(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON — Sudden, severe dry spells known as flash droughts are rising in intensity around the world, with a notable exception in mountainous Central Asia, where flash drought extent is shrinking, according to new research. Heat and changes to precipitation patterns caused by a warming climate are driving these trends, the study found.
Flash droughts arrive suddenly, within weeks, hitting communities that are often not prepared and causing lasting impact. They are an emerging concern for water and food security. The new study is the first to apply a systematic, quantitative approach to the global incidence of flash drought, mapping hotspots and regions of rapid increases in recent decades.
“For many parts of the world, we saw flash droughts extending over larger areas, for longer time, with faster onset speed,” said Maheshwari Neelam, a climate scientist at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center and the Universities Space Research Association. She is the lead author of the study, published in Geophysical Research Letters, AGU’s journal for high-impact, short-format reports with immediate implications spanning all Earth and space sciences.
The study defined and tracked three critical measures of drought severity: speed of onset, duration and geographic extent. It analyzed 40 years of NASA’s MERRA-2 climate data, from 1980 to 2019, drawn from weather observations, satellite imagery and modeled root-zone soil moisture, with the aim of improving prediction and disaster preparedness.
“For example, in watersheds in South America, onset is getting faster by about 0.12 days per year, so over a decade they are developing a day earlier. Extent is increasing by 1 to 3% per year,” Neelam said. “The metrics can be used by early warning systems to incorporate rates of change in flash drought characteristics in risk assessment and disaster preparedness.”
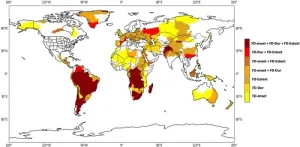
South America, particularly southern Brazil and the Amazon, is experiencing strong intensification in all three dimensions of flash drought, aligning with deforestation patterns in the region, high temperatures and less rain. Congo, Angola, Zambia, Zimbabwe, South Africa, Lesotho, and Madagascar are also hotspots. High temperatures were found to be more important than declining precipitation in the African watersheds.
Land cover is also important to flash drought vulnerability. Savanna and grasslands are more susceptible to flash droughts than other ecotypes, particularly in humid and semi-humid climates, the study found.
In Central Asian watersheds, centered on high mountains, including the Himalaya Karakoram, Tianshan and Hindu Kush, flash drought extent shrank over the study period, bucking the worldwide trend. Climate-driven changes in precipitation, melting snowpack and a shift from snow to rain in the mountains have kept soils moist. These changes can cause an increase in flash floods, which have been observed in the region, Neelam said.
Neelam emphasized the importance of understanding landscapes' response to disasters on a watershed scale for assessing water budgets and water management, transcending geopolitical boundaries.
“Natural hazards have no political values,” Neelam said. “This is why we looked at watersheds and not countries.”
#
Notes for journalists:
This study was published in Geophysical Research Letters, an open-access AGU journal. Neither the study nor this press release is under embargo. View and download a pdf of the study here.
Interview requests should be directed to the researchers and their press offices.
This work was supported by the NASA Research and Analysis Program, Weather and Atmospheric Dynamics Focus Area as part of the SPoRT project at Marshall Space Flight Center.
Paper title:
“Global Flash Droughts Characteristics: Onset, Duration, and Extent at Watershed Scales”
Authors:
Maheshwari Neelam (corresponding author) Universities Space Research Association and NASA Marshall Space Flight Center, Earth Science Branch, Huntsville, AL, USA
Christopher Hain, NASA Marshall Space Flight Center, Earth Science Branch, Huntsville, AL, USA
###
AGU (www.agu.org) is a global community supporting more than half a million advocates and professionals in Earth and space sciences. Through broad and inclusive partnerships, AGU aims to advance discovery and solution science that accelerate knowledge and create solutions that are ethical, unbiased and respectful of communities and their values. Our programs include serving as a scholarly publisher, convening virtual and in-person events and providing career support. We live our values in everything we do, such as our net zero energy renovated building in Washington, D.C. and our Ethics and Equity Center, which fosters a diverse and inclusive geoscience community to ensure responsible conduct.
#
To subscribe or change your emailing preferences for the AGU Newsroom, click here.
