(Press-News.org) COLUMBUS, Ohio – A university professor has found a way to help students – and himself – power through long lecture classes: exercise breaks.
In a new study, a professor at The Ohio State University showed that five-minute exercise sessions during lectures were feasible and that students reported positive impacts on their attention and motivation, engagement with their peers and course enjoyment.
The results may not be particularly surprising, but they do suggest a solution for a long-standing issue in college classrooms, said Scott Hayes, author of the study and associate professor of psychology at Ohio State.
“Nobody can stay on task for 80 minutes straight without their mind wandering and their attention waxing and waning,” Hayes said.
“If you give students a break and get their bodies moving for just a few minutes, it can help them get their minds back to the lecture and probably be more productive. I know it helps me, as well.”
The study was published recently in the journal Frontiers in Sports and Active Living.
Hayes said he was inspired to do this research by a similar laboratory-based study of how students responded to exercise breaks during a single video lecture.
That study found positive results, but Hayes wondered if it could work in the real world of in-person university lectures, over the course of a full semester.
He tested it in four of his own classes. One to two student-led exercise sessions (five minutes each) were implemented in each lecture during upper-level psychology courses with 20 to 93 students. The classes were 80 minutes long.
At the beginning of the course, Hayes broke the class into small groups, and each group was responsible for developing a five-minute exercise session. Hayes reviewed the exercise sessions beforehand to make sure they were workable and safe.
“I wanted the students to design and lead the sessions because I thought it would help them buy into the idea, and help with their engagement and investment,” he said.
Hayes admitted that the sessions were sometimes a bit awkward at the beginning of the semester. The students didn’t know exactly how to act, and they weren’t used to doing something like this during a class.
But students soon got into the flow and had fun with the sessions. Some of the exercises students included were jumping jacks, lunges, overhead press (with a backpack) and hamstring stretches.
Hayes said a few student groups got creative in designing their sessions.
“One of the groups designed a theme of going to an orchard and picking apples. So they had their fellow students reaching up as if they were picking apples from a tree and reaching down to put them in a basket,” Hayes said.
Hayes said he knew the program was a success when students spontaneously provided anonymous comments with their end-of-semester students evaluations. One student’s comment reflected a common response: “I enjoyed the exercise breaks in class and really felt like they motivated me to focus more.”
In one of the classes studied, Hayes gave the students a survey at the end of the course about the exercise sessions. All the students reported that they had never taken a class that had an exercise break during the lecture.
Students rated the exercise breaks as improving attention, enjoyable, and improving peer engagement. They reported that, compared to other classes, they preferred the class with an exercise break and they would like more classes to offer such sessions.
One open question could be whether these exercise sessions improved student learning and grades. Hayes said that is beyond the scope of this study, and it would be difficult to do that kind of research. Comparisons of different classes, at different times of day, and with a variety of teachers, would make comparisons challenging to make.
But this study found that exercise breaks were feasible to do and that students enjoyed them and found them useful – which he said may make it worthwhile for other faculty to try.
Some already have.
“Two colleagues in the psychology department here at Ohio State have told me they have started exercise breaks in their courses,” Hayes said. “It may be catching on.”
The study was supported by the National Institute on Aging.
END
A university lecture, with a dash of jumping jacks
Study finds possible value in class exercise breaks
2024-04-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How light can vaporize water without the need for heat
2024-04-24
It’s the most fundamental of processes — the evaporation of water from the surfaces of oceans and lakes, the burning off of fog in the morning sun, and the drying of briny ponds that leaves solid salt behind. Evaporation is all around us, and humans have been observing it and making use of it for as long as we have existed.
And yet, it turns out, we’ve been missing a major part of the picture all along.
In a series of painstakingly precise experiments, a team of researchers at MIT has demonstrated that heat isn’t alone in causing water to evaporate. Light, striking the water’s surface where air and water meet, can break water molecules away and float ...
These giant, prehistoric salmon had tusk-like teeth
2024-04-24
Oncorhynchus rastrosus, a giant species of salmon that lived in the North American Pacific Northwest a few million years ago, sported a pair of front teeth that projected out from the sides of its mouth like tusks, according to a study published April 24 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Kerin Claeson from the Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine, USA, and colleagues.
O. rastrosus, first described in the 1970s, has been estimated to reach up to 2.7 meters (8.9 feet) long, making it the largest member of the Salmonidae family ever discovered. Initially, researchers thought its oversized front teeth pointed backward into the mouth like fangs, in large ...
