(Press-News.org) Lugano, Switzerland, 07 March 2024 – The European Lung Cancer Congress 2024 is the annual appointment that brings together various experts in the field of thoracic oncology, including thoracic surgeons, respiratory physicians and pneumologists, medical and radiation oncologists, interventional radiologists and pathologists, to discuss the latest insights into the recent developments in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer.
The event will take place in Prague, Czech Republic, and through a dedicated virtual platform between 20-23 March.
Programme highlights
Novel results in the treatment of EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer
Related content: 3MO, 5MO, 8P, 4O
Insights into the opportunities related to the use of immunotherapy, and the challenges related to IO resistance mechanisms that may occur in the treatment of patients with lung cancer
Related content: Sessions on 20 March, 14:30-16:00 CET and 16:30-18:00 CET, session on 21 March, 11:15-12:45 CET
Prevention, screening and early diagnosis of thoracic tumours: from new technologies aimed at improving screening to prevention measures beyond smoking
Related content: Session on 23 March, 10:00-11:30 CET
Emerging evidence on the efficacy and the management of toxicities of antibody-drug conjugates
Related content: 59P, 11P, Session on 23 March, 10:00-11:30 CET
Keynote lecture
“Advancing precision oncology in lung cancer: A multidisciplinary-driven approach” by Enriqueta Felip, recipient of the Heine H. Hansen Award, 20 March 2024, 13:30-14:15 CET
“The rise of proteomics in never-smokers in lung cancer” by Yu-Ju Chen, 22 March 2024, 09:30-10:00 CET
“Incorporating ctDNA and other plasma-based assays into clinical trial design” by Maximilian Diehn, 22 March 2024, 14:30-15:00 CET
The results of more than 240 studies from various parts of the world will be presented and published online as a supplement to ESMO Open. The abstract titles can be viewed through the online programme.
Press accreditation
ESMO welcomes press representatives working for recognised press outlets interested in obtaining information and reporting on cancer issues, upon presentation of a letter of assignment and a valid press card. Press representatives are required to observe and abide by the ESMO Policy on Press Activities. To apply for press accreditation, please fill out the form available here. Requests for press accreditation should be sent by Monday, 18 March. Please be kindly informed that onsite press accreditation will not be available.
Further information
ELCC Press Office
press@esmo.org
Notes to editors
Please make sure to use the official name of the meeting in your reports: European Lung Cancer Congress 2024 or ELCC 2024 and the official congress hashtag #ELCC24. Follow it to stay up to date and use it to take part in the conversation on X (Twitter), LinkedIn, Instagram, Facebook
About the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO)
Representing more than 35,000 oncology professionals from 172 countries worldwide, ESMO is a reference for oncology education and information. Driven by a shared determination to secure the best possible outcomes for patients, ESMO is committed to standing by those who care about cancer through addressing the diverse needs of #ONEoncologycommunity, offering #educationforLIFE, and advocating for #accessiblecancerCARE. www.esmo.org
About the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC)
The International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC) is the only global organization dedicated solely to the study of lung cancer and other thoracic malignancies. Founded in 1974, the association's membership includes more than 10,000 lung cancer specialists across all disciplines in over 100 countries, forming a global network working together to conquer lung and thoracic cancers worldwide. The association also publishes the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, the primary educational and informational publication for topics relevant to the prevention, detection, diagnosis, and treatment of all thoracic malignancies. Visit www.iaslc.org for more information.
END
European Lung Cancer Congress 2024
Prague, Czech Republic, 20-23 March
2024-03-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pinging pipes could help to identify lead water lines without excavation
2024-03-07
As any percussionist or fidgety pen-tapper can tell you, different materials make different noises when you hit them. Researchers at Drexel University hope this foundational acoustic phenomenon could be the key to the speedy removal of lead water lines that have been poisoning water supplies throughout the country for decades. A recent study conducted with geotechnical engineering consultant Seaflower Consulting Services, showed that it is possible to discern a buried pipe’s composition by striking ...
A new manganese-fluorine catalyst with exceptional oxidizing power
2024-03-07
A research team, affiliated with UNIST has unveiled a cutting-edge catalyst with exceptional oxidizing power, capable of extracting electrons from compounds. Anticipated to revolutionize various fields, including the development of metal catalysts and synthetic chemistry, this catalyst marks a significant breakthrough in catalytic research.
Led by Professor Jaeheung Cho in the Department of Chemistry at UNIST, the research team successfully synthesized the pioneering manganese-fluorine catalyst, utilizing the Macrocyclic Pyridinophane System. This catalyst demonstrates the ability to induce oxidation reactions, ...
An aspirin a day? Poll of older adults suggests some who take it may be following outdated advice
2024-03-07
One in four older adults take aspirin at least three times a week, mostly in hopes of preventing heart attacks and strokes, a new poll shows.
