(Press-News.org) EDMONTON — New research shows an innovative education program is helping to address Alberta’s rural doctor shortage by making it more likely medical students will set up a rural family practice after graduation.
The University of Alberta was one of the first medical schools in Canada to set up its Rural Integrated Community Clerkship program back in 2007. It sends up to 25 third-year students for 10-month intensive work experiences with a single or small number of teaching physicians.
Instead of rotating to a new specialty placement every four to six weeks as in an urban clerkship, the students learn about surgery, pediatrics, internal medicine, psychiatry, obstetrics and gynecology in an integrated fashion in one community such as Bonnyville, Peace River, Hinton or Camrose.
“The biggest advantage the rural clerkship students have is the relationships they develop with their teachers, with their patients and with their community,” explains principal investigator Jill Konkin.
In a recently published study, researchers tracked 1,105 U of A medical grads from 2009 to 2016. Of that cohort, 195 chose to become rural practitioners and 510 became family practitioners. Taking part in the rural clerkship was found to be a more reliable predictor for those choices than having a rural background.
“Integrated Community Clerkship participation had more influence than rural background on students’ choice of rural and/or family practice,” the authors report. “Our results show that the rural pipeline principle works.”
“We know how to make rural physicians,” concludes first author Darren Nichols, associate professor of family medicine, noting the students develop “adaptive expertise” that allows them to be ready to treat a variety of patients, rather than seeing a limited set of problems repeatedly as a specialist. “We can take any student, regardless of background or future career plan, and provide them the opportunity to have their life changed,” Nichols says. “They know how to approach any problem. That’s much harder than being a specialist.”
END
Rural placements for medical students feed ‘pipeline’ for new family docs
New study underscores success of U of A program in helping address Alberta's shortage of rural doctors
2024-02-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
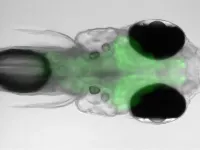
Zebrafish navigate to find their comfortable temperature
2024-02-01
All animals need to regulate their body temperature and cannot survive for long if it gets too high or too low. Warm-blooded organisms like humans have various ways to do this. They release heat by sweating or expanding the blood vessels in their skin, while shivering or burning fat in their brown adipose tissue has the opposite effect.
Cold-blooded animals such as the zebrafish, by contrast, cannot do any of these, so they have a different strategy. They look for places nearby that are at their “comfortable temperature,” just like how we might go out into the sun when we feel chilly or seek out some shade once it gets too ...
Buck scientists discover a potential way to repair synapses damaged in Alzheimer’s disease
2024-02-01
While newly approved drugs for Alzheimer’s show some promise for slowing the memory-robbing disease, the current treatments fall far short of being effective at regaining memory. What is needed are more treatment options targeted to restore memory, said Buck Assistant Professor Tara Tracy, PhD, the senior author of a study that proposes an alternate strategy for reversing the memory problems that accompany Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias.
Since most current research on potential treatments for Alzheimer’s focuses on reducing the toxic proteins, such as tau and amyloid beta, that accumulate in ...
Researchers identify critical pathway responsible for melanoma drug resistance
2024-02-01
(Boston)—One of the major challenges in cancer research and clinical care is understanding the molecular basis for therapeutic resistance as a major cause of long term treatment failures. In cases of melanoma, the main targeted therapeutic strategy is directed against the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. Unfortunately, in the vast majority of these patients, resistance to MAPK inhibitor therapies develops within one year of treatment.
In a new study from Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, ...
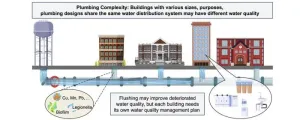
Pandemic lockdowns and water quality: a revealing study on building usage
2024-02-01
During the COVID-19 pandemic, lower occupancy in buildings led to reduced water use, raising concerns about water quality due to stagnation. Government warnings highlighted increased risks of chemical and microbiological contamination in water systems. Studies showed that reduced usage and stagnation could elevate heavy metal levels and decrease disinfectant effectiveness, affecting microbial growth. To address this, regular fixture flushing was recommended, which temporarily improved water quality but also revealed the complexities of managing building water systems effectively.
