(Press-News.org) College Park, Md. – Most people use Google Street View to find their way. Dr. Quynh Nguyen, an epidemiologist and statistician at the University of Maryland School of Public Health, uses it to locate spots where your journey might abruptly end. In a study published June 6 in the British Medical Journal (BMJ) of Injury Prevention, Nguyen identifies uses AI tools to identify key environmental elements impacting car-related collisions as well as cyclist-related and pedestrian-related accidents.
“Car crashes are the leading cause of death for young people between 5 and 29 years old. So it’s crucial to understand how the physical environment can increase or lessen fatal collisions and which communities are most affected by this,” says Nguyen, a professor whose work leverages technology and big data sources to address health disparities.
Nguyen and fellow researchers used Google Street View (GSV), an AI tool that offers 360-degree views of streets worldwide, to determine the relationship between car accidents and the built environment in locations where crashes occur. Using virtual mapping, researchers examined specific road features, such as streetlights or greenery, on a nationwide scale.
“Because we could crunch such a large amount of GSV data from across the country, we got precise results on which built elements influence car crashes. It was clear that places with higher levels of greenery, streetlights, single-lane roads, and sidewalks were associated with fewer fatal car crashes,” says Nguyen.
Sidewalks had the greatest impact on reducing crashes. Places with more sidewalks had 70% fewer traffic accidents, and places with one single-lane road, often found in rural areas, had 50% fewer accidents.
For pedestrians and cyclists, street lights and stop signs offered more safety – they were associated with fewer car accidents involving either group. Conversely, areas with road construction had an adverse effect with more collisions.
“Many of the public health issues communities face are often solvable,” said Xiaohe Yue, a data analyst in the UMD School of Public Health (SPH) and study co-author. “Emerging technologies and access to extensive data sources have been helpful in finding solutions to some of the public health issues that plague populations.”
Researchers hope the findings will inform transport and infrastructure policy by offering proven practical options for decision-makers to improve road safety for drivers, pedestrians and cyclists.
“We hope that our work will lead urban planners and developers to consider the built environment more carefully and so design safer streets and communities,” said co-author Heran Mane, data analyst working with Yue in SPH.
Nguyen sees a whole new research pathway emerging.
“We are seeing a rise in leveraging data science and AI to enable larger, more efficient and more timely studies like this one,” Nguyen said. “This research is one demonstration of how we can use AI to improve public health, and we know there’s so much more to come.”
Nguyen and colleagues are looking to expand the types of built environment indicators examined across the United States, as well as exploring these features in other countries.
This research was supported by the National Library of Medicine (R01LM012849) and the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities (R01MD015716, R01MD016037).
-Sumaya Abdel-Motagaly
END
What makes roads safer? New UMD study uses AI to find out
More greenery, sidewalks and streetlights mean fewer fatal collisions
2024-06-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Accessibility issues in cancer care
2024-06-07
Researchers at the University of Michigan are finding that many patients may be encountering significant barriers to cancer care, even from their first phone call to a clinic.
Patients attempting to access cancer care must go through several different levels of communication, both before their initial appointment with a physician and throughout their treatment.
Making those first calls to learn more about available cancer care services or to schedule an appointment at a clinic is an important step toward beginning their treatment journey.
“Racial and ethnic disparities have been observed in the outpatient visit rates for ...
Research details method to get efficient, environmentally friendly lithium
2024-06-07
As the electric vehicle market booms, the demand for lithium — the mineral required for lithium-ion batteries — has also soared. Global lithium production has more than tripled in the last decade. But current methods of extracting lithium from rock ores or brines are slow and come with high energy demands and environmental costs. They also require sources of lithium which are incredibly concentrated to begin with and are only found in a few countries.
Now, researchers at the University of Chicago Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (PME) have optimized a new method for extracting lithium from more dilute — and widespread — sources of the mineral, including seawater, ...
In new experiment, scientists record Earth’s radio waves from the moon
2024-06-07
On Feb. 22, a lunar lander named Odysseus touched down near the Moon’s South Pole and popped out four antennas to record radio waves around the surface—a moment University of Colorado Boulder astrophysicist Jack Burns hails as the “dawn of radio astronomy from the Moon.”
