(Press-News.org) Like Indiana Jones, thresher sharks (Alopias spp.) have mastered the art of the whip using their tails. With incredible speed, their long, machete-like tails can slap and stun their prey, allowing them to swallow multiple fish in one fell swoop. Their exceptionally elongated tail, which can often be as long as their entire body, not only makes this particular shark unique, but also a formidable hunter.
Thresher shark “tail-whipping” consists of four phases: preparation, strike, wind-down recovery, and prey collection. Overhead tail slaps begin in the preparation phase by lunging toward targeted prey. The strike phase begins by lowering the head and flexing the body, which raises the tail over their head to create a whip-like motion. The wind-down recovery phase consists of the shark returning to swimming posture, and consuming stunned prey.
The shark’s tail-whipping movement dramatically differs from the side-to-side motion produced by its body during swimming. The cartilaginous vertebral column, which is the main body axis, may have anatomical modifications to withstand the extreme bending during the tail-whipping behavior. Prior research has examined the vertebrae of thresher sharks, but in the context of the forces experienced during swimming.
Now, new research from Florida Atlantic University in collaboration with Apex Predators Program, Northeast Fisheries Science Center, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), provides intricate details showing that anatomy of the vertebrae might support the mechanics of extreme body bending in thresher sharks, enabling these expert hunters to weaponize their tails.
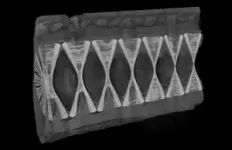
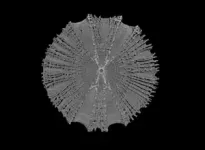
For this study, researchers examined vertebrae from the head and tail ends of the body. They investigated vertebral anatomy and measured variables like height, width and length along the vertebral column from 10 common thresher sharks (Alopias vulpinus) across a range of sizes from an embryo to large adults.
Researchers used micro-CT scanning, similar to CAT scans humans use in medical facilities, to image the internal architecture of each vertebra and quantified various mineral structures found in the calcified cartilage. They also used two-dimensional shape analysis techniques to examine variation in the spatial distribution of mineral structures along the vertebral column.
Results of the study, published in the journal Royal Society Open Science, suggest thresher shark vertebral anatomy and mineralized microstructure meet the demands required for fast swimming and tail-whipping behavior seen in these species.
Researchers found that the mineralized microarchitecture in thresher shark vertebrae changes in the front and the back of the body, and these anatomical modifications may support their unique tail-whipping behavior. Essentially, thresher shark vertebral column is fortified along its length and might work like a catapult, allowing the tail to launch over the head.
“We found that anatomy and microstructure significantly varied along the body and among developmental groups – embryonic, juvenile and adult common thresher sharks,” said Jamie L. Knaub, first author and a doctoral graduate student in FAU’s Department of Biological Sciences within the Charles E. Schmidt College of Science. “Based on our results, we believe that thresher shark vertebrae vary in anatomy, and the amount and arrangement of mineral, supporting the mechanical needs for tail-whipping.”
The researchers also discovered that juvenile-sized sharks acquire mineralized structures throughout development, likely to support a larger body as they grow and tail for whipping behaviors.
“We think that anterior body vertebrae stabilize the thresher shark’s main body, while vertebrae closer to the tail support overhead tail-whips,” said Marianne E. Porter, Ph.D., senior author and an associate professor, FAU Department of Biological Sciences. “Additionally, developmental changes suggest that vertebral anatomy shifts across development to support a larger body and caudal fin.”
Thresher sharks, part of the Alopiidae family, comprise three species: the pelagic thresher (Alopias pelagicus), the bigeye thresher (Alopias superciliousus), and the common thresher (Alopias vulpinus). All three thresher shark species have been listed as vulnerable to extinction by the World Conservation Union since 2007.
Study co-authors are Michelle Passerotti, Ph.D., a fish biologist, Apex Predators Program, NOAA Fisheries; Lisa J. Natanson, Ph.D., a shark researcher, Apex Predators Program, NOAA Fisheries (retired); and Tricia Meredith, Ph.D., director of research, FAU A.D. Henderson University School and FAU High School, and an assistant research professor, FAU College of Education.
The work was conducted as part of Knaub’s Ph.D. research, which was supported by a National Science Foundation (NSF) CAREER grant awarded to Porter (NSF, IOS-1941713), the Jim Elliot Award from Tomography for Scientific Advancement awarded to Knaub, and the Vincent Saurino Fellowship, the Newell Doctoral Fellowship, and the National Save the Sea Turtle Foundation Scholarship from FAU awarded to Knaub.
- FAU -
About Florida Atlantic University:
Florida Atlantic University, established in 1961, officially opened its doors in 1964 as the fifth public university in Florida. Today, the University serves more than 30,000 undergraduate and graduate students across six campuses located along the southeast Florida coast. In recent years, the University has doubled its research expenditures and outpaced its peers in student achievement rates. Through the coexistence of access and excellence, FAU embodies an innovative model where traditional achievement gaps vanish. FAU is designated a Hispanic-serving institution, ranked as a top public university by U.S. News & World Report and a High Research Activity institution by the Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching. For more information, visit www.fau.edu.
