(Press-News.org) Beginning annually on June 1, hurricane season poses a major threat to Texas coastal communities, causing both physical and financial damage to the areas they hit. This damage can be staggering; when Hurricane Harvey hit in 2017, it cost Galveston $132.73 billion in damages. Texas A&M University researchers have collaborated to understand the impacts of storm surge floods before they occur to potentially reduce the level of damage. Their study was published in “Urban Informatics.”
The researchers have implemented 3D visualization technology to identify the potential outcomes of hurricane flooding before it occurs. According to researchers, severe weather has been increasing over the last several years due to global climate change. If severe storms and flooding continue to increase in the future, implementing 3D visualization based on real-time weather forecasts could result in improved safety and less damage-inflicted costs.
The 3D modeling technique also allows researchers to examine the effects of damage-preventing infrastructure, such as the proposed Galveston “Ike Dike,” a dike designed to shield Galveston Island from future storm surge and flood events.
Using Galveston Island as an example, researchers used 3D visualization to model the damage that would occur to residential buildings as a result of hurricanes of varying intensities. They also modeled damage with preventative infrastructure — the “Ike Dike” — in place.
An advantage of 3D visualization over other damage modeling methods is that it allows researchers to model specific buildings, accounting for basements, back entrances, and windows. By identifying a residential building’s first-floor elevation level, researchers can predict the physical and financial damage that a hurricane will cause to the specific building.
“3D visualization of hurricanes and storm surges allows us to understand how flooding will impact our coastal communities by allowing us to vividly see how each building and road might be impacted by a given flood,” said Dr. Xinyue Ye, the Harold Adams Endowed Professor of Landscape Architecture and Urban Planning and affiliated faculty member in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, the Department of Multidisciplinary Engineering, the Department of Geography, and the Section of Visual Computing & Interactive Media.
Faculty collaborators on the project include Dr. David Retchless, associate professor in the Department of Marine and Coastal Environmental Science at Texas A&M University at Galveston, Dr. Galen Newman, professor and head of the Department of Landscape Architecture and Urban Planning and the Nicole and Kevin Youngblood Professor of Residential Land Development at Texas A&M, and Dr. Nick Duffield, the Royce E. Wisenbaker Professor I in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering and director of the Texas A&M Institute of Data Science.
Critical Information For Homeowners
Since 3D visualization highlights the potential damages hurricane flooding may cause, it can give homeowners a better understanding of what to invest in as far as insurance and preventative infrastructure. This technology also creates an increased community awareness around potential outcomes of hurricanes and flooding.
“Having used Galveston as an example, the next step would be to expand that to other coastal communities in Texas,” Ye noted. “In this study, we mainly used residential houses, but we can expand it to other business properties as well.”
Effective use of 3D models can protect Texas residents. By implementing this technology on other coastal communities or community buildings, such as schools and stores, researchers can help residents and officials create a plan for hurricane season. As real-time weather forecasts are implemented into the models, researchers may be able to determine when evacuation is necessary and use this data to alert residents.
“3D visualization serves as a universal language, bridging diverse disciplines and fostering communication between academia and the general public,” said Ye, who also serves as the director of the Texas A&M Center for Geospatial Sciences, Applications, and Technology and the founding director of Urban AI Lab at the Texas A&M Institute of Data Science.
Duffield adds that this project shows how the work at the intersection between geospatial data science and visualization can raise awareness for individuals, communities and government on the consequences of extreme weather and make informed planning decisions for responses.
This study combines the expertise of researchers in multiple fields, including computer engineering, landscape architecture, urban planning, geography, and marine and coastal environmental science. The positive impacts of this research highlight the importance of collaboration between computational science and domain-specific disciplines.
By Alyssa Schaechinger, Texas A&M University Engineering
###
END
Researchers use 3D visualization to predict, prevent hurricane damage
Galveston Island was used as an example to predict damage that would occur as a result of hurricanes of varying intensities.
2024-06-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Kepplinger, Vidyashankar to receive funding for conference
2024-06-10
David Kepplinger, Assistant Professor, Statistics, and Anand Vidyashankar, Professor, Statistics, are set to receive funding from the National Science Foundation for: “Conference: Building a robust community: Joint International Conference on Robust Statistics and Conference on Data Science, Statistics, and Data Science.”
Kepplinger and Vidyashankar will receive $20,993 from NSF for this award. Funding will begin in July 2024 and will end in late June 2025.
The funding will support 15–20 students and early-career researchers to participate in the joint International Conference on Robust Statistics (ICORS) and the Conference ...
Novel radiotracer produces high quality images of “Alzheimer’s disease of the heart”
2024-06-10
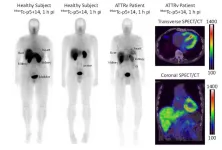
Toronto, Ontario—A newly developed radiotracer can generate high quality and readily interpretable images of cardiac amyloidosis, a condition referred to as the “Alzheimer’s disease of the heart.” As the first amyloid-specific and pan-amyloid binding radiotracer designed for planar and SPECT/CT imaging, 99mTc-p5+14 could play an important role in early detection and treatment of cardiac amyloidosis. This research was presented at the 2024 Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Annual Meeting.
