COP28 is one potential mechanism for funding local restoration. “Funding restoration work would empower communities to take back ownership of their futures,” says co-author Professor James Russell, a conservation biologist at the University of Auckland
People living on coral atolls are largely ignored when industrialised nations negotiate responses to climate change. “Local knowledge alongside cutting edge science needs to be included in atoll restoration programs,” says cultural director of the Tetiaroa Society and co-author Hinano Teavai-Murphy, “because the traditional knowledge of Oceanian people has always been about respecting and preserving the connected marine and terrestrial systems.”
END
Coral atoll islands may outpace sea-level rise with local ecological restoration, scientists say
2023-12-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NIH researchers create genetic atlas detailing early stages of zebrafish development
2023-12-18
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health have published an atlas of zebrafish development, detailing the gene expression programs that are activated within nearly every cell type during the first five days of development, a period in which embryos mature from a single cell into distinct cell types. These diverse cells become tissues and organs that form juvenile fish capable of swimming and looking for food. The findings are published in Developmental Cell.
“Perhaps surprisingly, tiny zebrafish provide us with significant insight ...
Unleashing canine travel: Hospitality and tourism sector urged to adapt to dog-friendly travel demands
2023-12-18
Estimated to be worth USD 50.1 billion by 2030, a Surrey team of researchers has uncovered the potential of the growing dog-friendly travel market. The Covid-19 pandemic drove an increase in UK household dog ownership, creating a need for tourism providers to adapt to accommodate these four-legged family members.
The Surrey team set out to understand why people travel with their dogs, how they feel about it, and what challenges they face doing so.
Lori Hoy, PhD Researcher and lead author of the study at the University of Surrey, said:
"Some reports suggest that the UK dog population stands at 11 million, with 29% of UK adults having a dog in their ...
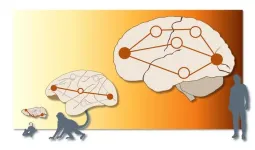
More parallel ‘traffic' observed in human brains than in animals
2023-12-18
In a study comparing human brain communication networks with those of macaques and mice, EPFL researchers found that only the human brains transmitted information via multiple parallel pathways, yielding new insights into mammalian evolution.
When describing brain communication networks, EPFL senior postdoctoral researcher Alessandra Griffa likes to use travel metaphors. Brain signals are sent from a source to a target, establishing a polysynaptic pathway that intersects multiple brain regions “like a road with many stops along the way.”
She explains that structural brain ...
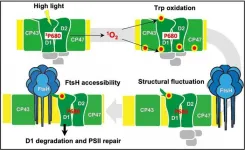
The role of oxidized tryptophan residues in repairing damaged photosystem II protein
2023-12-18
Photosynthesis refers to the fundamental biological process of the conversion of light energy into chemical energy by chlorophyll (a green pigment) containing plants. This seemingly routine process in plants sustains all the biological life and activities on Earth. First reaction of photosynthesis occurs at a site called photosystem II (PSII), present on the thylakoid membrane in the chloroplast where light energy is transferred to chlorophyll molecules. PSII is made up of a complex group of proteins, including the D1 and D2 reaction center proteins.
Light ...
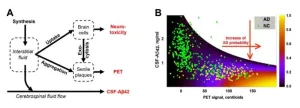
Breaking the mold: Zarbio and Georgia State scientists unveil game-changing theory on Alzheimer's disease
2023-12-18
Despite affecting millions worldwide, Alzheimer's disease (AD) has long lacked effective treatments due to a fundamental inadequacy of our understanding of its etiology and pathogenesis. The absence of an integrative theory connecting the molecular origins of AD with disturbances at the organelle and cell levels, changes in relevant biomarkers, and population-level prevalence has hindered progress. Even though most scientists only hope that an integrative theory of AD will emerge soon, scientists from Zarbio and Georgia State University discovered sufficient data to formulate a framework for such a theory.
The molecular and cellular ...
Scientists collect aardvark poop to understand how the species is impacted by climate in Africa
2023-12-18
CORVALLIS, Ore. – In a first-of-its-kind study of aardvarks, Oregon State University researchers spent months in sub-Saharan Africa collecting poop from the animal and concluded that aridification of the landscape is isolating them, which they say could have implications for their long-term survival.
“Everyone had heard of aardvarks and they are considered very ecologically important but there has been little study of them,” said Clint Epps, a wildlife biologist at Oregon State. “We wanted to see if we could collect enough data to begin to understand them.”
In ...
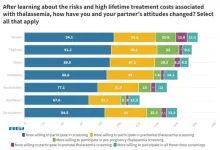
Thalassemia screening in Thailand: Medical Sciences Dean advocates for elevated trust
2023-12-18
- Insights from Professor Sakorn Pornprasert, Dean, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences at Chiang Mai University, on raising thalassemia awareness in Thailand.
Thalassemia, a genetic disorder affecting hemoglobin production, poses a significant public health challenge in Thailand, with a high prevalence and substantial healthcare costs. According to Thailand's Ministry of Public Health, approximately 18-24 million or 30-40 percent of the Thai population carries the thalassemia gene.
Professor Sakorn Pornprasert, Dean, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Chiang Mai University, shared his views on BGI Genomics Global 2023 State of Thalassemia Awareness ...
Lung nodule program provides benefits patients ineligible for lung cancer screening
2023-12-18
(Denver—December 18, 2023) – Adopting a lung nodule program (LNP) may increase the detection of early lung cancer for patients who are not eligible for lung cancer screening under existing age eligibility criteria, according to a study published in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, an official journal of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer.
LNPs are established to follow up on lung nodules that are frequently identified during routine imaging for reasons other than suspected lung cancer or lung cancer screening.
The research was conducted by a team led by Dr. Raymond U. Osarogiagbon, MBBS, FACP, chief scientist ...
Multi-site study reveals addressable socioeconomic barriers to prenatal diagnosis of congenital heart defects
2023-12-18
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital heart defects – the most common birth defects in the United States – is associated with improved outcomes. Despite its importance, however, overall prevalence of prenatal diagnosis is low (12-50 percent). A recent multi-center study surveyed caretakers of infants who received congenital heart surgery in the Chicago area and found that social determinants or influencers of health constitute significant barriers to prenatal diagnosis from the patients’ perspective.
In ...
Wildfires increasing across eastern U.S., new study reveals
2023-12-18
In a new analysis of data spanning more than three decades in the eastern United States, a team of scientists found a concerning trend – an increasing number of wildfires across a large swath of America.
“It’s a serious issue that people aren’t paying enough attention to: We have a rising incidence of wildfires across several regions of the U.S., not only in the West,” said Victoria Donovan, lead author of the study and an assistant professor of forest management at the UF/IFAS ...