(Press-News.org) School uniform policies could be restricting young people from being active, particularly primary school-aged girls, new research suggests.
The University of Cambridge study used data about the physical activity participation of more than a million five-to-17-year-olds internationally. It found that in countries where a majority of schools require students to wear uniforms fewer young people tend to meet the 60 minutes of physical activity per day recommended by the World Health Organisation (WHO).
Regardless of uniform policies, across most countries fewer girls than boys reach those recommended exercise levels. Among primary school students, however, the difference in activity between girls and boys was found to be wider in countries where most schools mandated uniforms. The same result was not found in secondary school-aged students.
The authors suggest that this could be explained by the fact that younger children get more incidental exercise throughout the school day than older students; for example, through running, climbing and various other forms of active play at break and lunchtimes. There is already evidence that girls feel less comfortable in participating in active play if they are wearing certain types of clothing, such as skirts or dresses.
Importantly, the results do not definitively prove that school uniforms limit children’s physical activity and the researchers stress that “causation cannot be inferred”. Previous, smaller studies however provide support for these findings, indicating that uniforms could pose a barrier. For the first time, the research examines large-scale statistical evidence to assess that claim.
The study was led by Dr Mairead Ryan, a researcher at the Faculty of Education and MRC Epidemiology Unit, University of Cambridge.
“Schools often prefer to use uniforms for various reasons,” Ryan said. “We are not trying to suggest a blanket ban on them, but to present new evidence to support decision-making. School communities could consider design, and whether specific characteristics of a uniform might either encourage or restrict any opportunities for physical activity across the day.”
The WHO recommends that young people get an average of 60 minutes of at least moderate-intensity physical activity per day during the week. The study confirms previous observations that most children and adolescents are not meeting this recommendation, especially girls. The difference in the percentage of boys and girls meeting physical activity guidelines across all countries was, on average, 7.6 percentage points.
Existing evidence suggests that uniforms could be a factor. Previous concerns have, for example, been raised about girls’ PE uniforms and school sports kits. A 2021 study in England found that the design of girls’ PE uniforms deterred students from participation in certain activities, while the hockey player Tess Howard proposed redesigning gendered sports uniforms for similar reasons, after analysing interview and survey data.
Children often get their exercise away from PE and sports lessons, however. “Activities like walking or cycling to school, breaktime games, and after-school outdoor play can all help young people incorporate physical activity into their daily routines,” Ryan said. “That’s why we are interested in the extent to which various elements of young people’s environments, including what they wear, encourage such behaviours.”
The study analysed existing data on the physical activity levels of nearly 1.1 million young people aged five to 17 in 135 countries and combined this with newly collected data on how common the use of school uniforms is in these countries.
In over 75% of the countries surveyed, a majority of schools required their students to wear uniforms. The study found that in these countries, physical activity participation was lower. The median proportion of all students meeting the WHO recommendations in countries where uniform-wearing was the norm was 16%; this rose to 19.5% in countries where uniforms were less common.
There was a consistent gender gap between boys’ and girls’ physical activity levels, with boys 1.5 times more likely to meet WHO recommendations across all ages. However, the gap widened from 5.5 percentage points at primary school level in non-uniform countries to a 9.8 percentage point difference in countries where uniforms were required in most schools.
The finding appears to match evidence from other studies suggesting that girls are more self-conscious about engaging in physical activity when wearing uniforms in which they do not feel comfortable. “Girls might feel less confident about doing things like cartwheels and tumbles in the playground, or riding a bike on a windy day, if they are wearing a skirt or dress,” said senior author Dr Esther van Sluijs, MRC Investigator. “Social norms and expectations tend to influence what they feel they can do in these clothes. Unfortunately, when it comes to promoting physical health, that’s a problem.”
The authors of the study argue that there is now enough evidence to warrant further investigation into whether there is a causal relationship between school uniforms and lower activity levels. They also highlight the importance of regular physical activity for all young people, regardless of their gender.
“Regular physical activity helps support multiple physical, mental, and well-being needs, as well as academic outcomes” Ryan said. “We now need more information to build on these findings, considering factors like how long students wear their uniforms for after school, whether this varies depending on their background, and how broader gendered clothing norms may impact their activity.”
The findings are reported in the Journal of Sport and Health Science.
END
School uniform policies linked to students getting less exercise, study finds
Study of 1.1 million young people in 135 countries found that physical activity levels are lower in countries where school uniforms are more commonplace
2024-02-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists are unravelling the secrets of red and grey squirrel competition
2024-02-15
In a first of its kind study, researchers have identified significant differences between the diversity of gut bacteria in grey squirrels compared to red squirrels which could hold the key to further understanding the ability of grey squirrels to outcompete red squirrels in the UK.
New research, published in the Journal of Medical Microbiology, looked to understand more about the mechanisms by which grey squirrels are able to gain an advantage over red squirrels. Chris Nichols, Conservation Evidence ...
Targeting the microenvironment rather than a specific cell type could be the key to healing injured hearts
2024-02-15
A groundbreaking scientific study published in Nature Cardiovascular Research has unveiled a remarkable discovery that may have far-reaching implications for the treatment of heart disease.
