(Press-News.org) Plants harness chlorophyll to capture sunlight and kickstart photosynthesis, a crucial process on our planet that converts luminous energy into chemical fuel while producing oxygen. This pivotal chemical energy is subsequently utilized by plants, algae, and select bacteria to metabolize carbon dioxide and water into sugars.
Now, scientists at the Center for Research in Biological Chemistry and Molecular Materials (CiQUS) have achieved a breakthrough by integrating non-native photosensitizers into mammalian cells. This revelation showcases the capability of these substances to also absorb green or blue light, thus instigating artificial chemical reactions within cellular environments. Notably, this innovative approach has been employed for synthesizing indoles, chemical compounds boasting significant biological activities. Such findings underscore the feasibility of leveraging light to fabricate functional molecular products, including fluorescent variants, within biological settings. Published in the renowned Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS), this study marks the pioneering demonstration of forging synthetic chemical bonds within cells through photocatalysis.
Photocatalysis emerges as a transformative chemical technology with vast socio-economic implications. It empowers the utilization of light as an energy source to activate catalysts and instigate chemical transformations, thereby facilitating sustainable synthetic endeavors. "The evidence of employing these synthetic photocatalysis technologies within biological milieus, we believe, heralds a new frontier at the frontier of chemistry and biology," remarks Professor José Luis Mascareñas, co-leading the research alongside Dr. María Tomás Gamasa. "Moreover, we anticipate that in the foreseeable future, these technologies will unveil novel strategies for precisely manipulating human cells, thus fostering the development of innovative therapeutic interventions." Dr. Sara Gutiérrez and PhD student Cinzia D'Avino spearheaded the experimental work, conducted entirely at CiQUS.
END
Researchers at CiQUS synthesize new compounds within living cells using light
Scientists at CiQUS have achieved a breakthrough by integrating non-native photosensitizers into mammalian cells.
2024-04-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Dr. Arati Dasgupta honored by the Nuclear and Plasma Science Society
2024-04-02
WASHINGTON – U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) plasma physicist, Arati Dasgupta, Ph.D., head, Radiation Hydrodynamics Branch, Plasma Physics Division, receives the 2024 IEEE Plasma Science and Applications Committee (PSAC) Award for her fundamental contributions to, and leadership of, high energy density plasma, atomic, and radiation physics, fusion applications, and service to the plasma science community.
Presented by the IEEE Nuclear and Plasma Sciences Society, the PSAC Award recognizes outstanding contributions to the field of plasma science and engineering. Dasgupta is the 37th winner of the PSAC Award — one of three women ever to receive ...
All-cash home buyers pay 10% less than mortgage buyers
2024-04-02
Owning a home has long been considered a crucial way to build wealth, but making such a purchase has become increasingly difficult for many residents. In addition to steep housing prices and high interest rates, there have been a growing number of all-cash buyers who can close a deal quickly, beating out competing offers from buyers who need to finance their home with a mortgage.
The convenience and certainty of all-cash offers appeals to sellers so much so, that they pay on average 10 % less than mortgage buyers, according to a new study from the University of California San Diego Rady School of Management.
“When sellers accept a mortgage offer, it comes with risk,” said Michael ...
Must mRNA be cloaked in a lipid coat to serve as a vaccine?
2024-04-02
The Uchida Laboratory (Lab Head: Prof. Satoshi Uchida, Department of Advanced Nanomedical Engineering, Medical Research Institute, Tokyo Medical and Dental University; abbreviated as TMDU) of Innovation Center of NanoMedicine (Center Director: Prof. Kazunori Kataoka, Location: Kawasaki, Japan; abbreviated as iCONM) has demonstrated that intradermal administration of mRNA alone (naked mRNA) without protected by nanoparticles induced robust vaccination against SARS CoV-2, a virus causing COVID-19, in mice and primates, ...
Infant gut microbes have their own circadian rhythm, and diet has little impact on how the microbiome assembles
2024-04-02
Infant gut microbiomes oscillate with a circadian rhythm, even when they are cultivated outside of the body. Researchers report April 2 in the journal Cell Host & Microbe that the rhythm is detectable as early as 2 weeks after birth but becomes more pronounced with age. The finding comes from a randomized controlled trial that also showed that diet has less impact on the development and composition of the infant microbiome than previously thought.
