Microplastics from natural fertilizers are blowing in the wind more often than once thought
2024-01-17
(Press-News.org) Though natural fertilizers made from treated sewage sludge are used to reintroduce nutrients onto agricultural fields, they bring along microplastic pollutants too. And according to a small-scale study published in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology Letters, more plastic particles get picked up by the wind than once thought. Researchers have discovered that the microplastics are released from fields more easily than similarly sized dust particles, becoming airborne from even a slight breeze.
Microplastics, or small bits of plastic less than 5 millimeters long, have appeared everywhere from clouds to heart tissues. And with these plastics’ increasing prevalence in people and water supplies, they’ve also been found in sewage and wastewater. Though sewage solids might not immediately seem like a useful product, after treatment they can form “biosolids,” which are applied to agricultural soils as a natural, renewable source of fertilizer. According to estimates by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, over 2 million dry metric tons of biosolids — roughly half of the total amount collected by wastewater treatment plants — are applied to land each year. As a result, microplastics in these biosolids have the chance to reenter the environment. Because the plastics could carry other pollutants from the wastewater they originated from, they can be potentially dangerous when inhaled. So, Sanjay Mohanty and colleagues wanted to investigate how wind could pick up and transport microplastic particles from biosolid-treated agricultural fields.
The team analyzed airborne microplastics in wind-blown sediments that were gathered during wind-tunnel experiments on two plots of biosolid-treated land in rural Washington state. The researchers discovered that these wind-blown sediments contained higher concentrations of microplastics than either the biosolids or the source soil itself. This enrichment effect is caused by the plastic particles being less dense than soil minerals, such as quartz, and less “sticky” — they’re not trapped as easily by moisture as the soil minerals are. As a result, microplastics can be picked up by a breeze more easily than soil minerals, and winds that might not be strong enough to kick up dust could still be introducing microplastics into the air.
The researchers say that previous models did not take this sticky effect and other unique properties of microplastics into account when estimating emissions from treated fields. Therefore, these older models are likely to underestimate the actual amount of plastic particles released into the air. Calculations by Mohanty and colleagues indicate that microplastics may be emitted from barren agricultural fields from nearly two and a half times more wind events than previously estimated. The researchers say this work highlights an underappreciated way that microplastics could become airborne.
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship Program and the McPike Zima Charitable Foundation.
The paper’s abstract will be available on Jan. 17 at 8 a.m. Eastern time here: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/10.1021/acs.estlett.3c00850
###
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note: ACS does not conduct research, but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-01-17
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., Jan. 17, 2024 — New insights from artificial intelligence about permafrost coverage in the Arctic may soon give policy makers and land managers the high-resolution view they need to predict climate-change-driven threats to infrastructure such as oil pipelines, roads and national security facilities.
“The Arctic is warming four times faster than the rest of the globe, and permafrost is a component of the Arctic that’s changing really rapidly,” said Evan Thaler, a Chick Keller Postdoctoral Fellow at Los Alamos National Laboratory. Thaler is corresponding ...
2024-01-17
Emotions exert a profound influence on human behavior, prompting extensive explorations in the realms of psychology and linguistics. Understanding central emotions also has practical utility since it can help organizations create messages that resonate better with people. For instance, businesses can enhance their connection with their customers, and non-profits can prompt quicker action by skillfully leveraging the salient emotions in humans.
Colexification is a phenomenon in which the occurrence of a single word is associated with multiple concepts that share semantic relationships. The analysis of colexification is an innovative linguistic method for ...
2024-01-17
Research Highlights:
Consistently high scores of perceived stress during adolescence through adulthood may contribute to worse cardiometabolic health including obesity in young adults..
Researchers suggest the adoption of healthy coping strategies for stress management early in life may help prevent cardiometabolic diseases, from heart disease to Type 2 diabetes.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Wednesday, January 17, 2024
DALLAS, January 17, 2024 — Young adults who reported higher stress during their teenage years to adulthood were more likely to ...
2024-01-17
Over the last decades, air pollution emissions have decreased substantially; however, the magnitude of the change varies by demographics, according to a new study by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. The results indicate there are racial/ethnic and socioeconomic disparities in air pollution emissions reductions, particularly in the industry and energy generation sectors. The findings are published in the journal Nature Communications.
The research provides a national investigation of air pollution emission ...
2024-01-17
New York, January 17, 2024 — In all species, brain function relies on an intricate network of connections that allows neurons to send information back and forth between one another, commanding thought and physical activity. But within those networks a small number of neurons share much stronger connections to one another than all the others. These abnormally strong connections—known as “heavy tailed” based on the shape of their distribution—are thought to play an outsized role in brain function.
Researchers ...
2024-01-17
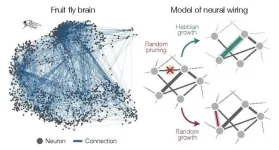
A new study by physicists and neuroscientists from the University of Chicago, Harvard and Yale describes how connectivity among neurons comes about through general principles of networking and self-organization, rather than the biological features of an individual organism.
The research, published on January 17, 2024 in Nature Physics, accurately describes neuronal connectivity in a variety of model organisms and could apply to non-biological networks like social interactions as well.
“When you’re building simple models to ...
2024-01-17
Sensors built with a new manufacturing approach are capable of recording activity deep within the brain from large populations of individual neurons–with a resolution of as few as one or two neurons–in humans as well as a range of animal models, according to a study published in the Jan. 17, 2024 issue of the journal Nature Communications. The research team is led by the Integrated Electronics and Biointerfaces Laboratory (IEBL) at the University of California San Diego.
The approach is unique in several ways. It relies on ultra-thin, flexible and customizable probes, made of clinical-grade materials, and equipped with sensors that can record extremely localized ...
2024-01-17
Large-scale genetic analysis has helped researchers uncover the interplay between cancer-driving genetic mutations and inherited genetic variants in a rare type of blood cancer.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, the University of Cambridge, and collaborators, combined various comprehensive data sets to understand the impact of both cancer-driving spontaneous mutations and inherited genetic variation on the risk of developing myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN).
The study, published today (17 January) in Nature Genetics, describes how inherited genetic variants can influence whether a spontaneous mutation in a particular ...
2024-01-17
When a person has one or more blocked arteries, providers may choose to conduct a minimally invasive procedure known as percutaneous coronary intervention, or PCI.
By inflating a balloon and potentially placing a stent, blood can flow more freely from the heart.
Despite carrying less risk than open surgery, stenting and balloon angioplasty can result in complications like bleeding and kidney injury.
Researchers at Michigan Medicine developed an AI-driven algorithm that accurately predicts death and complications after PCI — which could emerge as a tool ...
2024-01-17
A new analysis of trial data on pregnant smokers, led by researchers at Queen Mary University of London, finds that the regular use of nicotine replacement products during pregnancy is not associated with adverse pregnancy events or poor pregnancy outcomes.
The PREP 2 study used data collected from over 1100 pregnant smokers attending 23 hospitals in England and 1 stop-smoking service in Scotland to compare pregnancy outcomes in women who did or did not use nicotine in the form of e-cigarettes (EC) or nicotine patches ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Microplastics from natural fertilizers are blowing in the wind more often than once thought