(Press-News.org) The Korean artificial sun, KSTAR, has completed divertor upgrades, allowing it to operate for extended periods sustaining high-temperature plasma over the 100 million degrees.
The Korea Institute of Fusion Energy announced the successful installation of the newly developed tungsten divertor for KSTAR. KSTAR, now equipped with the new divertor, commenced a plasma experiment on the 21st of December 2023.
The divertor, a crucial plasma-facing component installed at the bottom of the vacuum vessel in a magnetic fusion device known as a Tokamak, manages the exhaust of waste gas and impurities from the reactor and also endures the highest surface heat loads. This is why it is important to develop and deploy a divertor that is highly heat-resistant.
Initially, KSTAR had a carbon divertor, but for KSTAR’s enhanced performance and prolonged operations at 100 million ℃, the heat flux exceeded the limit of the carbon divertor.
Consequently, the development of a divertor using tunsten has begun in 2018. The first prototype was completed in 2021, and installation of a new divertor took place from September 2022 for approximately one year. The recently installed divertor consists of 64 cassettes, each crafted from tungsten mono-blocks. These 64 cassettes fully surround the bottom of the vacuum vessel.
Tungsten material possesses a high melting point and low sputtering characteristics. Therefore, the heat flux limit has improved by over two-fold compared to the carbon divertor, reaching 10 MW/m².
The plasma experiments of KSTAR in the new tungsten divertor environment will continue until February 2024. The primary objectives include verifying stable operations in the new tungsten divertor environment and reproducing KSTAR’s 100-million-degree plasma.
KFE President, Dr. Suk Jae Yoo stated, "In KSTAR, we have implemented a divertor with tungsten material which is also the choice made in ITER. We will strive to contribute our best efforts in obtaining the necessary data for ITER through KSTAR experiments.”
Previously, KSTAR has demonstrated high performance plasma operation for 30 seconds with an ion temperatures over 100 million degrees, and now the goal is to achieve 300 seconds by the end of 2026 with this new divertor.
###
The Korea Institute of Fusion Energy(KFE) is Korea's only research institute specializing in nuclear fusion. Based on our development and operation of KSTAR, a superconducting fusion research device, the KFE seeks to achieve groundbreaking research results, develop core technology for commercializing nuclear fusion, and train outstanding nuclear fusion personnel. In addition, the institute is spearheading a joint effort to open the era of nuclear fusion energy in the mid-21st century through active participation in the ITER Project.
The Korean artificial sun, KSTAR, has completed divertor upgrades, allowing it to operate for extended periods sustaining high-temperature plasma over the 100 million degrees.
END
Korean Artificial Sun, KSTAR, installation of a tungsten divertor for long pulse operations
The aim is to operate 300 seconds at 100-million-degree by 2026
2023-12-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
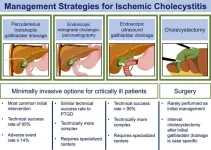
New perspectives on treating gallbladder inflammation
2023-12-28
Ischaemic cholecystitis is a form of gallbladder inflammation that occurs without gallstones or another form of external compression. It is caused by poor perfusion to the gallbladder tissue.
This new research is important because it helps to better understand the cause of ischaemic cholecystitis and to develop more effective treatments for this condition.
A team of researchers from the University of California, San Francisco, conducted a study investigating the cause of ischaemic cholecystitis. They found that the gallbladder is particularly susceptible to ischaemia ...
Brain health after COVID-19, pneumonia, heart attack, or critical illness
2023-12-28
About The Study: The findings of this study including 345 participants suggest that post–COVID-19 brain health was impaired but, overall, no more than the brain health of patients from 3 non–COVID-19 cohorts of comparable disease severity. Long-term associations with brain health might not be specific to COVID-19 but associated with overall illness severity and hospitalization. This information is important for putting understandable concerns about brain health after COVID-19 into perspective.
Authors: Daniel Kondziella, M.D., M.Sc., Dr.Philos., ...
Post–COVID-19 condition in children 6 and 12 months after infection
2023-12-28
About The Study: In this study of children tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection in Canadian pediatric emergency departments, although children infected with SARS-CoV-2 reported increased chronic symptoms, few of these children developed post–COVID-19 condition, and overall quality of life did not differ from children with negative SARS-CoV-2 tests.
Authors: Stephen Freedman, M.D.C.M., M.Sc., of the University of Calgary in Calgary, Alberta, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Self-reported frequency of adding salt to food and risk of incident chronic kidney disease
2023-12-28
About The Study: In this study of 465,000 individuals, a higher self-reported frequency of adding salt to foods was associated with a higher risk of chronic kidney disease in the general population. These findings suggest that reducing the frequency of adding salt to foods at the table might be a valuable strategy to lower chronic kidney disease risk in the general population.
Authors: Lu Qi, M.D., Ph.D., of Tulane University in New Orleans, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The ...
Breakthrough in hydrate-based desalination technique unveiled
2023-12-28
A research team, led by Professor Yongwon Seo in the Graduate School of Carbon Neutrality at UNIST has unveiled a highly efficient method for desalinating seawater using hydrate-based desalination (HBD) technology. The breakthrough is expected to have far-reaching implications for the application of hydrate-based desalination techniques, with the ability to calculate optimal temperatures for enhanced efficiency.
Hydrate desalination technology, known for its eco-friendly freshwater production capabilities, offers a low-energy solution that can be effectively used in treating high concentrations of brine or contaminated water. By ...
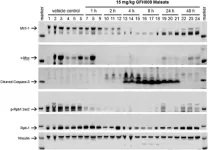
GFH009: A potent and highly selective CDK9 inhibitor for the treatment of hematologic malignancies
2023-12-28
“[...] the results of this preclinical investigation program suggest that induction of apoptosis is a key component of GFH009’s anti-tumor mechanism of action [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- December 28, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on December 20, 2023, entitled, “The pharmacodynamic and mechanistic foundation for the antineoplastic effects of GFH009, a potent and highly selective CDK9 inhibitor for the treatment of hematologic malignancies.”
To evade cell cycle controls, malignant cells rely upon rapid expression of select proteins to mitigate pro-apoptotic signals ...
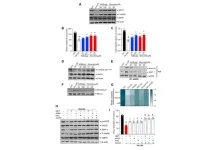
Angelica gigas extract inhibits acetylation of eNOS in vascular dysfunction
2023-12-28
“Angelica gigas Nakai (AG), a traditional medicinal herb, is garnering scientific attention for its potential in addressing a variety of health conditions.”
BUFFALO, NY- December 27, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 23, entitled, “Angelica gigas extract inhibits acetylation of eNOS via IRE1α sulfonation/RIDD-SIRT1-mediated posttranslational modification ...
Johns Hopkins researchers: Regret rarer than believed among patients who undergo gender affirming surgery
2023-12-28
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
In a Viewpoint article published Dec. 27, 2023, in JAMA Surgery, three Johns Hopkins researchers urge the medical community to dismiss a widely held, but scientifically unsupported belief that many people who are transgender and gender diverse (TGD), and undergo gender affirming surgery (GAS), later regret their decision to undergo such procedures.
The researchers are:
Harry Barbee, Ph.D., assistant professor and interdisciplinary social scientist at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health
Bashar ...
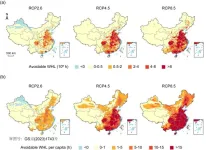
Future labor losses due to heat stress in China under climate change scenarios
2023-12-28
Climate change is the biggest global health threat in the 21st century, and the rising temperatures have undermined the health and safety of the working population, as well as caused labor losses, which are closely tied to social-economic development. Although the future temperatures increase in China has been forecasted by state-of-the-art climate change projections, to what extent the influence on labor has not been well studied. In a paper published in Science Bulletin, a Chinese research team presents evidence of future labor losses due to heat stress in China under climate change scenarios. This study was led by Cunrui Huang, a professor at the Vanke School of Public ...
Acellular players in the high cryosphere: diversity, function and activity of the global supraglacial DNA viruses
2023-12-28
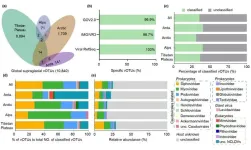
Supraglacial environments mainly consist of four main types of habitats for microbes and viruses, including snow, ice, meltwater, and cryoconites (the granular sediment on glacier surfaces). The paper revealed that there were more than 10,000 viral species in global supraglacial environments. This is a 15-fold expansion of DNA viral genomic inventory ever known. These viruses mainly belong to bacteriophages, viruses infecting bacteria. Liu et al., also found the viral communities showed a clear regional and habitat distribution pattern, with polar glacier samples separated from mountain ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] Korean Artificial Sun, KSTAR, installation of a tungsten divertor for long pulse operationsThe aim is to operate 300 seconds at 100-million-degree by 2026