(Press-News.org) AMSTERDAM and TUCSON, Ariz., January 25, 2024 — Critical Path Institute (C-Path) today announced the promotion of Cécile Ollivier, M.S., from Managing Director, Europe to Vice President of Global Affairs.
“We are thrilled to announce the promotion of Cécile Ollivier to Vice President of Global Affairs,” said C-Path Board member Tomas Salmonson Ph.D., M.S. “Cécile has been an invaluable contributor to our European operations, and her extensive experience in global drug development and regulatory science makes her the ideal choice for this expanded role. Her leadership will be crucial as we continue our mission to accelerate drug development globally.”
Ollivier has been a key figure at C-Path since joining as Managing Director in April 2021. In her new role, she will oversee global strategic initiatives, focusing on enhancing international collaborations and developing innovative approaches to address complex challenges in drug development. Her work will include expanding partnerships and harmonizing regulatory frameworks across multiple regions.
With over 16 years of experience in the healthcare sector, Ollivier has made significant contributions to pediatric and rare disease drug development. Her efforts have been recognized internationally, including as an expert in the International Conference of Harmonization (ICH) and leading the global strategy for pediatric extrapolation.
“Over the past two years, Cécile has orchestrated remarkable growth in C-Path’s European activities, elevated our recognition through insightful contributions at key conferences, and fostered invaluable collaborations,” said C-Path’s CEO Klaus Romero, M.D., M.S., FCP. “Her unwavering commitment to advancing our global initiatives showcases the power of hard work and strategic vision. I look forward to continuing to work closely with Cécile.”
Prior to joining C-Path, Ollivier contributed her expertise at the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and in the medical technology sector, focusing on developing digital endpoints in clinical trials.
“I am honored to take on this new role,” said Ollivier. “The opportunity to further influence global health outcomes and drive innovation in drug development melds perfectly with my passion and experience. I look forward to working with our talented team and our partners around the world to deliver meaningful impact to benefit the lives of individuals and families affected by diseases with unmet needs.” Ollivier’s promotion is effective immediately, and she will be based out of C-Path’s European office in Amsterdam.
About Critical Path Institute
Critical Path Institute (C-Path) is an independent, nonprofit established in 2005 as a public-private partnership, in response to the FDA’s Critical Path Initiative. C-Path’s mission is to lead collaborations that advance better treatments for people worldwide. Globally recognized as a pioneer in accelerating drug development, C-Path has established numerous international consortia, programs and initiatives that currently include more than 1,600 scientists and representatives from government and regulatory agencies, academia, patient organizations, disease foundations and pharmaceutical and biotech companies. With dedicated team members located throughout the world, C-Path’s global headquarters is located in Tucson, Arizona and C-Path’s Europe subsidiary is headquartered in Amsterdam, Netherlands. For more information, visit c-path.org.
END
C-Path promotes Cécile Ollivier to Vice President of Global Affairs, expanding leadership in drug development
Ollivier to steer global strategic initiatives, reinforcing C-Path’s commitment to accelerating medical innovation and regulatory science.
2024-01-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
David Brydges wins 2024 Dannie Heineman Prize for Mathematical Physics
2024-01-25
WASHINGTON, Jan. 25, 2024 – AIP and the American Physical Society (APS) are pleased to announce David Brydges as the recipient of the 2024 Dannie Heineman Prize for Mathematical Physics “for achievements in the fields of constructive quantum field theory and rigorous statistical mechanics, especially the introduction of new techniques including random walk representation in spin systems, the lace expansion, and mathematically rigorous implementations of the renormalization group.”
This annual award recognizes significant contributions within the ...
African smallholder farmers benefit from reduced crop losses and higher incomes from a novel pest alert service
2024-01-25
A newly published review of the CABI-led Pest Risk Information Service (PRISE) project shows that smallholder farmers in four African countries who received pest alerts created using earth observation data benefitted from reduced crop losses and higher incomes compared to farmers who did not.
Crop pests are the major cause of loss of smallholder productivity resulting in negative impacts on livelihoods – the estimated the economic impact of invasive alien pests alone on Africa’s agricultural sector is USD $65.58 billion a year (CABI, 2021, CABI Agriculture and Bioscience).
This review is a keystone ...
