(Press-News.org) University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill researchers have developed a new drug delivery platform that harnesses helical amyloid fibers designed to untwist and release drugs in response to body temperatures.
A new research paper published on Jan. 26 in Nature Communications reveals groundbreaking structural details into how diseases form much like Alzheimer’s disease. With this knowledge, the group may have uncovered a unique mechanism to reverse both the deposits and their impact on those suffering from these conditions.
UNC-Chapel Hill researcher Ronit Freeman is leading a research group with investigators from the Lynn lab at Emory University looked at the core beta amyloid-42 peptide, the key portion driving amyloid plaque assembly and deposits in the brains of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. By creating synthetic variations of the peptide in the lab, they were able to discover how to control the way that these molecules assemble and twist.
“The ability of these amyloid materials to be untwisted and degraded highlights potential for treatments modifying and subsequently reversing plaques found in Alzheimer’s, and other neurodegenerative diseases,” said Freeman. “We know that the direction of the amyloid fibril twists is associated with different disease progression states. Imagine that by a simple treatment, we could modify amyloids to change their shape and disappear – this is what our discovery might enable us to do in the future.”
Using advanced spectroscopic techniques, the researchers probed how individual peptides interact, revealing information about assembly rates, distances between peptides, peptide alignment, and importantly the direction of twist. High-resolution electron and fluorescent microscopy were used to characterize the morphology of the materials at different temperatures.
The investigators identified that the N-terminal domain of the peptide is important for programming the shape of the assembly such as tubes, ribbons, or fibers, while C-terminal modifications direct either a left- or right-handed twist within the material. Using these design rules, a series of peptides were tuned to switch on-demand between left-handed and right-handed twisted ribbons in response to changing temperatures. This twist inversion then renders the material susceptible to degradation by natural proteins, a desirable feature for materials used as delivery vehicles.
Read the published article in Nature Communications here. To learn more about current research efforts for advances and scientific discovery, visit the Freeman Lab website here.
END
Researchers find possible solutions to reverse Alzheimer’s Disease impact
New discovery could be useful in treatment to untwist and degrade amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease
2024-02-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A Mount Sinai-led study shows early success of a novel drug in treating a rare and chronic blood cancer
2024-02-21
New York, NY (February 21, 2024) – A novel treatment for polycythemia vera, a potentially fatal blood cancer, demonstrated the ability to control overproduction of red blood cells, the hallmark of this malignancy and many of its debilitating symptoms in a multi-center clinical trial led by the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
In the phase 2 study, the drug rusfertide limited excess production of red blood cells, the main manifestation of polycythemia vera, over the 28-week course of ...
Muscle as a heart-health predictor
2024-02-21
Body composition — often expressed as the amount of fat in relation to muscle — is one of the standard predictors of cardiac health. Now, new research from the University of California San Diego indicates more muscle doesn’t automatically mean lower risk of heart trouble.
The study, published in the Journal of the American Heart Association, found all muscle isn’t the same. Britta Larsen, PhD, says men with a higher area of abdominal muscle have a greater risk of cardiac trouble. It’s a completely different ...
Air pollution linked to more signs of Alzheimer’s in brain
2024-02-21
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, FEBRUARY 21, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – People with higher exposure to traffic-related air pollution were more likely to have high amounts of amyloid plaques in their brains associated with Alzheimer’s disease after death, according to a study published in the February 21, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. Researchers looked at fine particulate matter, PM2.5, which consists of pollutant particles of less than 2.5 microns in diameter suspended in air.
The study does not prove that air pollution causes more amyloid plaques in the brain. It only ...
More than 40% of Americans know someone who died of drug overdose
2024-02-21
More than 40% of Americans know someone who has died of a drug overdose and about one-third of those individuals say their lives were disrupted by the death, according to a new RAND study.
Analyzing a national representative survey of American adults, researchers found that the lifetime exposure to an overdose death is more common among women than men, married participants than unmarried participants, U.S.-born participants than immigrants, and those who live in urban settings as compared to those in rural settings.