The intensive investigations utilizing single-cell genomics and genetic experiments were conducted by a team of renowned scientists in the Cardiomyocyte Renewal Laboratory and McGill Gene Editing Laboratory at The Texas Heart Institute, including James F. Martin Vivian L. Smith Chair in Regenerative Medicine and Vice Chairman and Professor ...
Live from the brain: Visual cues inform decision to cooperate
2024-02-14
HOUSTON – (Feb. 14, 2024) – Eye contact and body language are critical in social interaction, but exactly how the brain uses this information in order to inform behavior in real time is not well understood.
By combining behavioral and wireless eye tracking and neural monitoring, a team of Rice University scientists and collaborators studied how pairs of freely moving macaques interacting in a naturalistic setting use visual cues to guide complex, goal-oriented cooperative behavior. The study published in Nature offers first evidence that the part of the brain that processes visual information ⎯ the visual cortex ⎯ plays an active role in social behavior by providing ...
Super-resolution microscopy harnesses digital display technology
2024-02-14
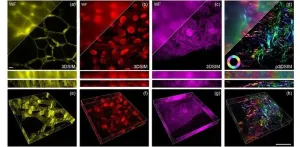
In the ever-evolving realm of microscopy, recent years have witnessed remarkable strides in both hardware and algorithms, propelling our ability to explore the infinitesimal wonders of life. However, the journey towards three-dimensional structured illumination microscopy (3DSIM) has been hampered by challenges arising from the speed and intricacy of polarization modulation.
Introducing the DMD-3DSIM System
Enter the high-speed modulation 3DSIM system “DMD-3DSIM,” combining digital display with super-resolution imaging, allowing scientists to see cellular structures in unprecedented detail. As ...
UW anthropologists’ research unveils early stone plaza in the Andes
2024-02-14
Two University of Wyoming anthropology professors have discovered one of the earliest circular plazas in Andean South America, showcasing monumental megalithic architecture, which refers to construction that uses large stones placed upright with no mortar.
Located at the Callacpuma archaeological site in the Cajamarca Basin of northern Peru, the plaza is built with large, vertically placed megalithic stones -- a construction method previously unseen in the Andes. Associate Professor Jason Toohey, project lead, and Professor Melissa Murphy have been researching ...
New epigenetic clocks reinvent how we measure age
2024-02-14
BOSTON – What causes us to age? New “clocks” developed by researchers may help point to the answers. Investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, unveil a new form of epigenetic clock – a machine learning model designed to predict biological age from DNA structure. The novel model distinguishes between genetic differences that slow and accelerate aging, predicts biological age and evaluates anti-aging ...
The roles of USP1 in Ewing sarcoma
2024-02-14
“This study uncovered important roles for USP1 in Ewing sarcoma.”
BUFFALO, NY- February 14, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Genes & Cancer on February 5, 2024, entitled, “Roles of USP1 in Ewing sarcoma.”
Ewing sarcoma is a cancer of bone and soft tissue in children and young adults that is driven by the EWS-ETS fusion transcription factor, most commonly EWS-FLI1.
Researchers Panneerselvam Jayabal, Xiuye Ma and Yuzuru Shiio from The University of Texas Health Science Center previously reported that Ewing sarcoma harbors two populations of cells, ...
New algorithm disentangles intrinsic brain patterns from sensory inputs
2024-02-14
Maryam Shanechi, Dean’s Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering and founding director of the USC Center for Neurotechnology, and her team have developed a new machine learning method that reveals surprisingly consistent intrinsic brain patterns across different subjects by disentangling these patterns from the effect of visual inputs.The work has been published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
When performing various everyday movement behaviors, such as reaching for a book, our brain has to take in information, often in the form of visual input — for example, seeing where the book is. Our brain then has to process ...
A new test could predict how heart attack patients will respond to mechanical pumps
2024-02-14
Every year, around 50,000 people in the United States experience cardiogenic shock — a life-threatening condition, usually caused by a severe heart attack, in which the heart can’t pump enough blood for the body’s needs.
Many of these patients end up receiving help from a mechanical pump that can temporarily help the heart pump blood until it recovers enough to function on its own. However, in nearly half of these patients, the extra help leads to an imbalance between the left and right ventricles, which can pose danger to the patient.
In a ...
Turning back the clock on photoaging skin
2024-02-14
Chronic exposure of human skin to ultraviolet light causes premature aging, or photoaging. As the skin undergoes photoaging, type I collagen bundles, which are found in the dermis beneath the top layer of the skin and provide strength and support to skin, become fragmented. This leads to wrinkles, fragility and loss of support and elasticity.
“The best way to prevent damage to type I collagen by sunlight is to wear sunscreen consistently, daily if possible and particularly when spending time outdoors,” said Frank Wang, MD, the William B. Taylor Endowed Professor of Clinical Dermatology at U-M Medical School.
Experts ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
[Press-News.org] School uniform policies linked to students getting less exercise, study findsStudy of 1.1 million young people in 135 countries found that physical activity levels are lower in countries where school uniforms are more commonplace