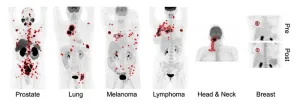
(Press-News.org) Toronto, Ontario—A novel AI approach can accurately detect six different types of cancer on whole-body PET/CT scans, according to research presented at the 2024 Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Annual Meeting. By automatically quantifying tumor burden, the new tool can be useful for assessing patient risk, predicting treatment response, and estimating survival.
“Automatic detection and characterization of cancer are important clinical needs to enable early treatment,” said Kevin H. Leung, PhD, research associate at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland. “Most AI models that aim to detect cancer are built on small to moderately sized datasets that usually encompass a single malignancy and/or radiotracer. This represents a critical bottleneck in the current training and evaluation paradigm for AI applications in medical imaging and radiology.”
To address this issue, researchers developed a deep transfer learning approach (a type of AI) for fully automated, whole-body tumor segmentation and prognosis on PET/CT scans. Data from 611 FDG PET/CT scans of patients with lung cancer, melanoma, lymphoma, head and neck cancer, and breast cancer, as well as 408 PSMA PET/CT scans of prostate cancer patients were analyzed in the study.
The AI approach automatically extracted radiomic features and whole-body imaging measures from the predicted tumor segmentations to quantify molecular tumor burden and uptake across all cancer types. Quantitative features and imaging measures were used to build predictive models to demonstrate prognostic value for risk stratification, survival estimation, and prediction of treatment response in patients with cancer.
“In addition to performing cancer prognosis, the approach provides a framework that will help improve patient outcomes and survival by identifying robust predictive biomarkers, characterizing tumor subtypes, and enabling the early detection and treatment of cancer,” noted Leung. “The approach may also assist in the early management of patients with advanced, end-stage disease by identifying appropriate treatment regimens and predicting response to therapies, such as radiopharmaceutical therapy.”
Leung noted that in the future generalizable, fully automated AI tools will play a major role in imaging centers by assisting physicians in interpreting PET/CT scans of patients with cancer. The deep learning approach may also lead to the discovery of important molecular insights about the underlying biological processes that may be currently understudied in large-scale patient populations.
Abstract 241979. “Fully Automated Whole-Body Tumor Segmentation on PET/CT using Deep Transfer Learning,” Kevin Leung, Steven Rowe, Moe Sadaghiani, Jeffrey Leal, Esther Mena, Peter Choyke, Yong Du, Martin Pomper, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland.
Link to Session
###
All 2024 SNMMI Annual Meeting abstracts can be found online.
About the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging
The Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) is an international scientific and medical organization dedicated to advancing nuclear medicine and molecular imaging—vital elements of precision medicine that allow diagnosis and treatment to be tailored to individual patients in order to achieve the best possible outcomes.
SNMMI’s members set the standard for molecular imaging and nuclear medicine practice by creating guidelines, sharing information through journals and meetings and leading advocacy on key issues that affect molecular imaging and therapy research and practice. For more information, visit www.snmmi.org.
END
New AI tool accurately detects six different cancer types on whole-body PET/CT scans
2024-06-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Galactic bloodlines: Many nearby star clusters originate from only three "families"
2024-06-10
An international team of astronomers led by the University of Vienna has deciphered the formation history of young star clusters, some of which we can see with the naked eye at night. The team, led by Cameren Swiggum and João Alves from the University of Vienna and Robert Benjamin from the University of Wisconsin-Whitewater, reports that most nearby young star clusters belong to only three families, which originate from very massive star-forming regions. This research also provides new insights into the effects of supernovae (violent explosions at the end of the life ...
New City of Hope study shows liver surgery to remove cancer can now be a safe, outpatient procedure
2024-06-10
LOS ANGELES — A new study guided by a renowned surgeon at City of Hope®, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, demonstrates that robotic liver surgery can be a safe, outpatient procedure. In fact, 8% of the patients sampled in the analysis were discharged to go home on the same day.
“We have made so much progress in liver cancer. We can now deliver more cures and use less invasive treatment options. This study is proof that for the right patients and with the right tools — meaning robotic surgery — we can get people through a liver operation quicker and toward recovery and normal ...