New study infers our wellbeing by analyzing the language we use around ageing, using language markers to enable "a different type of access to individuals’ inner worlds"
2024-04-24
New study infers our wellbeing by analyzing the language we use around ageing, using language markers to enable "a different type of access to individuals’ inner worlds"
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0302103
Article Title: When I am sixty-four… evaluating language markers of well-being in healthy aging narratives
Author Countries: Switzerland, USA, Australia
Funding: Funding by the Jacobs Foundation (https://jacobsfoundation.org/en/; awarded to TM) and the Swiss National Science Foundation SNF ((https://www.snf.ch/en/; fellowship P2ZHP1_199409 ...
New research confirms plastic production is directly linked to plastic pollution
2024-04-24
APRIL 24, 2024 – A research paper published today in Science Advances reveals a direct correlation between plastic production and plastic pollution, such that every 1% increase in plastic production is associated with a 1% increase in plastic pollution in the environment. The study finds that fast-moving consumer goods companies disproportionately contribute to the problem more than household and retail companies. The study marks the first robust quantification of the global relationship between plastic production and pollution.
The research, led by scientists ...
MSU researchers uncover 'parallel universe' in tomato genetics
2024-04-24
In a new paper appearing in Science Advances, Michigan State University researchers have unraveled a surprising genetic mystery centered on sugars found in what gardeners know as “tomato tar.”
Anyone who has pruned tomato plants barehanded has likely found their fingers darkened with a sticky, gold-black substance that won’t quite wash off.
This tomato tar is sticky for good reason. It’s made of sugars — acylsugars, to be precise — and acts as a sort of natural flypaper for ...
Grey cuckoo, red cuckoo: unveiling the genomic secrets of color polymorphism in female cuckoo birds
2024-04-24
NEW YORK, April 24, 2024 — Sexual dimorphism—the visible difference between females and males—can be seen in diverse animals, including humans. One intriguing aspect of this phenomenon is sex-limited polymorphism, where one sex displays greater variations in a particular trait than the other. In a recent study published in Science Advances, a team of researchers delve into the genetic underpinnings behind the color polymorphism observed in adult females of the brood parasitic Cuculus, more widely known as cuckoo birds, shedding light on the evolution and functional significance of this phenomenon.
Several species of cuckoos, a genus of birds ...
CHOP researchers discover underlying biology behind Fontan-associated liver disease
2024-04-24
Philadelphia, April 24, 2024 – As patients with congenital heart diseases live longer, researchers are attempting to understand some of the other complications they may face as they age. In a new study, a team from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) used state-of-the-art technologies to understand the underlying biology of Fontan-associated liver disease (FALD).
The findings, published today in Science Translational Medicine, reveal unprecedented insights into how the disease develops and potential therapeutic targets for future treatment options.
The Fontan operation is ...
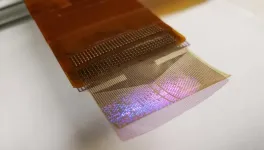
A flexible microdisplay can monitor brain activity in real-time during brain surgery
2024-04-24
A thin film that combines an electrode grid and LEDs can both track and produce a visual representation of the brain’s activity in real-time during surgery–a huge improvement over the current state of the art. The device is designed to provide neurosurgeons visual information about a patient’s brain to monitor brain states during surgical interventions to remove brain lesions including tumors and epileptic tissue.
Each LED in the device mirrors the activity of a few thousand neurons. In a series of proof-of-concept experiments in rodents and large non-primate mammals, researchers showed that ...
Diversity and productivity go branch-in-branch
2024-04-24
Kyoto, Japan -- Climate change can be characterized as the Grim Reaper or some other harbinger of dire times for humanity and natural environment, including forests. Previous studies reporting a decline in forest productivity due to climate warming and long-term drought may suggest that trees' survival hangs in the balance.
Now, a study by an international group, including Kyoto University, found that forests with higher trait diversity not only adapt better to climate change but may also thrive.
The study, conducted by researchers from Lakehead ...
Color variants in cuckoos: the advantages of rareness
2024-04-24
Every cuckoo is an adopted child – raised by foster parents, into whose nest the cuckoo mother smuggled her egg. The cuckoo mother is aided in this subterfuge by her resemblance to a bird of prey. There are two variants of female cuckoos: a gray morph that looks like a sparrowhawk, and a rufous morph. Male cuckoos are always gray.
“With this mimicry, the bird imitates dangerous predators of the host birds, so that they keep their distance instead of attacking,” says Professor Jochen Wolf from LMU Munich. Together with researchers at CIBIO (Centro de Investigação ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
[Press-News.org] A university lecture, with a dash of jumping jacksStudy finds possible value in class exercise breaks