(Press-News.org) Join the International Society of Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) to celebrate Earth Day on 22 April 2024 by diving into the science of conservation, where the potential of stem cells is harnessed to foster a more sustainable and biodiverse future. This enlightening webinar co-hosted by Ashlee Hutchinson and Jun Wu will spotlight the revolutionary intersection of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), embryo models and genome engineering technologies with the noble cause of species preservation.
As our planet faces unprecedented biodiversity loss, this program will unveil how cutting-edge scientific advancements offer a lifeline for endangered species, allowing us to replicate and preserve the intricate tapestry of life that inhabits Earth. The webinar will explore the latest breakthroughs, ethical considerations, challenges, and future directions in the field, showcasing how these technologies not only deepen our understanding of biology but also equip us with the tools to combat extinction.
Organizers
Ashlee Hutchinson, PhD, Revive & Restore, Australia
Jun Wu, PhD, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, USA
Presenters
Jef Boeke, PhD, NYU Langone Health, USA
Eriona Hysolli, PhD, Colossal Biosciences, USA
Nikki Traylor-Knowles, PhD, University of Miami, USA
Katsuhiko Hayashi, PhD, Osaka University, Japan
Jeanne Loring, PhD, Scripps Research Institute, USA
Gabriela Mastromonaco, PhD, Toronto Zoo, Canada
Oliver Ryder, PhD, San Diego Zoo Wildlife Alliance, USA
Jun Wu, PhD, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, USA
Qi-Long Ying, PhD, University of Southern California, USA
This webinar is free for anyone interested in species conservation and stem cells. Learn more and register. Media should contact kkilbourne@isscr.org for more information.
About the International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR.org)
With nearly 5,000 members from more than 70 countries, the International Society for Stem Cell Research is the preeminent global, cross-disciplinary, science-based organization dedicated to stem cell research and its translation to the clinic. The ISSCR mission is to promote excellence in stem cell science and applications to human health. Additional information about stem cell science is available AboutStemCells.org, an initiative of the Society to inform the public about stem cell research and its potential.
###
END
NORMAN, OKLA. – Hanping Ding, Ph.D., an assistant professor in the School of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering at the University of Oklahoma, has been awarded a $3.1 million grant from the Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Technologies Office in the Department of Energy through the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law to further research in clean hydrogen production. The funding is part of a $750 million effort in President Biden’s Investing in American agenda. The money from the Department of Energy will go to 52 projects across 24 states to position the United States as a global leader in the clean hydrogen industry.
The combined outcomes of the 52 projects should allow the ...
Professor dr. Linda Amaral-Zettler, Research Leader at NIOZ Royal Netherlands Institute of Sea Research and the Chair in Marine Microbiology at the University of Amsterdam has been awarded a prestigious Advanced ERC-grant by the European Commission today. Amaral-Zettler receives almost 3,5 million euros for her research into biodegradation in the marine environment. “Biodegradable sounds really nice”, she admits. “But before we repeat the mistakes we’ve made with fossil-fuel-based plastics back in the last millenium, we really want to understand how these materials interact with marine life and how long they last in the environment.” “Biodegradable ...
We depend on our cells being able to divide and multiply, whether it’s to replace sunburnt skin or replenish our blood supply and recover from injury. Chromosomes, which carry all of our genetic instructions, must be copied in a complete way during cell division. Telomeres, which cap the ends of chromosomes, play a critical role in this cell-renewal process—with a direct bearing on health and disease.
The enzyme telomerase plays a key role in maintaining the length of telomeres as chromosomes replicate during ...
Modern biology textbooks assert that only bacteria can take nitrogen from the atmosphere and convert it into a form that is usable for life. Plants that fix nitrogen, such as legumes, do so by harboring symbiotic bacteria in root nodules. But a recent discovery upends that rule.
In two recent papers, an international team of scientists describe the first known nitrogen-fixing organelle within a eukaryotic cell. The organelle is the fourth example in history of primary endosymbiosis — the process by which a prokaryotic cell is engulfed by a eukaryotic cell and evolves beyond symbiosis into an organelle.
“It’s very rare that organelles ...
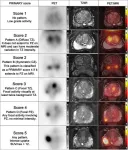
Reston, VA—PET/MRI can improve diagnostic accuracy for prostate cancer patients and help avoid unnecessary biopsies, according to new research published in the April issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. By applying the PRIMARY scoring system to PET/MRI results, researchers found that more than 80 percent of unnecessary biopsies could be avoided at the expense of missing one in eight clinically significant prostate cancer cases.
The Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) is a five-point ...
The concept of “One Health” – which emphasizes the relationship between human, animal, plant and environmental health – has been gaining ground in scientific discussions in recent years. Brazilian and North American researchers developing research using this approach presented their work on Tuesday (April 9th), in Chicago (United States), during FAPESP Week Illinois.
One of the panelists was Eduardo Esteban Bustamante, a professor at the University of Illinois in Chicago. He talked about behavioral interventions that have been tested to promote physical activity and healthy eating – practices that, according to the researcher, ...
AMHERST, Mass. – A team of computer scientists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst working on two different problems—how to quickly detect damaged buildings in crisis zones and how to accurately estimate the size of bird flocks—recently announced an AI framework that can do both. The framework, called DISCount, blends the speed and massive data-crunching power of artificial intelligence with the reliability of human analysis to quickly deliver reliable estimates that can quickly pinpoint and count specific features from very large collections ...
PRESS RELEASE
Chicago, IL and Philadelphia, PA, USA, April 11, 2024: The Society of Gynecologic Oncology (SGO) and The GOG Foundation, Inc. (GOG-F) Launch BRIDGES 2.0 Research Initiative with support from the Foundation for Women’s Cancer (FWC). After a successful inaugural year, the SGO and the GOG-F join forces to collaborate, and proudly announce the launch of an expanded two-year clinical trial education program supported by the FWC. This important career and clinical trial development initiative aims to cultivate the next generation of investigators in gynecologic oncology and will focus on clinical and translational research ...
It’s challenging to sustain a pregnancy when food is short, or conditions are otherwise tough. That’s why many mammalian embryos can postpone their growth to get through periods of environmental stress and then re-enter development when conditions improve. This stalling of development is known as embryonic diapause, and understanding the mechanisms behind it might help improve infertility treatments, such as embryo freezing. Now, researchers at the Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology, the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Shanghai, China, have discovered how nutrient depletion is sensed by embryos growing in hungry mouse mums to induce diapause. ...
LA JOLLA, CA—Most disease-causing bacteria are known for their speed: In mere minutes, they can double their population, quickly making a person sick. But just as dangerous as this rapid growth can be a bacterium’s resting state, which helps the pathogen evade antibiotics and contributes to severe chronic infections in the lungs and blood, within wounds, and on the surfaces of medical devices.
Now, Scripps Research scientists have discovered how long chains of molecules called polyphosphates (polyP) are needed for bacteria to slow down movements within cells and let them enter this resting ...