END
Cold, flu and COVID-19 season brings that now-familiar ritual: swab, wait, look at the result. But what if, instead of taking 15 minutes or more, a test could quickly determine whether you have COVID-19 with a glowing chemical? Now, in ACS Central Science, researchers describe a potential COVID-19 test inspired by bioluminescence. Using a molecule found in crustaceans, they have developed a rapid approach that detects SARS-CoV-2 protein comparably to one used in vaccine research.
From fireflies ...
Though natural fertilizers made from treated sewage sludge are used to reintroduce nutrients onto agricultural fields, they bring along microplastic pollutants too. And according to a small-scale study published in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology Letters, more plastic particles get picked up by the wind than once thought. Researchers have discovered that the microplastics are released from fields more easily than similarly sized dust particles, becoming airborne from even a slight breeze.
Microplastics, or small bits of plastic less than 5 millimeters long, have appeared everywhere from clouds to heart tissues. And with these plastics’ increasing prevalence in ...
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., Jan. 17, 2024 — New insights from artificial intelligence about permafrost coverage in the Arctic may soon give policy makers and land managers the high-resolution view they need to predict climate-change-driven threats to infrastructure such as oil pipelines, roads and national security facilities.
“The Arctic is warming four times faster than the rest of the globe, and permafrost is a component of the Arctic that’s changing really rapidly,” said Evan Thaler, a Chick Keller Postdoctoral Fellow at Los Alamos National Laboratory. Thaler is corresponding ...
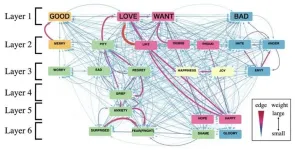
Emotions exert a profound influence on human behavior, prompting extensive explorations in the realms of psychology and linguistics. Understanding central emotions also has practical utility since it can help organizations create messages that resonate better with people. For instance, businesses can enhance their connection with their customers, and non-profits can prompt quicker action by skillfully leveraging the salient emotions in humans.
Colexification is a phenomenon in which the occurrence of a single word is associated with multiple concepts that share semantic relationships. The analysis of colexification is an innovative linguistic method for ...
Research Highlights:
Consistently high scores of perceived stress during adolescence through adulthood may contribute to worse cardiometabolic health including obesity in young adults..
Researchers suggest the adoption of healthy coping strategies for stress management early in life may help prevent cardiometabolic diseases, from heart disease to Type 2 diabetes.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Wednesday, January 17, 2024
DALLAS, January 17, 2024 — Young adults who reported higher stress during their teenage years to adulthood were more likely to ...
Over the last decades, air pollution emissions have decreased substantially; however, the magnitude of the change varies by demographics, according to a new study by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. The results indicate there are racial/ethnic and socioeconomic disparities in air pollution emissions reductions, particularly in the industry and energy generation sectors. The findings are published in the journal Nature Communications.
The research provides a national investigation of air pollution emission ...
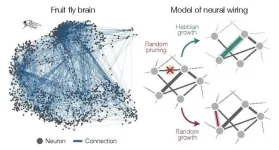
New York, January 17, 2024 — In all species, brain function relies on an intricate network of connections that allows neurons to send information back and forth between one another, commanding thought and physical activity. But within those networks a small number of neurons share much stronger connections to one another than all the others. These abnormally strong connections—known as “heavy tailed” based on the shape of their distribution—are thought to play an outsized role in brain function.
Researchers ...
A new study by physicists and neuroscientists from the University of Chicago, Harvard and Yale describes how connectivity among neurons comes about through general principles of networking and self-organization, rather than the biological features of an individual organism.
The research, published on January 17, 2024 in Nature Physics, accurately describes neuronal connectivity in a variety of model organisms and could apply to non-biological networks like social interactions as well.
“When you’re building simple models to ...
Sensors built with a new manufacturing approach are capable of recording activity deep within the brain from large populations of individual neurons–with a resolution of as few as one or two neurons–in humans as well as a range of animal models, according to a study published in the Jan. 17, 2024 issue of the journal Nature Communications. The research team is led by the Integrated Electronics and Biointerfaces Laboratory (IEBL) at the University of California San Diego.
The approach is unique in several ways. It relies on ultra-thin, flexible and customizable probes, made of clinical-grade materials, and equipped with sensors that can record extremely localized ...
Large-scale genetic analysis has helped researchers uncover the interplay between cancer-driving genetic mutations and inherited genetic variants in a rare type of blood cancer.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, the University of Cambridge, and collaborators, combined various comprehensive data sets to understand the impact of both cancer-driving spontaneous mutations and inherited genetic variation on the risk of developing myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN).
The study, published today (17 January) in Nature Genetics, describes how inherited genetic variants can influence whether a spontaneous mutation in a particular ...