(Press-News.org) About The Study: Despite a lack of clinical efficacy evidence, phenylephrine was the most common oral decongestant in the U.S. from 2012-2021, with hundreds of millions of units purchased by retail pharmacies annually, and sales remained stable during this time. In contrast to pseudoephedrine, which is often formulated as a stand-alone product, most phenylephrine products were co-formulated with antihistamines or antitussives, which are likely to provide some symptom relief for cough and cold symptoms.
Authors: Timothy S. Anderson, M.D., M.A.S., of the University of Pittsburgh, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.27932)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2023.27932?guestAccessKey=7ffce6da-c70e-4de3-8a0e-822d84331696&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=020824
END
Trends in phenylephrine and pseudoephedrine sales
JAMA
2024-02-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Visual impairment and real-world home physical activity with home environment in an older population
2024-02-08
About The Study: The results of this study demonstrated that home environment features, particularly lighting, may influence home activity metrics in older adults with visual impairment. Further prospective studies would be needed to confirm if home modifications can improve at-home activity.
Authors: Pradeep Y. Ramulu, M.D., M.H.S., Ph.D., of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2023.6436)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional ...
Stigmatizing language on liver transplant center websites may discourage patients from seeking treatment
2024-02-08
BOSTON – The vast majority of liver transplant centers in the United States use language on their websites that can be considered stigmatizing through their use of words like “alcoholism,” “alcoholic” and “alcohol abuse,’ potentially hindering care and the willingness of patients to seek treatment, a study by Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) has found.
In highlighting a significant gap between that online usage and the practice recommendations of medical ...
Heart-to-heart connection: Exploratorium and Gladstone bring a breakthrough science exhibit to life
2024-02-08
One of the country’s best-known science museums, San Francisco’s Exploratorium, is located less than three miles north of Gladstone Institutes—a proximity that has resulted in creative, high-science collaborations like the permanent exhibit featured in the latest issue of Stem Cell Reports.
Among the museum’s most popular exhibits, “Give Heart Cells A Beat” opens a rare window into the microscopic world of the beating human heart, using technology and materials made ...
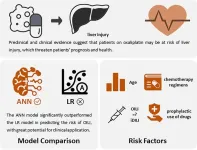
Predictive model of oxaliplatin-induced liver injury based on artificial neural network and logistic regression
2024-02-08
Since 2004, several clinical studies have reported that patients with OXA frequently experienced adverse effects of liver injury (LI), typically characterized by hepatic sinusoidal injury, splenomegaly, decreased platelet count and noncirrhotic portal hypertension, which can progress to nodular regenerative hyperplasia with long-term treatment. LI also decreased hepatic functional reserve and aggravated the postoperative course of colorectal cancer patients after hepatectomy, and may affect intraoperative bleeding, postoperative morbidity, and overall survival. LI can ...
The Galapagos comes to life in new RIT Press book
2024-02-08
Natural scientist and author Robert Rothman takes readers on a reptillian tour of the Galápagos Islands in his new book, A Paradise for Reptiles: Lizards, Snakes, and Giant Tortoises of the Galápagos Islands Vol. 1: Tortoises, Geckos, and Snakes, published by RIT Press.
For more than 30 years, Rothman has led hundreds of Rochester Institute of Technology students on tours to the Galápagos Islands to observe the wildlife and landscape that inspired Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection. Rothman’s A Paradise for Reptiles, an homage to the 19th century scientist, is an accessibly written guide for anyone interested in Darwin, the Galápagos, ...
Social media can reveal who needs the most help
2024-02-08
Language use in social media can be a useful tool for social scientists, because it reflects living conditions in areas the posts originate from.
“There is a correlation between social inequalities and language patterns in social media,” says Associate Professor Lucas M. Bietti at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU’s) Department of Psychology.
Researchers studied 30 million X/Twitter posts from the United States. They compared the language used in the tweets to the living conditions in the counties from which the ...
Clues to cancer drug’s deadly side effects could make it safer
2024-02-08
For some leukemia patients, the only potential chemotherapy option is a drug that also carries a high risk of heart failure. This means that some patients who recover from their cancer will end up dying of heart disease brought on by the cure.
In a new study, researchers from the University of Illinois Chicago and other universities have identified mechanisms that cause the drug, ponatinib, to harm the heart. They also identified a promising treatment that could reverse this process. The paper, with senior author Sang Ging Ong, assistant professor of pharmacology and medicine at UIC, is published in Circulation Research. The study is part of a growing field called cardio-oncology ...
Surprise discovery of tiny insect-killing worm
2024-02-08
UC Riverside scientists have discovered a tiny worm species that infects and kills insects. These worms, called nematodes, could control crop pests in warm, humid places where other beneficial nematodes are currently unable to thrive.
This new species is a member of a family of nematodes called Steinernema that have long been used in agriculture to control insect parasites without pesticides. Steinernema are not harmful to humans or other mammals and were first discovered in the 1920s.
“We spray trillions of them on crops every year, and they’re ...
Are environmental toxins putting future generations at risk?
2024-02-08
In a study that signals potential reproductive and health complications in humans, now and for future generations, researchers from McGill University, the University of Pretoria, Université Laval, Aarhus University, and the University of Copenhagen, have concluded that fathers exposed to environmental toxins, notably DDT, may produce sperm with health consequences for their children.
The decade-long research project examined the impact of DDT on the sperm epigenome of South African Vhavenda and Greenlandic ...
Protecting the protector boosts plant oil content
2024-02-08
UPTON, NY—Biologists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory have demonstrated a new way to boost the oil content of plant leaves and seeds. As described in the journal New Phytologist, the scientists identified and successfully altered key portions of a protein that protects newly synthesized oil droplets. The genetic alterations essentially protect the oil-protector protein so more oil can accumulate.
“Implementing this strategy in bioenergy or oil crop plants could ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] Trends in phenylephrine and pseudoephedrine salesJAMA