(Press-News.org) PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — A new study by Brown University researchers may help redefine how scientists map the surface of the Moon, making the process more streamlined and precise than ever before.
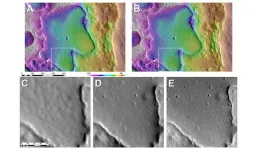
Published in the Planetary Science Journal, the research by Brown scholars Benjamin Boatwright and James Head describes enhancements to a mapping technique called shape-from-shading. The technique is used to create detailed models of lunar terrain, outlining craters, ridges, slopes and other surface hazards. By analyzing the way light hits different surfaces of the Moon, it allows researchers to estimate the three-dimensional shape of an object or surface from composites of two-dimensional images.
Accurate maps can help lunar mission planners to identify safe landing spots and areas of scientific interest, making mission operations smoother and more successful.
“It helps us piece together a better idea of what is actually there,” said Boatwright, a postdoctoral researcher in Brown’s Department of Earth, Environmental and Planetary Sciences and lead author of the new paper. “We need to understand the surface topography of the Moon where there isn’t as much light, like the shadowed areas of the lunar south pole where NASA’s Artemis missions are targeting. That will allow autonomous landing software to navigate and avoid hazards, like large rocks and boulders, that could endanger a mission. For that reason, you need models that map the topography of the surface at as high a resolution as possible because the more detail you have, the better.”
The process to develop precision maps, however, is labor intensive and has limitations when it comes to complex lighting conditions, inaccurate shadow interpretation and handling terrain variability. The Brown researchers’ improvements to the shape-from-shading technique focuses on addressing these issues.
The scholars outline in the study how advanced computer algorithms can be used to automate much of the process and significantly heighten the resolution of the models. The new software gives lunar scientists the tools to create larger maps of the Moon’s surface that contain finer details at a much faster pace, the researchers say.
“Shape-from-shading requires that the images that you're using be perfectly aligned with one another so that a feature in one image is in the exact same place in another image to build up those layers of information, but current tools are not quite in a place where you can just give it bunches of images and it'll spit out a perfect product,” Boatwright said. “We implemented an image alignment algorithm where it picks out features in one image and tries to find those same features in the other and then line them up, so that you're not having to sit there manually tracing interest points across multiple images, which takes a lot a of hours and brain power.”
The researchers also implemented quality control algorithms and additional filters to reduce outliers from the alignment process — tools to ensure the aligned images actually match and remove images that don’t align as well. By only selecting images that end up being usable, this improves quality and takes precision down to submeter resolutions. The speed also allows for larger surface areas to be examined, increasing the production of these maps.
The researchers evaluated the accuracy of their maps by comparing them with other existing topographic models, looking for discrepancies or errors in lunar surface features. They found the maps generated using their refined shape-from-shading method were more precise compared to those derived from traditional techniques, showing more subtle features and variations of lunar surface terrain.
For the study, the researchers primarily used data from Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter and Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera, instruments onboard NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, which has been orbiting the Moon since 2009.
The scientists plan to use their refined shape-from-shading software to produce lunar maps, and they hope others will use it in their modeling efforts, as well. It’s why they used open-source algorithms to produce the tool.
“These new map products are significantly better than what we had in exploration planning during the Apollo missions, and they will very much improve the mission planning and scientific return for Artemis and robotic missions,” said Head, a professor of geological sciences at Brown who worked in the Apollo program.
The researchers hope the new tool will add to the current interest in the science and exploration of the Moon happening at NASA and in space agencies around the world.
“There's a wealth of information to be gained from making these types of tools accessible to all,” Boatwright said. “It’s an egalitarian way of doing science.”
The work was supported by the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center.
END
New technique from Brown University researchers offers more precise maps of the Moon’s surface
The team’s study describes enhancements that make a popular lunar mapping technique more streamlined and precise than ever at a time when space agencies are gearing up for lunar missions.
2024-05-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Dariusz Stramski selected as 2024 recipient of the Nils Gunnar Jerlov Medal
2024-05-29
Professor Dariusz Stramski of Scripps Institution of Oceanography at UC San Diego has been selected by The Oceanography Society as the 2024 recipient of the Nils Gunnar Jerlov Medal in recognition of his significant and wide-ranging contributions to the field of optical oceanography.
With a distinguished career spanning over 40 years, Dr. Stramski has made profound impacts on the study of ocean optics. Born in Poland, Stramski received his M.S. with honors in oceanography (1978) and Ph.D. in Earth ...
AI health coach lowers blood pressure and boosts engagement in patients with hypertension
2024-05-29
(Toronto, May 28, 2024) A new study in JMIR Cardio, published by JMIR Publications, shows that a fully digital, artificial intelligence (AI)–driven lifestyle coaching program can effectively reduce blood pressure (BP) in adults with hypertension. This AI-based program leverages data from wearable activity trackers and BP monitors as well as a mobile app questionnaire to tailor lifestyle guidance. The research team, led by Jared Leitner of the University of California, San Diego, used this innovative intervention to help manage ...
