(Press-News.org)
“A fundamental hypothesis we sought to test was whether biomarkers from the TGF-β signaling pathway might be of novel value in risk stratification of HCC in the clinical cirrhotic setting.”
BUFFALO, NY- February 9, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Genes & Cancer on February 5, 2023, entitled, “Mechanistically based blood proteomic markers in the TGF-β pathway stratify risk of hepatocellular cancer in patients with cirrhosis.”
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the third leading cause of death from cancer worldwide but is often diagnosed at an advanced incurable stage. Yet, despite the urgent need for blood-based biomarkers for early detection, few studies capture ongoing biology to identify risk-stratifying biomarkers.
In this new study, researchers Xiyan Xiang, Krishanu Bhowmick, Kirti Shetty, Kazufumi Ohshiro, Xiaochun Yang, Linda L. Wong, Herbert Yu, Patricia S. Latham, Sanjaya K. Satapathy, Christina Brennan, Richard J. Dima, Nyasha Chambwe, Gulru Sharifova, Fellanza Cacaj, Sahara John, James M. Crawford, Hai Huang, Srinivasan Dasarathy, Adrian R. Krainer, Aiwu R. He, Richard L. Amdur, and Lopa Mishra, from The Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, University of Maryland, University of Hawaii, University of Hawaii Cancer Center, The George Washington University, North Shore University Hospital, Northwell Health, Hofstra Northwell School of Medicine, Cleveland Clinic, and Georgetown Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center, address this gap using the TGF-β pathway because of its biological role in liver disease and cancer, established through rigorous animal models and human studies.
“Alterations in the TGF-β signaling pathway could reflect a continuum of fibrosis to cirrhosis to cancer in the liver. Thus, we hypothesize that the TGF-β pathway-enriched biomarkers may serve as biomarkers in the evolution of HCC and stratify patients at risk for HCC. In addition, we hypothesized that the integrated animal model-to-human studies program would yield new TGF-β driven mechanistic biomarkers that could be valuable in yielding additional biomarkers that could stratify the risk of HCC.”
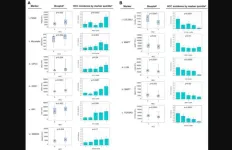
Using machine learning methods with blood levels of 108 proteomic markers in the TGF-β family, the team found a pattern that differentiates HCC from non-HCC in a cohort of 216 patients with cirrhosis, which they refer to as TGF-β based Protein Markers for Early Detection of HCC (TPEARLE) comprising 31 markers. Notably, 20 of the patients with cirrhosis alone presented an HCC-like pattern, suggesting that they may be a group with as yet undetected HCC or at high risk for developing HCC.
In addition, the researchers found two other biologically relevant markers, Myostatin and Pyruvate Kinase M2 (PKM2), which were significantly associated with HCC. They tested these for risk stratification of HCC in multivariable models adjusted for demographic and clinical variables, as well as batch and site. These markers reflect ongoing biology in the liver.
“They potentially indicate the presence of HCC early in its evolution and before it is manifest as a detectable lesion, thereby providing a set of markers that may be able to stratify risk for HCC.”
Read the full study: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/genesandcancer.234
Correspondence: Lopa Mishra, Richard L. Amdur - Emails: magdalena-bieniasz@omrf.org, lmishra1@northwell.edu, ramdur@northwell.edu
Keywords: TGF-β, hepatocellular carcinoma, myostatin, pyruvate kinase M2, biomarker
About Genes & Cancer: Genes & Cancer covers all aspects of the structure and function of oncogenes, growth suppressor and apoptotic genes, their role in signal transduction and the mechanisms by which their expression and function are altered during tumor development. In addition to publishing manuscripts that directly relate to these areas of research, Genes & Cancer also aims to attract papers in the areas of genomics, drug development and systems biology.
To learn more about Genes & Cancer, visit www.genesandcancer.com and connect with us on social media:
X, formerly Twitter
Facebook
YouTube
LinkedIn
Instagram
For media inquiries, please contact: media@impactjournals.com.
Genes & Cancer Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Str., Suite 1C
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-212-659-5400
###
END
There may, as they say, be plenty of fish in the sea — but angling opportunities on Utah’s streams, rivers and lakes are getting more crowded.
The number of anglers trying their luck on Utah waters has consistently increased over the years, meanwhile it’s getting more expensive for state managers to raise and stock gamefish and increasingly difficult to access water-based recreation during the ongoing megadrought.
