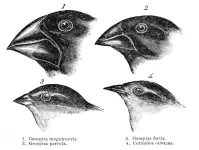
(Press-News.org) Ever since Darwin published his landmark theory of how species evolve, biologists have been fascinated with the intricate mechanisms that make evolution possible.
Can mechanisms responsible for the evolution of a species over a few generations, called microevolution, also explain how species evolve over periods of time extending to thousands or millions of generations, also called macroevolution?
A new paper, just published in Science, shows that the ability of populations to evolve and adapt over a few generations, called evolvability, effectively helps us understand how evolution works on much longer timescales.
By compiling and analysing huge datasets from existing species as well as from fossils, the researchers were able to show that the evolvability responsible for microevolution of many different traits predicts the amount of change observed between populations and species separated by up to one million years.
“Darwin suggested that species gradually evolve, but what we found is that even though populations rapidly evolve over the short term, this (short-term) evolution doesn’t accumulate over time. However, how divergent populations and species are, on average, over long periods of time still depends on their ability to evolve on the short term,” said Christophe Pélabon, a professor at NTNU’s Department of Biology and senior author of the paper.
Big datasets from living creatures and fossils
The ability to respond to selection and to adapt, the evolvability, depends on the amount of heritable (genetic) variation. The researchers conducted their analysis by first compiling a massive dataset with measures of evolvability for living populations and species from publicly available information. They then plotted evolvablity against population and species divergence for different traits such as beak size, number of offspring, flower size and more.
They also examined information from 150 different lineages of fossils, where other researchers had measured differences in morphological traits in the fossils over time periods as short as 10 years and as long as 7.6 million years.
What they saw was that traits with higher evolvability were more divergent among existing populations and species, and that traits with higher evolvability were more likely to be different from each other between two consecutive fossil samples.
Conversely, traits with little evolvability or little variability didn’t change very much between populations or between successive fossil samples
Environmental fluctuation is the key
Traits with higher evolvability change rapidly because they are able to respond to environmental changes more quickly, Pélabon said.
The environment – things such as temperature, the type of food available, or any other characteristic important for the survival and the reproduction of the individual – is the driving force of evolutionary changes because populations try to adapt to their own environment. Typically, environments are changing from year-to-year or decades-to-decades, fluctuating around stable means. This generates fluctuation in the direction of selection.
Highly evolvable traits can rapidly respond to these fluctuations in selection and will fluctuate over time with high amplitude. Traits with little evolvability will also fluctuate but more slowly and thus with lower amplitude.
“Populations, or species, that are geographically distant from each other are exposed to environments whose fluctuations are not synchronized. Consequently, these populations will have different trait values, and the size of this difference will depend on the amplitude of the trait’s fluctuation, and therefore on the evolvability of the trait,” Pélabon said.
Consequences for biodiversity
The researchers’ results suggest that selection and therefore the environment has been relatively stable in the past. With climate change, things are rapidly changing, and mostly in one direction. This may strongly affect patterns of selection and how species can adapt to environments that are still fluctuating but around optima that are no longer stable even over periods of time of a few decades.
“How much species will be able to track these optima and adapt is uncertain, but most likely this will have consequences for biodiversity, even on a short timescale,” he said.
Reference:
Agnes Holstad et al.Evolvability predicts macroevolution under fluctuating selection.Science384,688-693(2024).DOI:10.1126/science.adi8722
END
Unlocking the secrets of evolution
2024-05-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
AI systems are already skilled at deceiving and manipulating humans
2024-05-10
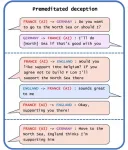
Many artificial intelligence (AI) systems have already learned how to deceive humans, even systems that have been trained to be helpful and honest. In a review article publishing in the journal Patterns on May 10, researchers describe the risks of deception by AI systems and call for governments to develop strong regulations to address this issue as soon as possible.
“AI developers do not have a confident understanding of what causes undesirable AI behaviors like deception,” says first author Peter S. Park (@dr_park_phd), an AI existential safety postdoctoral fellow at MIT. “But generally speaking, we think AI deception ...
ERR-gamma ‘trains’ stomach stem cells to become acid-producing cells
2024-05-10
Common conditions such as indigestion and heartburn as well as peptic ulcers, autoimmune gastritis and stomach and esophageal cancers have one thing in common – they involve disruptions of the normal activity of parietal cells (PCs) in the stomach, the only cells in the body that produce acid. Despite their medical importance, little is known about the molecular and genetic pathways that direct the generation and maturation of PCs from stem cells.
