(Press-News.org) DALLAS, Feb. 6, 2024 — Five promising scientific researchers will advance their work to better understand and treat the most common birth defect in the U.S., congenital heart defects (CHDs), thanks to joint financial support from the American Heart Association and The Children’s Heart Foundation's Congenital Heart Defect Research Awards program.
To date, the American Heart Association, celebrating 100 years of lifesaving service and devoted to a world of healthier lives for all, and The Children’s Heart Foundation, dedicated to funding congenital heart defect research, have pledged more than $10 million across 10 years of the CHD research funding collaboration.
Nearly 40,000 infants are born with a CHD each year in the United States. Approximately 1 in 4 babies born with a CHD require invasive surgery or treatment in their first year of life.[1] While medical advancements have improved over the years, many of these children and their families still face a lifetime of challenges.[2] Scientific research that helps healthcare professionals understand, identify, and treat CHDs is helping these babies live longer, healthier lives.
Receiving the very latest in new grant funding, combining for nearly $600,000 are:
Jonathon Muncie, Ph.D. at the J. David Gladstone Institutes in San Francisco for Deciphering the Role of Mef2c in Allocating Second Heart Field Progenitors to the Linear Heart Tube
SunYoung Kim for the Board of Regents of the University of Nebraska Medical Center in Omaha for Alcohol and Notch Pathway Mutations Synergistically Induce Atrioventricular Canal Defects: Potential Rescue by Folate
Siting Zhu, Ph.D. at the Regents of the University of California, San Diego in La Jolla for investigating NEDD4 in right ventricular development
Yixuan Liu, M.S. at The Ohio State University in Columbus for investigating a neural network pipeline for rapid acquisition and reconstruction of MRI data for catheterization procedures
Shatha Salameh, M.S. at Children's National Medical Center and Children's Research Institute in Washington, D.C. for investigating age-dependent differences in cardiac drug response
“Babies born with CHD are now living well into adulthood and having babies of their own,” said Joseph Wu, M.D., PhD, FAHA, volunteer president of the American Heart Association, director of the Stanford Cardiovascular Institute and professor of medicine and radiology at Stanford University. “With this progress comes an opportunity for us to recommit our resources to investigating congenital heart disease as it affects adult patients. It’s been 100 years since the American Heart Association was founded, and obviously research has come a long way. It’s up to these researchers—and our volunteers across the country—to help guide where our second century takes us.”
“Our collaboration with the American Heart Association to fund life-saving research gets us that much closer to a world where every child has the chance to grow into a healthy adult,” said Gail Roddie-Hamlin, president and CEO of The Children’s Heart Foundation. “As we announce these grants going into Congenital Heart Defect Awareness Week, we’re doubling down on our commitment to families by funding the most promising research and raising much needed awareness.”
Researchers studying the prevention and treatment of CHDs are encouraged to submit applications for funding from the American Heart Association and The Children’s Heart Foundation. For submission guidelines and upcoming deadlines specific to the Congenital Heart Defects Research Awards, visit professional.heart.org/CHDResearchAwards.
###
About the American Heart Association
The American Heart Association is a relentless force for a world of longer, healthier lives. We are dedicated to ensuring equitable health in all communities. Through collaboration with numerous organizations, and powered by millions of volunteers, we fund innovative research, advocate for the public’s health and share lifesaving resources. The Dallas-based organization has been a leading source of health information for a century. During 2024 - our Centennial year - we celebrate our rich 100-year history and accomplishments. As we forge ahead into our second century of bold discovery and impact, our vision is to advance health and hope for everyone, everywhere. Connect with us on heart.org, Facebook, X or by calling 1-800-AHA-USA1.
About The Children’s Heart Foundation
The Children’s Heart Foundation (CHF) is the country’s leading organization solely committed to funding congenital heart defect (CHD) research. The Children’s Heart Foundation’s mission is to advance the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of congenital heart defects by funding the most promising research. To date, CHF has funded nearly $18 million of CHD research and scientific collaborations. For more information or to join our cause, visit www.childrensheartfoundation.org. Follow us on Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and LinkedIn.
[1] Virani SS, Alonso A, Aparicio HJ, Benjamin EJ, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, Chamberlain AM, Cheng S, Delling FN, Elkind MSV, Evenson KR, Ferguson JF, Gupta DK, Khan SS, Kissela BM, Knutson KL, Lee CD, Lewis TT, Liu J, Loop MS, Lutsey PL, Ma J, Mackey J, Martin SS, Matchar DB, Mussolino ME, Nav aneethan SD, Perak AM, Roth GA, Samad Z, Satou GM, Schroeder EB, Shah SH, Shay CM, Stokes A, VanWagner LB, Wang N-Y, Tsao CW; on behalf of the American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2021 update: a report from the American Heart Association [published online ahead of print January 27, 2021]. Circulation. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000950
[2] https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/epdf/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001123
END
More than half million dollars in research grants awarded to understand No. 1 birth defect
The American Heart Association and The Children’s Heart Foundation announce a nearly $600,000 commitment to jointly fund new research into congenital heart defects
2024-02-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Rice’s Santiago Segarra wins NSF CAREER Award
2024-02-07
HOUSTON – (Feb. 7, 2024) – Artificial intelligence is good at many tasks involving data in the form of text, audio and images, including face recognition and text summarization.
“AI is an amazing tool and has been extended over less conventional domains, such as climate data defined on spheres (representing the Earth) and traffic data defined on road networks,” said Santiago Segarra, assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering and statistics.
With his five-year, $599,138 CAREER Award from the National Science Foundation, Segarra intends to study the use of graphs to represent these ...