For type 1 diabetes distress, focus first on managing emotions
2024-06-10
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Media Contact: Jess Berthold (628) 399-0432
Jess.Berthold@ucsf.edu
Subscribe to UCSF News
For Type 1 Diabetes Distress, Focus First on Managing Emotions
Virtual, emotion-centered program cuts distress in half after one year, while also improving patients’ glucose control.
The most effective way to reduce the distress that comes with having diabetes – and improve glucose control – is to focus on managing the emotional strain of living with the condition, a new study of adults that was led by researchers at UC San Francisco has found.
Diabetes distress, or DD, refers to ...
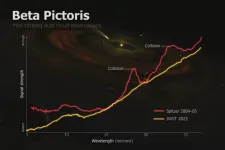
Webb telescope reveals asteroid collision in neighboring star system
2024-06-10
Astronomers have captured what appears to be a snapshot of a massive collision of giant asteroids in Beta Pictoris, a neighboring star system known for its early age and tumultuous planet-forming activity.
The observations spotlight the volatile processes that shape star systems like our own, offering a unique glimpse into the primordial stages of planetary formation.
“Beta Pictoris is at an age when planet formation in the terrestrial planet zone is still ongoing through giant asteroid collisions, so what we could be seeing here is basically how rocky planets and other bodies are forming in real time,” said Christine Chen, a Johns Hopkins University astronomer ...
When is genome sequencing advisable?
2024-06-10
Genetic mutations in human DNA can prevent proteins that perform important functions in the body from being formed correctly. This can lead to serious disorders that cause disease or even disability. Many of these diseases are already known and can be attributed to specific genes. To diagnose them, clinicians use a standard procedure known as exome sequencing. This involves analysing those segments of human DNA that are directly responsible for the correct formation of proteins. This coding part, the exome, makes up only around ...
Association found between media diet and science-consistent beliefs about climate change
2024-06-10
In a paper titled “The Politicization of Climate Science: Media Consumption, Perceptions of Science and Scientists, and Support for Policy,” published May 26, 2024, in the Journal of Health Communication, researchers probed the associations between media exposure and science-consistent beliefs about climate change and the threat it posed to the respondent.
Expanding on earlier work associating Fox News consumption with doubts about the existence of human-caused climate change, a team of scholars affiliated with the Annenberg Public Policy ...
Older, poorer, Black, Medicaid beneficiaries less likely to be placed on liver transplant lists
2024-06-10
INDIANAPOLIS – A new, healthy liver offers the best survival for patients with early-stage liver cancer. But a new study, led by Katie Ross-Driscoll, PhD, MPH, of Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Surgery, has identified disparities in liver transplant referral and evaluation, which must precede waitlisting, for these potentially lifesaving procedures.
While other studies have demonstrated disparities in placement on organ waitlists, the new study is one of the first to examine the transplant ...
Imposing cost-efficient trade sanctions
2024-06-10
By Alistair Jones
SMU Office of Research – Global condemnation of Russia over its invasion of Ukraine has prompted the imposition of trade sanctions. Such measures are a form of economic coercion, commonly used for reasons of foreign policy.
Trade sanctions can be put in place in an attempt to alter objectionable behaviour – in Russia's case, waging a war – or to punish an offending state through the disruption of economic exchange.
"Sanctions can be in many forms and raising ...
Statins for heart disease prevention could be recommended for far fewer Americans if new risk equation is adopted
2024-06-10
PITTSBURGH – If national guidelines are revised to incorporate a new risk equation, about 40% fewer people could meet criteria for cholesterol-lowering statins to prevent heart disease, according to a study by researchers at the University of Pittsburgh, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and University of Michigan. Published today in JAMA Internal Medicine, the study examines the potential impact of widespread adoption of the PREVENT equations, which were released by the American Heart Association ...
Multicenter clinical study supports safety of deep general anesthesia
2024-06-10
General anesthesia makes it possible for millions of patients each year to undergo lifesaving surgeries while unconscious and free of pain. But the 176-year-old medical staple uses powerful drugs that have stoked fears of adverse effects on the brain — particularly if used in high doses.
New findings published June 10 in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), however, support an earlier study that indicates that anesthesia is no more hazardous for the brain at higher doses than at lower doses, ...