END
About The Study: Public health authorities in nearly all states and territories surveyed reported the ability to monitor and test persons exposed to highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) A(H5N1) virus. However, jurisdictions varied in their capacity to monitor exposed persons, in recommendations for use of antivirals, and in potential use of H5N1 vaccines, if available, among first responders.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Noah Kojima, M.D., email nkojima@cdc.gov.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
Today, DRI, one of our nation’s leading applied environmental research institutes, together with its Foundation, announced a new global initiative with the first in a series of summits. The event will be held at Encore Las Vegas from August 21-23, 2024.
The AWE+ initiative will promote an Adaptable World Environment of strong, resilient communities in a climate shifting world. AWE+ 2024 - Wildfire Recovery and Resilience: Working Across Silos to Drive Solutions - is a global call-to-action for communities ...
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Recent developments at MD Anderson offer insights into biomarkers that predict immunotherapy responses, a possible treatment strategy for patients with LKB1-deficient cancers, therapeutic targets to prevent acute myeloid leukemia (AML) progression ...
Sensors enable us to monitor changes in systems of all kinds.
The materials at the heart of those sensors, of course, ultimately determine their end-use application. Devices made of silicon, for example, enable ultrafast processing in computers and phones, but they aren’t pliable enough for use in physiological monitoring.
They also require a lot of energy to produce.
Lehigh University professor Elsa Reichmanis, Carl Robert Anderson Chair in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, recently received a grant from the National ...
Birmingham researchers have shown PEPITEM, a naturally occurring peptide (small protein) holds promise as a new therapeutic for osteoporosis and other disorders that feature bone loss, with distinct advantages over existing drugs.
PEPITEM (Peptide Inhibitor of Trans-Endothelial Migration) was first identified in 2015 by University of Birmingham researchers.
The latest research, published today in Cell Reports Medicine, show for the first time that PEPITEM could be used as a novel and early clinical intervention to reverse the impact of age-related musculoskeletal diseases, with ...
About The Study: This cohort study of Japanese older adults identified that upward and downward socioeconomic status transitions were associated with risk of dementia and the length of dementia-free periods over the lifespan. The results may be useful to understand the association between social mobility and healthy longevity.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Hiroyasu Iso, Ph.D., email iso@pbhel.med.osaka-u.ac.jp.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.12303)
Editor’s Note: Please see ...
Osaka, Japan – Upward social mobility may ward off dementia, according to a new study. Dementia, a collective term for conditions marked by memory loss and diminished cognitive functioning, strains healthcare systems and devastates quality of life for patients and their families. Research thus far has found correlations between socioeconomic status (SES) – Parent’s asset, education level, income, and work status – and susceptibility to dementia, and SES changes throughout a person’s life, known as social mobility, seem to influence this risk; however, scientific ...
Scientists discover ‘zoned development’ in dinosaur skin, with zones of reptile-style scales and zones of bird-like skin with feathers
New dinosaur skin fossil found to be composed of silica – the same as glass
Discovery sheds light on evolution from scales to feathers
Palaeontologists at University College Cork (UCC) in Ireland have discovered that some feathered dinosaurs had scaly skin like reptiles today, thus shedding new light on the evolutionary transition from scales to feathers.
The researchers studied a new specimen of the feathered dinosaur Psittacosaurus from the early Cretaceous ...
Surgical teams at NYU Langone Health performed the world’s first genetically modified pig kidney transplants into a human body in September and November 2021, and then transplanted two pig hearts in the summer of 2022. These procedures were done in patients declared dead based on neurologic criteria (decedents) and maintained on ventilators with the consent of their families. Demonstrating the field’s progress, NYU Langone in April 2024 transplanted a pig kidney into a living patient.
Now two new analyses, one published online on May 17 in Nature Medicine and the other May ...
SRI’s Targeted Antigen Loaded Liposomes (TALL) — a treatment that expands the benefits of immunotherapy such as check-point inhibitors — has been granted Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) by the U.S. Federal Drug Administration (FDA).
As a result, SRI’s future strategic partners can gain tax credits for qualified clinical trials and potentially receive market exclusivity for a period of seven years after the drug’s approval, among other benefits.
“FDA's orphan drug designation brings worthy attention to the demonstrated impact of SRI's TALL biotherapeutic for pancreatic cancer,” said Kathlynn Brown, ...