Rates of exposure were significantly higher in New England (Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, ...
Notre Dame receives Chan Zuckerberg Initiative award for neurodegenerative disease research
2024-02-21
The University of Notre Dame has received a Collaborative Pairs Pilot Project Award from the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative to study genes that affect neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease.
This is Notre Dame’s first award from the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative.
The award will fund a partnership between Cody Smith, the Elizabeth and Michael Gallagher Associate Professor of Biological Sciences at Notre Dame and a 2017 Alfred P. Sloan Fellow, and Beth Stevens, member of the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard and a 2015 MacArthur Fellow. With their combined expertise in neurological development, they will explore how gene expression and function changes with ...
Shaping the Future of Skin Aging: 15th International Conference on Skin Challenges, November 2024
2024-02-21
Following the huge success of the previous edition, the 15th edition of the Skin Ageing & Challenges International Conference is set to take place on November 7-8, 2024, at Corinthia Palace in Malta. The conference will provide attendees with a comprehensive overview of the current landscape and future prospects in skin aging research.
Professor Jean Krutmann, conference president, is just as excited as we are: “Skin aging is complex, but by working together across different fields, we’re making incredible strides. This conference is where all that collaboration shines, helping us find new ways to keep our skin healthy and vibrant.”
Skin ...
Black hole at center of the Milky Way resembles a football
2024-02-21
BERKS, Pa. — The supermassive black hole in the center of the Milky Way is spinning so quickly it is warping the spacetime surrounding it into a shape that can look like a football, according to a new study using data from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and the U.S. National Science Foundation’s Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA). That football shape suggests the black hole is spinning at a substantial speed, which researchers estimated to be about 60% of its potential limit.
The work, led by Penn State Berks Professor of Physics Ruth Daly, was published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
Astronomers call this giant ...
Stowers Institute Scientific Director Kausik Si receives coveted award from the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative
2024-02-21
KANSAS CITY, MO—February 21, 2024—The Chan Zuckerberg Initiative (CZI) has announced the awardees of their second cycle of Collaborative Pairs Pilot Project Awards, part of the CZI Neurodegeneration Challenge Network (NDCN).
Scientific Director Kausik Si, Ph.D., from the Stowers Institute for Medical Research will receive an award for the project titled, “Tuning memory by altering amyloids,” which will be conducted alongside Investigator Lukasz Joachimiak, Ph.D., from the University of Texas Southwestern.
The Collaborative Pairs Pilot Project Awards were launched in 2018 to investigate unsolved mysteries ...
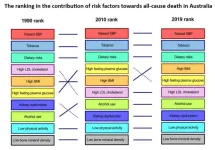
Raised blood pressure is the leading risk factor for death in Australia
2024-02-21
Raised blood pressure has been the leading risk factor for death in Australia for the past three decades, according to a study published February 21, 2024, in the open-access journal PLOS ONE led by Alta Schutte and Xiaoyue Xu from The George Institute for Global Health and UNSW, Sydney, with colleagues across Australia. It is also the main contributor to deaths from cardiovascular disease (CVD) specifically.
Raised blood pressure has long been recognized as a contributing factor to CVD and death, but is not always prioritized in national health plans. In this study, researchers focused on Australia, which lags ...
Biodiversity footprints for 151 dishes from around the world show that dishes with a larger impact on biodiversity tend to be meat, legume, or rice-based
2024-02-21
Dishes like Brazilian steak and Indian kidney bean curry have an especially large biodiversity footprint, or impact on biodiversity, according to a study published February 21, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Elissa Cheng from the National University of Singapore, Singapore, and colleagues.
Food choices can have significant environmental impacts. Previous research has begun to develop datasets that identify the encroachment of specific crops on the ranges of birds, mammals and amphibians. Based on these data, Cheng and colleagues estimated how 151 ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
[Press-News.org] Researchers find possible solutions to reverse Alzheimer’s Disease impactNew discovery could be useful in treatment to untwist and degrade amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease