(Press-News.org) The huge, long-lasting wildfires that have become increasingly common in recent years can cause changes in soil chemistry that affect water contamination, air quality, and plant growth. But these changes are poorly monitored and rarely factor into post-fire recovery efforts or risk assessments, according to a review study published May 14 in Nature Reviews Earth & Environment.
The study, led by Stanford University and Colorado State University scientists, found that better techniques are needed to monitor changes in soil and surrounding ecosystems. This enhanced monitoring could inform decisions on how to treat drinking water sourced from burned areas, support reforestation, and protect workers against toxins during cleanup, rebuilding, or revegetation.
“In our study, we mesh organic and inorganic chemistry together, whereas a lot of fire research will typically just consider one subject area,” said soil biogeochemist Claudia Avila, who co-led the study with Alandra Lopez, PhD ’22, while both researchers were postdoctoral scholars in the lab of Stanford Doerr School of Sustainability Professor Scott Fendorf.
“A better understanding of the molecular mechanisms in soil can help explain, for instance, why drinking water from a forest fire-impacted watershed is suddenly more toxic, or why a forest is not coming back,” said Colorado State University soil chemist Thomas Borch, a senior author of the study.
Climate and ecosystem impacts
The review highlights evidence from recent studies suggesting wildfires may release more planet-warming carbon dioxide into the atmosphere than anticipated. Charcoal-like remnants of burned wood and other organic materials, known as black carbon, may not trap carbon dioxide for long periods, as scientists had hoped. “Carbon that's gone through forest fires and becomes black carbon can actually turn more readily into carbon dioxide by microbes than previously thought,” said Fendorf, the Terry Huffington Professor at Stanford.
“From a climate perspective, we still have a poor understanding of how much of the carbon that is left after a fire has the potential to be transformed into greenhouse gasses, such as carbon dioxide,” said Borch, who worked in Fendorf’s lab as a postdoctoral fellow 20 years ago.
Wildfires can have many benefits for ecosystems, the authors note. Some fires can increase the nitrogen in soils and augment the water solubility of soil organic carbon, for example, setting the stage for regrowth. However, recovery depends on the presence of other chemicals. For instance, certain types of organic molecules formed in soil during fires are needed for many seeds to germinate. If the local soil chemistry and fire conditions do not produce enough of these molecules, called karrikins, revegetation may be stunted.
Other research included in the new review has shown that wildfires can double the soil concentration of a group of toxic chemicals known as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, which can induce chemical reactions that inhibit revegetation. These molecular-scale effects could well explain the mystery of vast areas where trees have struggled to reestablish after wildfires in the Rocky Mountains, Borch said.
Wildfires can also alter the chemical properties of inorganic materials such as metals within soils. Fire can change the metals into dangerous forms that readily move through the environment, ending up in the air or nearby water, the authors explained, citing Fendorf and Lopez’s own recent research. The scientists documented high levels of a hazardous form of the metal chromium at wildfire sites resulting from heat-induced transformation of naturally occurring, benign forms of chromium. At sites where extremely hot, long-lasting fires cooked soils to high temperatures for extended periods, chromium persisted for many months until the next large rain event.
Other research on chromium indicates that after lower-intensity fires, remnant plant and animal tissue in soil can allow the toxic form of chromium to return to its inert form. Taken together, these studies illustrate the broader reality that wildfire impacts on soil chemistry depend on the intricate nature of the fire and landscape, including fire duration and temperature.
Predicting and mitigating wildfire risks
Broader surveillance and modeling could inform strategies for protecting lives, property, and natural resources, as well as wildlife management decisions. Avila offers an example of how this approach to informed stewardship could help prevent the leaching of metals into drinking water supplies. “By identifying an area that has a high potential for, say, chromium release, we can call for prescribed burns that are lower intensity and reduce the potential for high-intensity, toxin-releasing fires,” said Avila, who is now an assistant professor of environmental and ocean sciences at the University of San Diego.
“If we can grasp the complexity of the intertwined processes that are happening both on the organic and the inorganic side, then that helps give us the ability to predict outcomes for different fire, landscape, and geological conditions,” said Fendorf.
Fendorf is also a senior fellow at the Stanford Woods Institute for the Environment. Lopez is a postdoctoral scholar in Earth system science in the Stanford Doerr School of Sustainability; a Planetary Health Postdoctoral Fellow at the Stanford Center for Innovation in Global Health (CIGH) and the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine; and a Global Health Postdoctoral Affiliate at CIGH. Avila was a Stanford Earth Postdoctoral Fellow. Co-authors Jacob VanderRoest and Holly Roth are affiliated with Colorado State University.
This research was supported by the Center for Innovation in Global Health at Stanford University and the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine under the Planetary Health Postdoctoral Fellowship, Stanford Doerr School of Sustainability under the Stanford Earth Postdoctoral Fellowship, Stanford Woods Institute for the Environment, the National Science Foundation, and the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture. END
How wildfires change soil chemistry
Understanding how wildfires change soil could aid recovery
2024-05-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Genes driving age-related blood cell mutations uncovered
2024-05-14
Scientists have discovered 17 additional genes that drive the abnormal overgrowth of mutated blood cells as we age. The findings, published today (14 May) in Nature Genetics, provide a more complete view of the genetic factors behind clonal haematopoiesis – a process associated with ageing and linked to increased risks of blood cancers1.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Calico Life Sciences, California, and the University of Cambridge analysed sequencing data from over 200,000 individuals in the UK Biobank cohort. They searched for genes showing signals of "positive selection" – where mutations ...
WASP-193b, a giant planet with a density similar to that of cotton candy
2024-05-14
An international team led by researchers from the EXOTIC Laboratory of the University of Liège, in collaboration with MIT and the Astrophysics Institute in Andalusia, has just discovered WASP-193b, an extraordinarily low-density giant planet orbiting a distant Sun-like star.
This new planet, located 1,200 light-years from Earth, is 50% larger than Jupiter but seven times less massive, giving it an extremely low density comparable to that of cotton candy. "WASP-193b is the second least dense planet discovered to date, after Kepler-51d, which is much smaller," explains ...
IOP Publishing report reveals peer review capacity not used to its full potential
2024-05-14
A new global study from IOP Publishing (IOPP) has found that certain peer review communities continue to feel overburdened by reviewer requests, while others remain underrepresented.
The survey, which generated over 3,000 responses from peer reviewers from across the globe, revealed regional and career-stage disparities:
30% of reviewers from high-income countries indicated that they receive too many peer review requests, compared with just 10% from low and middle-income countries*
Just 6% of respondents from China and 7% from India indicated that they ...
Eco-friendly and affordable battery for low-income countries
2024-05-14
A battery made from zinc and lignin that can be used over 8000 times. This has been developed by researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, with a vision to provide a cheap and sustainable battery solution for countries where access to electricity is limited. The study has been published in the journal Energy & Environmental Materials.
“Solar panels have become relatively inexpensive, and many people in low-income countries have adopted them. However, near the equator, the sun sets at around 6 PM, leaving households and businesses without electricity. The hope is that ...
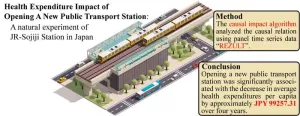
New transit station in Japan significantly reduced cumulative health expenditures
2024-05-14
The declining population in Osaka is related to an aging society that is driving up health expenditures. Dr. Haruka Kato, a junior associate professor at Osaka Metropolitan University, teamed up with the Future Co-creation Laboratory at Japan System Techniques Co., Ltd. to conduct natural experiments on how a new train station might impact healthcare expenditures.
JR-Sojiji Station opened in March 2018 in a suburban city on the West Japan Railway line connecting Osaka and Kyoto. The researchers used a causal impact algorithm to analyze the medical expenditure data gathered from the time series medical ...
USC study reveals racial disparities in diagnosis and drug use for dementia symptoms
2024-05-14
Compared to Black and Asian people, white and Hispanic people with Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias were most likely to be diagnosed with symptoms like depression and agitation, according to a new study from the USC Schaeffer Center for Health Policy & Economics.
White and Hispanic people with these diagnoses were also most likely to be prescribed central nervous system (CNS) active drugs, including antidepressants, antipsychotics and anticonvulsants. Yet, these drugs have been associated with higher risk of falls, cardiovascular events, hospitalization and death, according to the study published today in the Journal of Alzheimer’s ...
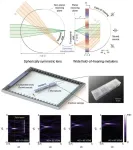
Metalens expands Its reach from light to sound
2024-05-14
Junsuk Rho from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, the Department of Chemical Engineering, and the Department of Electrical Engineering, Dr. Dongwoo Lee from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Beomseok Oh, a PhD student, from the Department of Chemical Engineering at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) have achieved a breakthrough in surpassing the limitations of traditional acoustic metalenses. They have successfully developed the first wide field-of-hearing metalens. This research has been recently published in the international journal, Nature Communications.
Sound ...
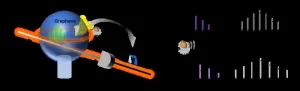
Ultrasensitive gas detection empowered by synergy of graphene and sub-comb dynamics
2024-05-14
Since the inception of microcomb, whose generation relies on Kerr nonlinearity in microresonator, the coherent soliton state has attracted intense researches. Although the operation of sub-comb outputs is straightforward, as noncoherent comb state, it was often overlooked in previous techniques. With graphene sensitization, this sub-comb heterodyne sensing device exhibits an exceptional response to gas molecular adsorption, achieving detect limits of 1.2 ppb for H2S gas and 1.4 ppb for SO2 gas, respectively. In summary, our research synergizes flexible ...
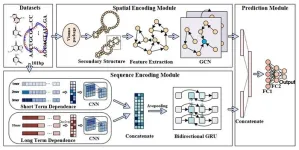
DeepCRBP: Improved predicting function of circRNA-RBP binding sites with deep feature learning
2024-05-14
There is growing evidence that it is essential to predict the interactions between circRNAs and RBP binding sites for diagnosing diseases and providing a potential target to treat diseases. Many studies have predicted the binding sites of circRNA-RBPs by using deep learning methods based on the sequence information of circRNAs for each RBP. However, the most of previous works only extract sequence feature, with a lack of exploiting the essential topological information from the secondary structure which contains rich spatial information.
To ...
Concussion, CTE experts warn term used to describe head impacts – “subconcussion” – is misleading and dangerous
2024-05-14
BOSTON (May 14, 2024) – A new editorial published this May in the British Journal of Sports Medicine by experts from Spaulding Rehabilitation, Boston University, Mayo Clinic, and the Concussion Legacy Foundation, argues that the term “subconcussion” is a dangerous misnomer that should be retired. The authors are appealing to the medical community and media to substitute the term with more specific terms so the public can better understand the risks of brain injuries and advance effective efforts to prevent chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE).
“The public has been led to believe through media coverage ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Globe-trotting ancient ‘sea-salamander’ fossils rediscovered from Australia’s dawn of the Age of Dinosaurs
Roadmap for Europe’s biodiversity monitoring system
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
[Press-News.org] How wildfires change soil chemistryUnderstanding how wildfires change soil could aid recovery