Managers of fisheries in the state are being asked to do more with less these days, and they’re working more strategically to create sustainable opportunities for everyone picking up a rod and ...
Research Highlights:
In the EMBOLISE clinical trial, obstructing (or blocking) an artery that supplies blood to the dura, the protective covering of the brain, along with surgery to remove pooled blood reduced the chances by nearly 3-fold that blood would reaccumulate and require additional surgery. According to researchers, complications related to the embolization procedure were low, and neurological function was comparable to those without embolization.
Chronic subdural hematoma, a pooling of blood between the brain and one of its outer coverings, is one ...
Waltham — February 8, 2024 — For patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty (THA), the use of robotic-assisted surgery and surgical navigation techniques is not associated with an increased risk of periprosthetic joint infection (PJI), suggests a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
Computer navigation (CN) and robotic assistance (RA) do not alter the risk of PJI after total hip replacement surgery, according to the new research by Alberto V. Carli, MD, and colleagues of Hospital for Special Surgery, New York.
Could CN and RA increase risks during hip replacement?
Computer ...
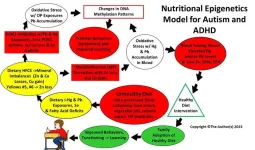
In a recent publication released by PubMed, American scientists led by Dr. Dufault at the Food Ingredient and Health Research Institute, reported the results of a clinical trial in which parents who received nutritional epigenetics education significantly reduced their consumption of ultra-processed foods while increasing their intake of whole and/or organic foods. The education intervention used curriculum focused on the constructs of the nutritional epigenetics model that explains how autism and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) may develop from the excess consumption of ultra-processed ...
· First-of-its-kind study of immune genes in Alzheimer’s patients’ blood
· Immune T cells are altered and entering brain
· Uncertain whether changes precipitate the disease
CHICAGO --- A new Northwestern Medicine study has found the immune system in the blood of Alzheimer’s patients is epigenetically altered. That means the patients’ behavior or environment has caused changes that affect the way their genes work.
Many of these altered immune genes are the same ones that increase an ...
ROCKVILLE, MD – Erdinc Sezgin, of Karolinska Institutet, Sweden will be honored as the recipient of the Biophysical Journal Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator Award at the 68th Annual Meeting of the Biophysical Society, held February 10-14 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. This award recognizes the work of outstanding early career investigators in biophysics. The winning paper is titled “Influence of the Extracellular Domain Size on the Dynamic Behavior of Membrane Proteins.” The paper was published in Volume 121, Issue ...
In writing a good online dating profile, the average love-seeker is likely to fill it up with all the appealing qualities and interests that make them special. They paraglide and do hot yoga on the weekends; enjoy Riesling on the beach or seeing indie bands in basements; are a Libra with Scorpio rising; or have a dog or three kids or an iguana. There’s one thing they routinely leave out, however: what they want to know about their potential partner.
Yet, that detail might the most important thing to include, according ...
Snail shells are often colourful and strikingly patterned. This is due to pigments that are produced in special cells of the snail and stored in the shell in varying concentrations. Fossil shells, on the other hand, are usually pale and inconspicuous because the pigments are very sensitive and have already decomposed. Residues of ancient colour patterns are therefore very rare. This makes this new discovery by researchers from the University of Göttingen and the Natural History Museum Vienna (NHMW) all the more astonishing: they found pigments in ...
There are no substitutes for native vegetation, but replacing large areas of monoculture with diversified crops in places where agricultural activities are widespread can have beneficial effects on the mammals that still inhabit the region.
This is one of the conclusions of a study conducted by researchers at the University of São Paulo (USP) supported by FAPESP. They focused on the northeast of São Paulo state, where the predominant biome is the Cerrado (Brazilian savanna). The region is one of the nation’s agribusiness centers.
An article on the study is published in the Journal of Applied Ecology. The study showed that ...
Semiconductors are ubiquitous in modern technology, working to either enable or prevent the flow of electricity. In order to understand the potential of two-dimensional semiconductors for future computer and photovoltaic technologies, researchers from the Universities of Göttingen, Marburg and Cambridge investigated the bond that builds between the electrons and holes contained in these materials. By using a special method to break up the bond between electrons and holes, they were able to gain a ...