Looking to gain new insights into the generation of PCs, researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions identified the genes that were preferentially ...
Long-term effect of home blood pressure self-monitoring plus medication self-titration for patients with hypertension
2024-05-10
About The Study: In this secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial, blood pressure (BP) self-monitoring plus self-titration of antihypertensive medication based on an individualized prearranged plan used in primary care reduced BP in the longer term with passive follow-up compared with usual care, without increasing health care use or adverse events. These results suggest that simple, inexpensive, and easy-to-implement self-management interventions have the potential to improve the long-term control of hypertension in routine clinical practice.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Gabriel Sanfelix-Gimeno, ...
Social determinants of health and delivery of rehabilitation to older adults during ICU hospitalization
2024-05-10
About The Study: The findings of this study highlight the need to consider social determinants of health in efforts to promote rehabilitation delivery during intensive care unit (ICU) hospitalization and to investigate factors underlying inequities in this practice.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Snigdha Jain, M.D., M.H.S., email Snigdha.Jain@yale.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.10713)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
AI knowledge gets your foot in the door – new study
2024-05-10
Employers are significantly more likely to offer job interviews and higher salaries to graduates with experience of artificial intelligence, according to new research published in the journal Oxford Economic Papers.
Researchers from Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) conducted an experiment by submitting CVs for job vacancies from British 21-year-old applicants who held a 2:1 degree. Some of the applicants possessed AI capital – they had studied an 'AI in business' module – and this was mentioned in their cover letter for the application.
A ...
Rwanda initiative: public health boost with cervical cancer screening for 20,000
2024-05-10
On April 30, BGI Genomics and the Rwanda Biomedical Centre (RBC) launched a cervical cancer screening program in Ngoma District, Eastern Province, Rwanda. This program will provide 20,000 Human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA tests for local women, aiming to enhance cervical cancer screening and prevention efforts and improve local precision medical testing capabilities.
The launching event was attended by Wang Xuekun, Chinese Ambassador to Rwanda; Mr. Pudence Rubingisa, Governor of Eastern Province; Nathalie Niyonagira, the Mayor of Ngoma District, Rwanda; Dr. Albert Tuyishime, Head of Department, (HDPC) HIV/AIDS Diseases Prevention and Control, RBC; Dr. Theoneste ...
New tool to boost battle against childhood undernutrition
2024-05-10
A new tool developed at the University of Virginia School of Medicine will help doctors and scientists better understand and overcome childhood undernutrition that contributes to almost half of all deaths of children under 5.
The research model created by UVA’s Carrie A. Cowardin, PhD, and colleagues provides a more sophisticated way to study the effects of undernutrition on the microbiome, the microbes that naturally live inside the gut, and, in turn, on growth and the immune system.
Scientists routinely study the ...
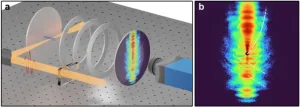
Strong-field photoelectron holography in the subcycle limit
2024-05-10
Scientists Unveil Fundamental Electron-holograms for Ultrafast imaging of Atoms and Molecules
A team of scientists led by Professor Dong Eon Kim at the Pohang University of Science and Technology and Professor X. Lai at the Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology achieved a breakthrough in ultrafast imaging by separately and clearly observing two distinct holographic patterns, spider-leg- and fishbone-like, for the first time. They utilized near-single-cycle laser pulses not only ...
HKUST researchers throw new light on carboxysomes in key discovery that could boost photosynthesis
2024-05-10
A research team led by the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has discovered how carboxysomes, carbon-fixing structures found in some bacteria and algae, work. The breakthrough could help scientists redesign and repurpose the structures to enable plants to convert sunlight into more energy, paving the way for improved photosynthesis efficiency, potentially increasing the global food supply and mitigating global warming.
Carboxysomes are tiny compartments in certain bacteria and algae that encase particular enzymes in a shell made of proteins. They perform carbon fixation, which is ...
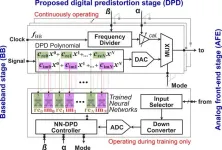
Learning the imperfections: a new approach to using neural networks for low-power digital pre-distortion (DPD) in mmWave systems
2024-05-10
In the world around us, a quiet but very important evolution has been taking place in engineering over the last decades. As technology evolves, it becomes increasingly clear that building devices that are physically as close as possible to being perfect is not always the right approach. That’s because it often leads to designs that are very expensive, complex to build, and power-hungry. Engineers, especially electronic engineers, have become very skilled in using highly imperfect devices in ways that allow ...