Cervical cancer rates rising in low-income U.S. counties
2024-01-25
HOUSTON ― Women in low-income areas of the U.S. face a stark rise in cervical cancer incidence and mortality, according to a new study led by researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
The results, published in the International Journal of Cancer, demonstrate that the incidence rate for distant-stage cervical cancer has increased most among white women living in low-income counties, at 4.4% annually since 2007. The largest increase in cervical cancer mortality rates occurred ...
Press registration opens for ACS Spring 2024
2024-01-25
Journalists who register for the American Chemical Society’s (ACS’) upcoming hybrid meeting and exposition — ACS Spring 2024 — will have access to nearly 12,000 presentations on topics including agriculture and food, energy and fuels, health and medicine, sustainability, and more. ACS Spring 2024 is being held virtually and in person in New Orleans on March 17-21, with the theme “Many Flavors of Chemistry.”
ACS considers requests for press credentials and complimentary meeting registration from reporters ...
UTSA to establish new college in AI, cyber, computing and data science
2024-01-25
UTSA announced a pioneering initiative to reshape its academic landscape with the creation of a new college dedicated to artificial intelligence (AI), cybersecurity, computing, data science and related disciplines. This initiative aligns with the university's commitment to innovation and academic excellence while also positioning UTSA to lead in the rapidly evolving landscape of advanced technologies.
Nearly 6,000 students are enrolled in AI, cyber, computing and data science-related degree programs at UTSA, reflecting ...
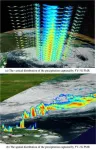
New satellite capable of measuring Earth precipitation from space
2024-01-25
Measuring the amount of precipitation that falls in a specific location is simple if that location has a device designed to accurately record and transmit precipitation data. In contrast, measuring the amount and type of precipitation that falls to Earth in every location is logistically quite difficult. Importantly, this information could provide a wealth of data for characterizing and predicting Earth’s water, energy and biogeochemical cycles. Researchers from China recently deployed a satellite, FengYun 3G (FY-3G), that is successfully collecting Earth precipitation data from space.
Scientists from the China Meteorological Administration developed and launched ...
Women exposed to toxic metals may experience earlier aging of their ovaries
2024-01-25
WASHINGTON—Middle-aged women who are exposed to toxic metals may have fewer eggs in their ovaries as they approach menopause, according to new research published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Diminished ovarian reserve is when women have fewer eggs compared to others their age. The condition may be linked to health problems such as hot flashes, weak bones and a higher chance of heart disease.
Menopause is a normal part of the aging process a woman goes through that causes her monthly periods to end. The menopausal transition includes the years leading up to that point, when women may experience symptoms such as changes in ...
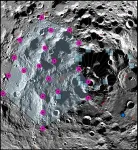
The moon is shrinking, causing landslides and instability in lunar south pole
2024-01-25
Earth’s moon shrank more than 150 feet in circumference as its core gradually cooled over the last few hundred million years. In much the same way a grape wrinkles when it shrinks down to a raisin, the moon also develops creases as it shrinks. But unlike the flexible skin on a grape, the moon’s surface is brittle, causing faults to form where sections of crust push against one another.
A team of scientists discovered evidence that this continuing shrinkage of the moon led to notable surface warping in its south polar ...
Icahn Mount Sinai School of Medicine receives Helmsley Charitable Trust grant for Crohn's disease research
2024-01-25
New York, NY [January 25, 2024]—The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has been awarded a grant of more than $4 million from The Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust to support an innovative research project aimed at understanding the early stages of Crohn’s disease before noticeable symptoms develop.
Led by the Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences along with the Dr. Henry D. Janowitz Division of Gastroenterology in the Department of Medicine at the Icahn School of ...
Sika deer overpopulation endangers beech forests in Southern Kyushu, Japan
2024-01-25
Fukuoka, Japan—Kyushu University researchers have found that Japanese beech (Fagus crenata) in the forests of southern Kyushu have seen reduced growth, due to soil erosion caused by the overpopulation of sika deer (Cervus nippon). Their findings, which were published in the journal Catena, could help in the development of new strategies for forest conservation.
Conservation is more than just preserving forests; it's about protecting the diverse web of life. One area where conservation has become critical is a beech forest in Shiiba Village, in the remote mountains of Southern Kyushu. The Japanese beech is a prominent and iconic species in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] C-Path promotes Cécile Ollivier to Vice President of Global Affairs, expanding leadership in drug developmentOllivier to steer global strategic initiatives, reinforcing C-Path’s commitment to accelerating medical innovation and regulatory science.