(Press-News.org) FINDINGS
A study led by UCLA Health Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center researchers found that using a combination of experimental immunotherapy drugs with chemotherapy significantly improves progression-free survival and overall survival for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer who have previously undergone standard chemotherapy treatment when compared to those who received the targeted therapy regorafenib alone.
The median progression-free survival, which is the amount of time during and after treatment when the cancer does not worsen or progress, with the combination treatment was 6.2 months compared to 2.1 months for those in the targeted therapy only group.
The median overall survival with the combination treatment was 19.7 months as compared to 9.5 months for those in the targeted therapy only group.
The results of the study also showed treatment with the novel combination therapy either partially or completely shrank tumors in 17.3% of patients. For patients on regorafenib only, 2.7% had tumor shrinkage.
BACKGROUND
When colorectal cancer starts to spread to other parts of the body, it can be more challenging to treat and often requires a combination of therapies, including surgery, chemotherapy, targeted therapies and immunotherapy. While these advancements in treatment options have improved outcomes for many patients with metastatic colorectal cancer, it still remains a significant health issue. Conventional treatments often become ineffective as the disease progresses, requiring the development of innovative therapeutic approaches.
METHOD
This group of investigators looked at evaluating the efficacy of a novel treatment combination, called EZFB, which consists of etrumadenant (E), a dual A2a/A2b adenosine receptor antagonist, zimberelimab (Z), an immune checkpoint inhibitor, and a chemotherapy regimen (FB: mFOLFOX-6 ± bevacizumab), to see if it could improve outcomes for people who were previously treated for this aggressive form of cancer.
The team enrolled 112 participants with metastatic colorectal cancer who had previously undergone treatment with oxaliplatin and irinotecan-containing regimens in the Phase Ib/II trial. The patients were randomized into two groups: 75 receiving the EZFB combination and 37 receiving regorafenib alone.
IMPACT
The study's findings underscore the potential of combining immune-targeted therapy with traditional chemotherapy to better control the spread of the cancer and enhance the effectiveness of the treatment in metastatic colorectal cancer.
"The improvement in both progression-free survival and overall survival observed with the EZFB combination represents a significant advancement in the management of refractory metastatic colorectal cancer,” said first author of the abstract Dr. Zev Wainberg, co-director of the UCLA Health GI Oncology Program and researcher at the UCLA Health Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center. “These results pave the way for further exploration of this promising treatment approach."
AUTHORS
The abstract’s senior author is Michael Cecchini from Yale University School of Medicine. Other authors are Sae-Won Han, Soohyeon Lee, Keun-Wook Lee, Scott Kopetz, Jonathan Mizrahi, Yong Sang Hong, François Ghiringhelli, Antoine Italiano, David Tougeron, Brandon Beagle, Mathew Boakye, Tingting Zhao, Joon Rhee and Dimitry Nuyten.
SESSION
Wainberg will present the findings (Abstract 3508) at the annual American Society of Clinical Oncology meeting on Sunday, June 2 during the Oral Abstract Session of the Gastrointestinal Cancer—Colorectal and Anal Track from 8 to 11am CT.
The study was sponsored by Arcus Biosciences.
END
ASCO: Combination therapy significantly improves outcomes for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer
Combining immune-targeted therapy with chemotherapy improves both progression-free survival and overall survival when compared to those who received regorafenib alone
2024-05-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Euclid space mission releases first scientific results and new images of the cosmos
2024-05-24
European space mission Euclid has released early scientific papers based on observations made by the space telescope, along with five new astronomical images of the Universe, as the project sets about unravelling the secrets of the cosmos.
The new images are part of Euclid’s Early Release Observations (EROs) and accompany the mission’s first scientific data and 10 forthcoming science papers. Their publication comes less than a year after the space telescope’s launch and some six months after it returned its first full-colour ...
Sociodemographic heterogeneity in the associations of social isolation with mortality
2024-05-24
About The Study: Social isolation was associated with increased risks of all-cause, cardiovascular diseases, and malignant neoplasm mortality, with associations varying across populations. This study fills an important gap in research on social isolation, emphasizing its varied associations across demographic and socioeconomic groups.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Atsushi Nakagomi, M.D., Ph.D., email anakagomi0211@gmail.com.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.13132)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
COVID-19 admission rates and changes in care quality in us hospitals
2024-05-24
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study, COVID-19 surges were associated with declines in hospital quality, highlighting the importance of identifying and implementing strategies to maintain care quality during periods of high hospital use.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Giacomo Meille, Ph.D., email giacomo.meille@ahrq.hhs.gov.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.13127)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
Preterm and early-term delivery after heat waves in 50 US metropolitan areas
2024-05-24
About The Study: Preterm and early-term birth rates increased after heat waves, particularly among socioeconomically disadvantaged subgroups in this cohort study. Extreme heat events have implications for perinatal health.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Lyndsey A. Darrow, Ph.D., email ldarrow@unr.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.12055)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and ...