It was a major achievement for the tenacious lander, which was built by the Houston-based company Intuitive Machines and had to overcome a series of technical difficulties to make it to the lunar surface. Burns is co-investigator on the radio experiment that flew aboard Odysseus called Radio wave Observations at the Lunar Surface ...
Restoring our ubiquitination machinery to overcome resistance to cancer therapy
2024-06-07
“[...] the identification of ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes like UBE2J1 and the innovative deployment of PROTAC-type androgen receptor degraders are crucial in combating prostate cancer and overcoming therapeutic resistance.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 7, 2024 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncoscience (Volume 11) on May 6, 2024, entitled, “Restoring our ubiquitination machinery to overcome resistance in cancer therapy.”
In this new editorial, researchers Xiaoling Li and Ping Mu from ...
Sky’s the limit for biofuels
2024-06-07
The United States has enough biomass potential to produce 35 billion gallons per year of aviation biofuel by 2050, a new report confirms.
Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s John Field provided biomass feedstock production expertise to the report focused on the role of the bioeconomy in U.S. decarbonization strategies, which was produced by the Department of Energy’s DECARB program.
The report examined the role of biomass in reducing greenhouse gas emissions across the economy, including opportunities to reach negative emissions. It includes data ...
Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir and symptoms in adults with postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection
2024-06-07
About The Study: The results of this randomized clinical trial showed that a 15-day course of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in a population of patients with postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC) was generally safe but did not demonstrate a significant benefit for improving select PASC symptoms in a mostly vaccinated cohort with protracted symptom duration. Further studies are needed to determine the role of antivirals in the treatment of PASC.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding authors, email Linda N. Geng, M.D., Ph.D. (geng@stanford.edu) and Upinder Singh, M.D. (usingh@stanford.edu).
To ...
Stanford Medicine trial:15-day Paxlovid regimen safe but adds no clear long-COVID benefit
2024-06-07
In a clinical trial conducted by Stanford Medicine investigators and their colleagues, a 15-day course of Paxlovid — an antiviral drug combination targeting SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19 — proved safe as an extended-duration treatment but didn’t lessen select symptoms of the syndrome known as long COVID: the persistence, or reappearance, of COVID-related symptoms three months or more after an initial COVID-19 infection.
The findings are described in a paper to be published ...
Antioxidant gel preserves islet function after pancreas removal
2024-06-07
Northwestern University researchers have developed a new antioxidant biomaterial that someday could provide much-needed relief to people living with chronic pancreatitis.
The study will be published on June 7 in the journal Science Advances.
Before surgeons remove the pancreas from patients with severe, painful chronic pancreatitis, they first harvest insulin-producing tissue clusters, called islets, and transplant them into the vasculature of the liver. The goal of the transplant is to preserve a patient’s ability to control their own blood-glucose levels without insulin injections.
Unfortunately, the ...
Tiny new species of great ape lived in Germany 11 million years ago
2024-06-07
Ancient apes in Germany co-existed by partitioning resources in their environment, according to a study published June 7, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Madelaine Böhme of Eberhard Karls University of Tübingen, Germany and David R. Begun, of University of Toronto, Canada and colleagues.
The Hammerschmiede fossil site in Bavaria, Germany is best known for exceptional remains of the ancient great ape Danuvius dating to the late Miocene Epoch, 11.6 million years ago. Other experts contest the strength of the evidence to support whether Danuvius is a hominid or whether ...
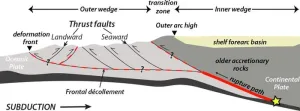
Cascadia Subduction Zone, one of Earth’s top hazards, comes into sharper focus
2024-06-07
Off the coasts of southern British Columbia, Washington, Oregon and northern California lies a 600 mile-long strip where the Pacific Ocean floor is slowly diving eastward under North America. This area, called the Cascadia Subduction Zone, hosts a megathrust fault, a place where tectonic plates move against each other in a highly dangerous way. The plates can periodically lock up and build stress over wide areas―eventually to be released when they finally lurch against each other. The result: the world’s greatest earthquakes, shaking both seabed and land, and generating tsunamis 100 feet high or more. Such a fault ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] What makes roads safer? New UMD study uses AI to find outMore greenery, sidewalks and streetlights mean fewer fatal collisions