AI saving humans from the emotional toll of monitoring hate speech
2024-05-29
A team of researchers at the University of Waterloo have developed a new machine-learning method that detects hate speech on social media platforms with 88 per cent accuracy, saving employees from hundreds of hours of emotionally damaging work.
The method, dubbed the Multi-Modal Discussion Transformer (mDT), can understand the relationship between text and images as well as put comments in greater context, unlike previous hate speech detection methods. This is particularly helpful in reducing false positives, which are often ...
Chicken feathers to deliver chemotherapy drugs and repair enzymes
2024-05-29
A new method of drug delivery using proline, an amino acid found in chicken feathers and skin tissue, could be used to limit the side effects of chemotherapy and repair important enzymes, new research suggests.
Published in the journal Chem today, researchers have designed a cage (a box made of single molecules) from biologically compatible peptides, short amino acids that form the basis of proteins. These cages can house drugs of different sizes and transport them in the body with high levels of precision.
The negative ...
Bio-inspired cameras and AI help drivers detect pedestrians and obstacles faster
2024-05-29
It’s every driver’s nightmare: a pedestrian stepping out in front of the car seemingly out of nowhere, leaving only a fraction of a second to brake or steer the wheel and avoid the worst. Some cars now have camera systems that can alert the driver or activate emergency braking. But these systems are not yet fast or reliable enough, and they will need to improve dramatically if they are to be used in autonomous vehicles where there is no human behind the wheel.
Quicker detection using less computational ...
Graphene gets cleaned up
2024-05-29
Graphene has been called “the wonder material of the 21st century.” Since its discovery in 2004, the material—a single layer of carbon atoms—has been touted for its host of unique properties, which include ultra-high electrical conductivity and remarkable tensile strength. It has the potential to transform electronics, energy storage, sensors, biomedical devices, and more. But graphene has had a dirty little secret: it's dirty.
Now, engineers at Columbia University and colleagues at the University of Montreal and the National Institute of Standards and Technology are poised to clean things up with an oxygen-free chemical vapor ...
Study finds older adults hospitalized for heart failure had high risk of kidney complications
2024-05-29
In a study of Medicare beneficiaries, researchers from Brigham and Women’s Hospital found that one year after hospitalization for heart failure, 6 percent of patients had progressed to dialysis.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Study led by Brigham researchers found that among older adults hospitalized for heart failure, nearly 3 in 4 were discharged with reduced kidney function.
Lower kidney function was associated with substantially higher risk of kidney complications and other adverse clinical outcomes among older adults, with more than 1 in 20 progressing to dialysis within one year after heart failure hospitalization.
These findings emphasize the need ...
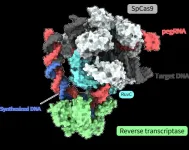
Editing without “cutting”: Molecular mechanisms of new gene-editing tool revealed
2024-05-29
Joint research led by Yutaro Shuto, Ryoya Nakagawa, and Osamu Nureki of the University of Tokyo determined the spatial structure of various processes of a novel gene-editing tool called “prime editor.” Functional analysis based on these structures also revealed how a “prime editor” could achieve reverse transcription, synthesizing DNA from RNA, without “cutting” both strands of the double helix. Clarifying these molecular mechanisms contributes greatly to designing gene-editing tools accurate enough for gene therapy treatments. The findings were published in the journal Nature.
The ...
Identifying the initial steps in colorectal cancer formation
2024-05-29
Research led by Weill Cornell Medicine provides new evidence that most colorectal cancers begin with the loss of intestinal stem cells, even before cancer-causing genetic alterations appear. The results, published on May 29 in Developmental Cell, overturn the prevailing theory for colorectal tumor initiation and suggest new ways to diagnose the disease before it has a chance to become established.
“Colorectal cancer is very, very heterogeneous, which has made it difficult for many years to classify these tumors in order to inform therapy,” said senior author Dr. ...
hnRNPM, a guardian of the integrity of cellular protein production
2024-05-29
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions have discovered that a protein called hnRNPM helps protect the integrity of the process cells use to make proteins. hnRNPM works by preventing the cell from making mistakes while it is putting together the different components leading to newly produced proteins. In cancer cells, loss of hnRNPM triggers an interferon immune response, suggesting that this protein may hold clinical promise. The findings appeared in Molecular Cell.
“Synthesizing a protein is like putting together the different parts of a machine. If during the assembly process parts that do not belong are incorporated ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
[Press-News.org] New technique from Brown University researchers offers more precise maps of the Moon’s surfaceThe team’s study describes enhancements that make a popular lunar mapping technique more streamlined and precise than ever at a time when space agencies are gearing up for lunar missions.