Research spotlight: Virtual scribes reduced physicians’ time spent on electronic health records
2024-05-24
Lisa Rotenstein, MD, of the Department of Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, is the lead author of a new study published in JAMA Network Open, “Virtual Scribes and Physician Time Spent on Electronic Health Records.”
What question were you investigating?
We sought to understand the impact of virtual scribes (human scribes who are not physically present in the exam room with the physician and patient) on how physicians spend their time and which characteristics are associated with physicians responding best to scribes.
What methods or approach did you use?
We studied the experiences of 144 physicians across specialties treating patients ...
Duke-NUS researchers develop new light-controlled ‘off switch’ for brain cells
2024-05-24
Researchers from Duke-NUS Medical School have found that a new class of light-sensitive proteins are capable of turning off brain cells with light, offering scientists an unprecedentedly effective tool to investigate brain function. The study, recently published in Nature Communications, opens exciting new opportunities to apply optogenetics to investigate the brain activity underlying neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and depression.
Optogenetics is a technique where specific cells are bioengineered to include light-sensitive proteins that act as switches, allowing ...
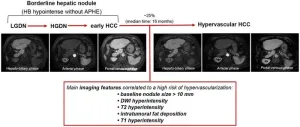
Liver lesions at risk of transformation into hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients
2024-05-24
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) represents a significant global health burden as one of the most common malignancies in individuals with chronic liver disease or cirrhosis. This malignancy evolves through a multistep process, beginning with dysplastic nodules (DNs) and early HCC, progressing to overt HCC. Recent advancements in liver imaging, particularly the use of hepatocyte-specific contrast agents, have enhanced the detection of these precursor lesions, known as borderline hepatic nodules. These nodules, especially those hypointense in the hepatobiliary phase (HBP) without arterial phase hyperenhancement (APHE), present ...
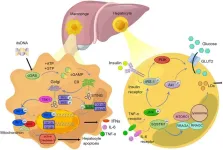
Update on the STING signaling pathway in developing nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
2024-05-24
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become the most prevalent chronic liver condition worldwide, affecting about 25% of the global population due to the increasing rates of obesity and metabolic syndrome. NAFLD encompasses a spectrum of liver conditions ranging from simple hepatic steatosis to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Despite its prevalence, there are limited effective treatment options available. Inflammation driven by metabolic disturbances is a key factor in the development and progression of ...
Autonomous medical intervention extends ‘golden hour’ for traumatic injuries with emergency air transport
2024-05-24
For the first time, a closed loop, autonomous intervention nearly quadrupled the “golden hour” during which surgeons could save the life of a large animal with internal traumatic bleeding while in emergency ground and air transport.
This breakthrough in trauma care, announced today in Intensive Care Medicine Experimental by physician-scientists at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine and funded by the U.S. Department of Defense, has enormous potential for saving the lives of traumatically injured ...
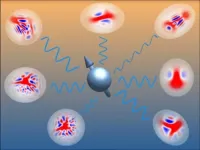
More than spins: Exploring uncharted territory in quantum devices
2024-05-24
Many of today’s quantum devices rely on collections of qubits, also called spins. These quantum bits have only two energy levels, the ‘0’ and the ‘1’. However, spins in real devices also interact with light and vibrations known as bosons, greatly complicating calculations. In a new publication in Physical Review Letters, researchers in Amsterdam demonstrate a way to describe spin-boson systems and use this to efficiently configure quantum devices in a desired state.
Quantum devices use the quirky behaviour of quantum ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
Study: Electrical stimulation can restore ability to move limbs, receive sensory feedback after spinal cord injury
Rice scientists unveil new tool to watch quantum behavior in action
Gene-based therapies poised for major upgrade thanks to Oregon State University research
Extreme heat has extreme effects r—but some like it hot
Blood marker for Alzheimer’s may also be useful in heart and kidney diseases
Climate extremes hinder early development in young birds
Climate policies: The swing voters that determine their fate
Building protection against infectious diseases with nanostructured vaccines
Oval orbit casts new light on black hole - neutron star mergers
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
[Press-News.org] ASCO: Combination therapy significantly improves outcomes for patients with metastatic colorectal cancerCombining immune-targeted therapy with chemotherapy improves both progression-free survival and overall survival when compared to those who received regorafenib alone