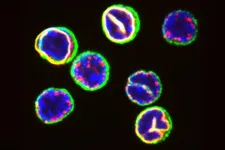
(Press-News.org) Heat production in fat tissue, a trait also known as adipose tissue thermogenesis, evolved over two stages in mammals, fully developing in eutherian mammals after the group’s evolutionary divergence from marsupials, according to a new study. The results could provide insights that inform future therapies related to metabolism and obesity. Many organisms produce heat internally to regulate body temperature. It is thought that the evolution of the ability to maintain high body temperatures provided evolutionary advantages, including adaptability to a wider range of environments and the ability to maintain optimal metabolism. For example, brown adipose tissue (BAT), the main organ for nonshivering thermogenesis (NST) in mammals, enables newborns, small-sized species, and hibernators to increase heat output to overcome cold stress. Expression of the thermogenic uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1) is crucial for heat production in BAT thermogenesis. However, while BAT thermogenesis is considered a key trait in eutherian mammals, its evolutionary origin is unknown.
To investigate the evolutionary origins, Susanne Keipert and colleagues employed a comparative genomics approach combined with ancient protein reconstructions. According to Keipert et al., although mouse UCP1 is thermogenic, the adipose tissue of marsupials expresses a nonthermogenic UCP1 variant, and only the ancestral eutherian UCP1 possessed thermogenic capabilities. This finding suggests that UCP1 gained thermogenic activity after the marsupial-eutherian mammal split roughly 150 million years ago. Transcriptome sequencing of marsupial opossum adipose tissue indicates that UCP1-mediated thermogenesis likely involved two stages: a prethermogenic stage where adipose tissue appears to have first undergone a rewiring linking nonthermogenic UCP1 expression in adipose tissue to cold stress in the common therian ancestor. This was followed by the acquisition of thermogenic function only after placental mammals diverged from marsupials. “BAT and beige adipose tissue have undergone an explosion of research in the past 15 years owing to their role as regulators of metabolism and potential for treating human obesity. However, despite their importance in activating NST, human therapies that target the pathways occurring in these tissues remain rare,” write Katherine Grabek and Ryan Sprenger in a related Perspective. “The approach of Keipert et al., using comparative genomics across a wider range of mammals, could thereby provide new insights on NST and endothermy that inform future therapies.”
END
Mammalian adipose tissue thermogenesis evolved in eutherian mammals
2024-06-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The first example of cellular origami
2024-06-06
“There are some things in life you can watch and then never unwatch,” said Manu Prakash, associate professor of bioengineering at Stanford University, calling up a video of his latest fascination, the single-cell organism Lacrymaria olor, a free-living protist he stumbled upon playing with his paper Foldscope. “It’s … just … it’s mesmerizing.”
“From the minute Manu showed it to me, I have just been transfixed by this cell,” said Eliott Flaum, a graduate student ...
Planet-forming disks around very low-mass stars are different
2024-06-06
Planets form in disks of gas and dust, orbiting young stars. The MIRI Mid-INfrared Disk Survey (MINDS), led by Thomas Henning from the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy (MPIA) in Heidelberg, Germany, aims to establish a representative disk sample. By exploring their chemistry and physical properties with MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument) on board the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), the collaboration links those disks to the properties of planets potentially forming there. In a new study, a team of researchers ...
Researchers identify key differences in inner workings of immune cells
2024-06-06
From the outside, most T cells look the same: small and spherical. Now, a team of researchers led by Berend Snijder from the Institute of Molecular Systems Biology at ETH Zurich has taken a closer look inside these cells using advanced techniques. Their findings show that the subcellular spatial organisation of cytotoxic T cells – which Snijder refers to as their cellular architecture – has a major influence on their fate.
Characteristics that determine a cell’s fate
When cells with nuclear invaginations encounter a pathogen, they turn into powerful effector cells that rapidly proliferate and kill the pathogen. Their fellow ...
Molecular pathway that impacts pancreatic cancer progression and response to treatment detailed
2024-06-06
CHAPEL HILL, North Carolina – Researchers at UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center and colleagues have established the most comprehensive molecular portrait of the workings of KRAS, a key cancer-causing gene or "oncogene," and how its activities impact pancreatic cancer outcomes. Their findings could help to better inform treatment options for pancreatic cancer, which is the third leading cause of all cancer deaths in the United States.
The research was published as two separate articles in Science.
“Because ...
Ferroelectric material is now fatigue-free
2024-06-06
Researchers at the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with research groups from the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China and Fudan University, have developed a fatigue-free ferroelectric material based on sliding ferroelectricity.
The study was published in Science.
Ferroelectric materials have switchable spontaneous polarization that can be reversed by an external electric field, which have been widely applied to non-volatile memory, sensing, and ...
Marsupials key to discovering the origin of heater organs in mammals
2024-06-06
Around 100 million years ago, a remarkable evolutionary shift allowed placental mammals to diversify and conquer many cold regions of our planet. New research from Stockholm University shows that the typical mammalian heater organ, brown fat, evolved exclusively in modern placental mammals.
In collaboration with the Helmholtz Munich and the Natural History Museum Berlin in Germany, and the University of East Anglia in the U.K., the Stockholm research team demonstrated that marsupials, our distant relatives, possess a not fully evolved form of brown fat. They discovered that the pivotal heat-producing protein called ...
Epstein-Barr Virus and brain cross-reactivity: possible mechanism for Multiple Sclerosis
2024-06-06
The role that Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) plays in the development of multiple sclerosis (MS) may be caused a higher level of cross-reactivity, where the body’s immune system binds to the wrong target, than previously thought.
In a new study published in PLOS Pathogens, researchers looked at blood samples from people with multiple sclerosis, as well as healthy people infected with EBV and people recovering from glandular fever caused by recent EBV infection. The study investigated how the immune system deals with EBV infection as part of worldwide efforts to understand how this common virus can lead to the development of multiple ...
Fish out of water: How killifish embryos adapted their development
2024-06-06
The annual killifish lives in regions with extreme drought. A research group at the University of Basel now reports in “Science” that the early embryogenesis of killifish diverges from that of other species. Unlike other fish, their body structure is not predetermined from the outset. This could enable the species to survive dry periods unscathed.
The turquoise killifish inhabits areas characterized by extreme conditions. The species, native to Africa, can survive prolonged periods of drought ...
Novel AI method could improve tissue, tumor analysis and advance treatment of disease
2024-06-06
Researchers at the University of Michigan and Brown University have developed a new computational method to analyze complex tissue data that could transform our current understanding of diseases and how we treat them.
Integrative and Reference-Informed tissue Segmentation, or IRIS, is a novel machine learning and artificial intelligence method that gives biomedical researchers the ability to view more precise information about tissue development, disease pathology and tumor organization.
The findings are published ...
Omega-3 therapy prevents birth-related brain injury in newborn rodents
2024-06-06
NEW YORK, NY--An injectable emulsion containing two omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil markedly reduced brain damage in newborn rodents after a disruption in the flow of oxygen to the brain near birth, a study by researchers at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons has found.
Brain injury due to insufficient oxygen is a severe complication of labor and delivery that occurs in one to three out of every 1,000 live births in the United States. Among babies who survive, the condition can lead to cerebral palsy, cognitive disability, epilepsy, pulmonary hypertension, and neurodevelopmental conditions.
“Hypoxic ...