But many people aged 50 to 80 who said they take aspirin may not need to, the findings from the University of Michigan National Poll on Healthy Aging suggest.
In all, 57% of people aged 50 to 80 who say they take aspirin regularly also said they don’t have a history of cardiovascular disease. Such people should have a conversation with their health care provider about what’s best for them before stopping or starting aspirin use.
National guidelines have changed in recent years for using aspirin for prevention, ...
What makes a pathogen antibiotic-resistant?
2024-03-07
Antimicrobial resistance is a story of constantly moving parts and players. With every new or tweaked antibiotic or antimicrobial drug, the targeted pathogens begin the evolutionary dance of acquiring resistance, prompting researchers to constantly develop workarounds or entirely new classes of medicine.
Understanding the underlying mechanisms of acquired antimicrobial resistance is critical to the fight, a case of knowing one’s enemy. In a new paper published March 2, 2024 in npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, part of the Nature Portfolio, researchers at Sanford Burnham Prebys, working with Roche Pharma Research and Early Development, ...
Method rapidly verifies that a robot will avoid collisions
2024-03-07
Before a robot can grab dishes off a shelf to set the table, it must ensure its gripper and arm won’t crash into anything and potentially shatter the fine china. As part of its motion planning process, a robot typically runs “safety check” algorithms that verify its trajectory is collision-free.
However, sometimes these algorithms generate false positives, claiming a trajectory is safe when the robot would actually collide with something. Other methods that can avoid false positives are typically too slow for robots in the real world.
Now, MIT researchers have developed a safety check technique which can prove with 100 percent accuracy ...
Eating habits, physical activity practice and clinical prognosis of colorectal cancer patients with overweight/obesity
2024-03-07
Background and objectives
Obesity is a chronic metabolic disease associated with the development of several other diseases, including cancer. The present study aims to evaluate the eating habits, physical activity, and clinical profiles of colorectal cancer (CRC) patients with overweight/obesity.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted with data collected from the medical records of patients diagnosed with CRC (n = 41) from June 2019 to June 2022. Additionally, a questionnaire (n = 35) was applied to gather information on eating habits and physical activity. The data were ...
Exploring the effectiveness of a novel pain management device for endometriosis pain
2024-03-07
Endometriosis is a chronic condition affecting women, often resulting in painful symptoms such as menstrual cramps and pelvic pain. Pain caused by endometriosis significantly lowers the quality of life and reproductive health of affected women, with around one-third of women still experiencing pain and discomfort despite treatment. While hormonal therapies and surgeries are common treatments, they often do not result in complete alleviation of symptoms. Effectively managing pain is, therefore, crucial for managing ...
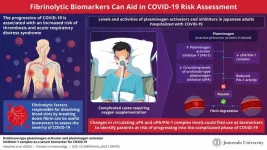
Fibrinolytic biomarkers for identifying patients at risk of severe COVID-19
2024-03-07
The global impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on healthcare systems has been significant. The sudden surge in infected cases overwhelmed hospitals and disrupted routine healthcare services, thus further worsening public health. Managing patients, too, has been challenging due to the variation of COVID-19 symptoms, ranging from mild to severe, that require medical intervention.
To help hospitals prioritize patients in need of care, researchers have been looking into various biological markers that can determine the risk of the disease becoming more severe. Among these, proteins in the blood related to blood clot formation, increased inflammation, and ...
Exploring the surface properties of NiO with low-energy electron diffraction
2024-03-07
Spintronics is a field that deals with electronics that exploit the intrinsic spin of electrons and their associated magnetic moment for applications such as quantum computing and memory storage devices. Owing to its spin and magnetism exhibited in its insulator-metal phase transition, the strongly correlated electron systems of nickel oxide (NiO) have been thoroughly explored for over eight decades. Interest in its unique antiferromagnetic (AF) and spin properties has seen a revival lately, since NiO is a potential material for ultrafast spintronics devices.
Despite this rise in popularity, exploration of its surface magnetic properties using ...
What drives students to take up teaching? New study explores aspirations and challenges faced by prospective teachers in Japan
2024-03-07
As role models and mentors for the youth, teachers play an important role in guiding children into well-rounded adults. However, excessive workloads and high skill expectations have allegedly led to teacher shortages in Japan. In 2022, the Ministry of Education Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT) reported a record low in applicants for primary school teaching positions, and a survey from the same year revealed that 65.8% of 924 full-time educators expressed a desire to quit due to overwhelming demands.
To address the teacher shortage, Associate Professor Akihiro Saito from ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
[Press-News.org] European Lung Cancer Congress 2024Prague, Czech Republic, 20-23 March