“We found that even at very early ages of colonization, the microbial ecosystem develops this circadian rhythmicity,” ...
New study finds triple-negative breast cancer tumors with an increase in immune cells have lower risk of recurrence after surgery
2024-04-02
ROCHESTER, Minn. — A new multicenter, international study suggests that people who have early-stage triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) and high levels of immune cells within their tumors may have a lower risk of recurrence and better survival rates even when not treated with chemotherapy. The study was published in the Journal of American Medical Association (JAMA).
TNBC is a breast cancer subtype that does not respond to drugs that target the estrogen receptor or the HER2 protein. It grows rapidly, is more likely to spread beyond the breast before diagnosis ...
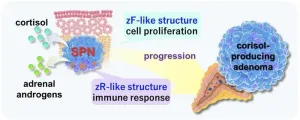
New insights into how tumors on adrenal glands develop
2024-04-02
Fukuoka, Japan—Researchers from Kyushu University's Faculty of Medical Sciences report on new insights into the mechanisms of how adrenal gland tumors are formed. The team identified a new type of tumor cell population that they termed 'steroids-producing nodules' or SPNs, that exhibits the unique characteristic of producing two different hormones. Specific structures in SPNs were found to lead to cortisol-producing adenomas, or CPAs, noncancerous tumors that produce excessive cortisol.
Their findings, published in eBioMedicine, ...
Ask Chat GPT about your radiation oncology treatment
2024-04-02
· AI responses to common patient questions were on par or exceeded answers from professional societies
· Goal also to reduce clinician workload and burnout
· More than 60% of cancer patients require radiation oncology treatment
CHICAGO --- Cancer patients about to undergo radiation oncology treatment have lots of questions. Could ChatGPT be the best way to get answers?
A new Northwestern Medicine study tested a specially designed ChatGPT to see if it could successfully provide answers to patients’ common questions about radiation oncology. Patients may be too overwhelmed to address all their concerns during a clinical visit ...
Surveillance colonoscopy findings in older adults with a history of colorectal adenomas
2024-04-02
About The Study: In this study of 9,740 surveillance colonoscopies among 9,601 adults ages 70 to 85 with prior colorectal adenoma, colorectal cancer detection was rare regardless of prior adenoma finding, whereas the advanced neoplasia yield was 12% overall. Yields were higher among those with a prior advanced adenoma than among those with prior nonadvanced adenoma and did not increase significantly with age. These findings can help inform whether to continue surveillance colonoscopy in older adults.
Authors: Jeffrey K. Lee, M.D., M.P.H., of Kaiser Permanente Northern California in Oakland, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Metabolic profile and long-term risk of depression, anxiety, and stress-related disorders
2024-04-02
About The Study: High levels of glucose and triglycerides and low levels of high-density lipoprotein were associated with future risk of depression, anxiety, and stress-related disorders in this study of more than 200,000 participants. These findings may support closer follow-up of individuals with metabolic dysregulations for the prevention and diagnosis of psychiatric disorders.
Authors: Charilaos Chourpiliadis, M.D., of the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, is the corresponding ...
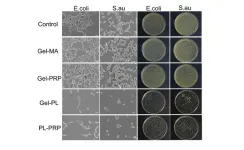
Wound treatment gel fights the battle against antibacterial resistance
2024-04-02
WASHINGTON, April 2, 2024 – Hydrogels are popular for use in skin ailments and tissue engineering. These polymer-based biocompatible materials are useful for their abilities to retain water, deliver drugs into wounds, and biodegrade. However, they are complicated to manufacture and not very resilient to external forces like rubbing against clothing, sheets, or wound dressings. They are also not inherently able to battle bacterial infections, so they are often infused with antimicrobial drugs or metal ions, which can ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] Researchers at CiQUS synthesize new compounds within living cells using lightScientists at CiQUS have achieved a breakthrough by integrating non-native photosensitizers into mammalian cells.