In a recent study (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ese.2023.100314) ...
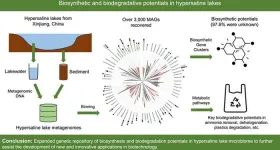
Exploring the unseen: microbial wonders in earth's saltiest waters
2024-02-01
The study delves into hypersaline lakes in Xinjiang, China, exploring the genetic and metabolic diversity of microbial communities termed "microbial dark matters". Hypersaline lake ecosystems, characterized by extreme salinity, harbor unique microorganisms with largely unexplored biosynthesis and biodegradation capabilities. The research seeks to uncover novel biological compounds and pathways, potentially revolutionizing biotechnology, medicine, and environmental remediation by tapping into the untapped potential of these extremophiles.
A recent study (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ese.2023.100359) published ...
As cancer therapies improve, more patients with rectal cancer forego surgery
2024-02-01
While surgery to remove rectal cancer can be necessary and lifesaving, it can sometimes come with significant drawbacks, like loss of bowel control. According to a study led by Wilmot Cancer Institute researchers, patients with rectal cancer who respond well to radiation and chemotherapy are increasingly foregoing surgery and opting for a watch-and-wait approach.
The study, published in JAMA Oncology, shows that the number of patients opting out of surgery rose nearly 10 percent between 2006 and 2020. These data reflect a shift toward what ...
Stanford Medicine-led study shows why women are at greater risk of autoimmune disease
2024-02-01
Somewhere between 24 and 50 million Americans have an autoimmune disease, a condition in which the immune system attacks our own tissues. As many as 4 out of 5 of those people are women.
Rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and scleroderma are examples of autoimmune disorders marked by lopsided female-to-male ratios. The ratio for lupus is 9 to 1; for Sjogren’s syndrome, it’s 19 to 1.
Stanford Medicine scientists and their colleagues have traced this disparity to the most fundamental feature differentiating ...
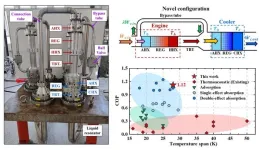
Researchers develop highly efficient heat-driven thermoacoustic refrigerator
2024-02-01
Researchers led by Prof. LUO Ercang from the Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry (TIPC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and their collaborators have developed an innovative heat-driven thermoacoustic refrigerator (HDTR) with a novel bypass configuration that significantly improves the efficiency of this technology.
The study was published in Cell Reports Physical Science on Feb. 1.
HDTR is recognized as a new, promising cooling technology with many advantages. For example, it has no moving parts, uses eco-friendly substances (e.g., helium and nitrogen), and is highly reliable. However, its relatively low efficiency ...
Animals: Small, long-nosed dogs live the longest
2024-02-01
Small long-nosed (or dolichocephalic) dog breeds such as Whippets have the highest life expectancies in the UK, whilst male dogs from medium-sized flat-faced (or brachycephalic) breeds such as English Bulldogs have the lowest. The results, published in Scientific Reports, have been calculated from data on over 580,000 individual dogs from over 150 different breeds, and could help to identify those dogs most at risk of an early death.
Kirsten McMillan and colleagues assembled a database of 584,734 individual dogs using data from 18 different UK sources, including breed registries, vets, pet insurance companies, animal welfare ...
Physical activity and cognitive decline among older adults
2024-02-01
About The Study: Physical activity was associated with better late-life cognition, but the association was weak in this systematic review and meta-analysis including 104 studies with 341,000 participants. However, even a weak association is important from a population health perspective.
Authors: Paula Iso-Markku, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Helsinki, Finland is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.54285)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Rural placements for medical students feed ‘pipeline’ for new family docsNew study underscores success of U of A program in helping address Alberta's shortage of rural doctors