Applications open for 2024 Michelson prizes: $150,000 grants available to immunology innovators
Grants to be awarded to early-career scientists for pioneering research in immunology, vaccine discovery, and immunotherapy research
2024-04-01
(Press-News.org) LOS ANGELES – Today, Michelson Medical Research Foundation (MMRF) and the Human Immunome Project (HIP) opened the application period for the 2024 Michelson Prizes: Next Generation Grants. The annual prizes award $150,000 research grants to early-career scientists advancing human immunology, vaccine discovery, and immunotherapy research for major global diseases.
The international prize supports high-risk, high-reward research poised to tackle global health crises and address current roadblocks in human vaccine development and our understanding of key immune processes.
“Securing funding for innovative research is a significant hurdle for young scientists, often stifling groundbreaking ideas before they can even be explored,” said Dr. Gary K. Michelson, founder and co-chair of Michelson Philanthropies. “By supporting promising, early-career scientists, these grants pave the way for advancements in immunology that hold the potential to develop new treatments, further our understanding, and save lives.”
The scope of the Michelson Prizes encompasses research across immunology, vaccine, and immunotherapy discovery. However, applicants from the full spectrum of related disciplines, including clinical research, biochemistry, molecular biology, protein engineering, computer science, artificial intelligence/machine learning, biophysics, nanotechnology, etc., are encouraged to apply.
An international committee of esteemed scientists will evaluate proposals. The selection process prioritizes bold research concepts that reach beyond convention to make a lasting impact on the fields of vaccine development and immunology.
Prize details and application criteria:
$150,000 grants for one year of research support
Open to researchers aged 35 and under.
Submission deadline: Sunday, June 9, 2024 at 11:59 PM ET.
Apply now at: https://michelsonprizes.smapply.org.
For more information about the Michelson Prizes: Next Generation Grants, as well as past prize laureates, please visit https://www.michelsonmedicalresearch.org/michelson-prizes-next-generation.
###
About the Michelson Medical Research Foundation: Founded by Dr. Gary K. Michelson in 1995, the Michelson Medical Research Foundation accelerates solutions to global health challenges by fostering high-risk, high-reward approaches that disrupt the status quo to make innovative ideas a reality. Through convergent collaboration among engineers, scientists, and physicians, the foundation helps rapidly move bold concepts and technologies from the laboratory into clinics and communities around the world. Michelson Medical Research Foundation is a division of Michelson Philanthropies. For more information, visit: www.michelsonmedicalresearch.org
About the Human Immunome Project: The Human Immunome Project (HIP) is a global NGO that generates diverse immunological datasets at scale and builds publicly available AI models of the immune system to accelerate medical research and drug discovery, decrease healthcare costs, and, most importantly, improve health for all. HIP operates globally and is a registered US nonprofit organization.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-04-01
ATLANTA – Chemical Insights Research Institute (CIRI) of UL Research Institutes is examining what it means to support human health in the face of many environmental stressors, including extreme heat, extreme precipitation and wildfires through the upcoming webinar "Protecting Human Health While Adapting to Extreme Climate Conditions."
The webinar takes place on Wednesday, April 3, 2024, at 2:00 p.m. ET.
The webinar will begin with a brief overview of resilience for health in the built environment, followed by a discussion among expert panelists ...
2024-04-01
Supercapacitors have the superb ability to capture and store energy. Researchers can use different materials and fabrication methods to make them flexible, thin and appropriate for use in wearable or implantable electronics, like smart watches or pacemakers, but those approaches tend to be intricate and costly. Now, however, a team from Jilin University in China has developed a kind of all-in-one adhesive electrode that solves one of the major issues facing advancing flexible 2D supercapacitors - making the ...
2024-04-01
Trichoderma spp. are globally distributed and are considered significant fungal resources. They are widely studied and applied due to their economic and ecological importance, offering numerous benefits, such as producing enzymes and antibiotics, aiding in plant growth, and protecting them from pathogens.
This study led by Prof. Chu-Long Zhang (Fungal Resources Utilization and Plant Protection Research Group, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China) presents the discovery of eleven new species of Trichoderma. The team obtained a total of 618 Trichoderma ...
2024-04-01
WASHINGTON, April 1, 2024 — Adding milk to an alcoholic drink and then curdling that milk is a 300-year-old preservation technique that was used by none other than Ben Franklin. Join George as he discovers the chemistry that makes this technique so useful, and learn how to make the best espresso martini you’ll ever taste. https://youtu.be/ef0heKtiuvQ?si=W5uDUccoh_bOWtZy
Reactions is a video series produced by the American Chemical Society and PBS Digital Studios. Subscribe to Reactions at http://bit.ly/ACSReactions and follow us on Twitter @ACSReactions.
The American ...
2024-04-01
About The Study: In this quality improvement study of 35 health care facilities in Orange County, California, using quasi-experimental design, chlorhexidine bathing and nasal decolonization were associated with significantly lower multidrug-resistant organism prevalence and incident clinical cultures. Infection-related hospitalizations, associated costs, and deaths among nursing home residents also decreased.
Authors: Susan S. Huang, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of California Irvine School of Medicine in Irvine, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The ...
2024-04-01
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that smartphones could offer a feasible, reliable, valid, and scalable solution for remote evaluations of frontotemporal lobar degeneration, a neurodegenerative pathology causing early-onset dementia syndromes, and may improve early detection. Smartphone assessments should be considered as a complementary approach to traditional in-person trial designs. Future research should validate these results in diverse populations and evaluate the utility of these tests for longitudinal monitoring.
Authors: Adam ...
2024-04-01
UCSF-led research shows smartphone cognitive testing is comparable to gold-standard methods; may detect FTD in gene carriers before symptoms start.
A smartphone app could enable greater participation in clinical trials for people with frontotemporal dementia (FTD), a devastating neurological disorder that often manifests in midlife.
Research into the condition has been hampered by problems with early diagnosis and difficulty tracking how people are responding to treatments that are only likely to be effective at the early stages ...
2024-04-01
About The Study: In this nationally representative cohort study, polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) exposure was significantly associated with an increased risk of cancer mortality. Since the 1970s, PBDEs have been used as flame retardants in a wide array of consumer products, such as building materials, furnishings, and electronics. Further studies are needed to replicate the findings and determine the underlying mechanisms.
Authors: Wei Bao, M.D., Ph.D., and Buyun Liu, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Science and Technology of China in Hefei, Anhui, China, ...
2024-04-01
About The Study: In this survey study, binge drinking in both men and women was reported at greater frequency among sports wagering individuals compared with nongamblers and non–sports gamblers.
Authors: Joshua B. Grubbs, Ph.D., of the University of New Mexico in Albuquerque, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.5473)
Editor’s Note: Please see the ...
2024-04-01
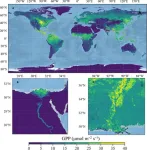
In the field of environmental and climate science, researchers have developed the Comprehensive Mechanistic Light Response (CMLR) gross primary production (GPP) dataset. Derived from the TROPOMI satellite's solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF) observations, this global dataset offers unprecedented insights into Earth's GPP, the process through which plants convert carbon dioxide and sunlight into essential resources.
Gross Primary Production (GPP), the process through which plants convert carbon dioxide and sunlight into glucose and oxygen, is the Earth's largest carbon flux. Accurate quantification ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Applications open for 2024 Michelson prizes: $150,000 grants available to immunology innovators
Grants to be awarded to early-career scientists for pioneering research in immunology, vaccine discovery, and immunotherapy research