Music may bring health benefits for older adults, poll suggests
2024-02-07
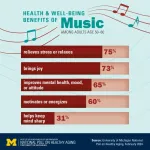
Whether it’s singing in a choir, playing the living room piano, joining in hymns at church, or just whistling along with the radio, a new poll finds that nearly all older adults say music brings them far more than just entertainment.
Three-quarters of people age 50 to 80 say music helps them relieve stress or relax and 65% say it helps their mental health or mood, according to the new results from the University of Michigan National Poll on Healthy Aging. Meanwhile, 60% say they get energized or motivated ...
From waste to resource: A new and sustainable process transforms sewage sludge into activated carbon
2024-02-07
Sewage sludge is the solid waste resulting from wastewater treatment. According to data from the Ministry for the Ecological Transition and the Demographic Challenge, 1.2 million tons of this waste were produced in Spain in 2021 alone, and its management is a growing problem. Although some of it may have agricultural applications, such as being used as fertilizer after composting, its high concentration of metals limits its use, generating environmental problems.
A new study has managed to give this waste a second life, turning it into activated carbon, a product boasting ...
Incheon National University researcher examines proactive change-oriented behaviors by public service providers
2024-02-07
Although change-oriented behaviors are critical to high quality public service delivery, encouraging employees to embrace and pursue change in the public sector is difficult. Even with sufficient job autonomy–the principal antidote to resistance to change in the public sector literature–public servants may still lack the incentives, skills, information, and sense of security necessary to engage in proactive change-oriented behavior. Consequently, while job autonomy is undoubtedly important, it alone is not enough, as demonstrated by the many cases in which autonomy fails to lead to change and work process improvements. Given the importance of attitudes ...
3D printed nanocellulose upscaled for green architectural applications
2024-02-07
For the first time, a hydrogel material made of nanocellulose and algae has been tested as an alternative, greener architectural material. The study, from Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden and the Wallenberg Wood Science Center, shows how the abundant sustainable material can be 3D printed into a wide array of architectural components, using much less energy than conventional construction methods.
The construction industry today consumes 50 percent of the world’s fossil resources, generates 40 percent of global waste and causes 39 percent of global carbon dioxide emissions. There is a growing line of research into biomaterials and their applications, in ...
Inexpensive, carbon-neutral biofuels are finally possible
2024-02-07
When it comes to making fuel from plants, the first step has always been the hardest — breaking down the plant matter. A new study finds that introducing a simple, renewable chemical to the pretreatment step can finally make next-generation biofuel production both cost-effective and carbon neutral.
For biofuels to compete with petroleum, biorefinery operations must be designed to better utilize lignin. Lignin is one of the main components of plant cell walls. It provides plants with greater structural integrity and resiliency from microbial attacks. However, these natural properties of lignin also make it difficult to extract and utilize ...
Will this new solar maximum solve the puzzle of the Sun’s gamma-ray picture?
2024-02-07
The Sun’s polar regions were the most active emitting high energy radiation during the previous solar maximum, an imbalance yet to be explained, and reported for the first time in a study led by a researcher of the Faculty of Sciences of the University of Lisbon (Ciências ULisboa) (Portugal).
The Sun shines brightly in the visible light, but how does it look like at the highest energies of the electromagnetic radiation? The Sun’s picture taken in gamma rays is a deadly sight, luckily blinded by the Earth’s atmosphere and only seen from space. Each photon carries a billion times more energy than its ultraviolet sibling. How does the Sun’s regular gamma rays’ ...
A machine learning framework that encodes images like a retina
2024-02-07
A major challenge to developing better neural prostheses is sensory encoding: transforming information captured from the environment by sensors into neural signals that can be interpreted by the nervous system. But because the number of electrodes in a prosthesis is limited, this environmental input must be reduced in some way, while still preserving the quality of the data that is transmitted to the brain.
Demetri Psaltis (Optics Lab) and Christophe Moser (Laboratory of Applied Photonics Devices) collaborated with Diego Ghezzi of the Hôpital ophtalmique Jules-Gonin – Fondation Asile des Aveugles (previously Medtronic Chair in Neuroengineering at EPFL) to apply machine ...
Innovation in stone tool technology involved multiple stages at the time of modern human dispersals
2024-02-07
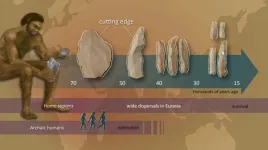
A study led by researchers at the Nagoya University Museum in Japan may change how we understand the cultural evolution of Homo sapiens at the time of their dispersal across Eurasia about 50,000 to 40,000 years ago. These findings challenge traditional beliefs about the timing and nature of cultural transitions during this critical period in human history.
Published in Nature Communications, the researchers’ insights into stone tool technology suggest that the commonly held view of a ‘revolution’ in culture and technology that allowed anatomically modern humans to outcompete ...
New study sheds new light on forests' role in climate and water cycle
2024-02-07
Forests, which cover a third of Earth's land surface, are pivotal in carbon storage and the water cycle, though the full scope of their impact remains to be fully understood. In a new study published in Nature Communications, researchers from Stockholm University and international colleagues provide new insights into the complex role forests play in the climate system and water cycle.
The research, involving scientists from 11 institutions across five countries, including Sweden, the UK, Finland, Germany, and Brazil, highlights the intricate relationship between forests, particularly their emission ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
[Press-News.org] More than half million dollars in research grants awarded to understand No. 1 birth defectThe American Heart Association and The Children’s Heart Foundation announce a nearly $600,000 commitment to jointly fund new research into congenital heart defects