Systemic amyloidosis is an incurable disease in which abnormal amounts of ...
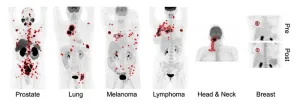
New AI tool accurately detects six different cancer types on whole-body PET/CT scans
2024-06-10
Toronto, Ontario—A novel AI approach can accurately detect six different types of cancer on whole-body PET/CT scans, according to research presented at the 2024 Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Annual Meeting. By automatically quantifying tumor burden, the new tool can be useful for assessing patient risk, predicting treatment response, and estimating survival.
“Automatic detection and characterization of cancer are important clinical needs to enable early treatment,” said Kevin H. ...
Galactic bloodlines: Many nearby star clusters originate from only three "families"
2024-06-10
An international team of astronomers led by the University of Vienna has deciphered the formation history of young star clusters, some of which we can see with the naked eye at night. The team, led by Cameren Swiggum and João Alves from the University of Vienna and Robert Benjamin from the University of Wisconsin-Whitewater, reports that most nearby young star clusters belong to only three families, which originate from very massive star-forming regions. This research also provides new insights into the effects of supernovae (violent explosions at the end of the life ...
New City of Hope study shows liver surgery to remove cancer can now be a safe, outpatient procedure
2024-06-10
LOS ANGELES — A new study guided by a renowned surgeon at City of Hope®, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, demonstrates that robotic liver surgery can be a safe, outpatient procedure. In fact, 8% of the patients sampled in the analysis were discharged to go home on the same day.
“We have made so much progress in liver cancer. We can now deliver more cures and use less invasive treatment options. This study is proof that for the right patients and with the right tools — meaning robotic surgery — we can get people through a liver operation quicker and toward recovery and normal ...
For type 1 diabetes distress, focus first on managing emotions
2024-06-10
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Media Contact: Jess Berthold (628) 399-0432
Jess.Berthold@ucsf.edu
Subscribe to UCSF News
For Type 1 Diabetes Distress, Focus First on Managing Emotions
Virtual, emotion-centered program cuts distress in half after one year, while also improving patients’ glucose control.
The most effective way to reduce the distress that comes with having diabetes – and improve glucose control – is to focus on managing the emotional strain of living with the condition, a new study of adults that was led by researchers at UC San Francisco has found.
Diabetes distress, or DD, refers to ...
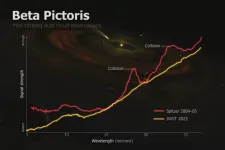
Webb telescope reveals asteroid collision in neighboring star system
2024-06-10
Astronomers have captured what appears to be a snapshot of a massive collision of giant asteroids in Beta Pictoris, a neighboring star system known for its early age and tumultuous planet-forming activity.
The observations spotlight the volatile processes that shape star systems like our own, offering a unique glimpse into the primordial stages of planetary formation.
“Beta Pictoris is at an age when planet formation in the terrestrial planet zone is still ongoing through giant asteroid collisions, so what we could be seeing here is basically how rocky planets and other bodies are forming in real time,” said Christine Chen, a Johns Hopkins University astronomer ...
When is genome sequencing advisable?
2024-06-10
Genetic mutations in human DNA can prevent proteins that perform important functions in the body from being formed correctly. This can lead to serious disorders that cause disease or even disability. Many of these diseases are already known and can be attributed to specific genes. To diagnose them, clinicians use a standard procedure known as exome sequencing. This involves analysing those segments of human DNA that are directly responsible for the correct formation of proteins. This coding part, the exome, makes up only around ...
Association found between media diet and science-consistent beliefs about climate change
2024-06-10
In a paper titled “The Politicization of Climate Science: Media Consumption, Perceptions of Science and Scientists, and Support for Policy,” published May 26, 2024, in the Journal of Health Communication, researchers probed the associations between media exposure and science-consistent beliefs about climate change and the threat it posed to the respondent.
Expanding on earlier work associating Fox News consumption with doubts about the existence of human-caused climate change, a team of scholars affiliated with the Annenberg Public Policy ...
Older, poorer, Black, Medicaid beneficiaries less likely to be placed on liver transplant lists
2024-06-10
INDIANAPOLIS – A new, healthy liver offers the best survival for patients with early-stage liver cancer. But a new study, led by Katie Ross-Driscoll, PhD, MPH, of Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Surgery, has identified disparities in liver transplant referral and evaluation, which must precede waitlisting, for these potentially lifesaving procedures.
While other studies have demonstrated disparities in placement on organ waitlists, the new study is one of the first to examine the transplant ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] Researchers use 3D visualization to predict, prevent hurricane damageGalveston Island was used as an example to predict damage that would occur as a result of hurricanes of varying intensities.