(Press-News.org) A research article published June 10 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences highlights the importance of careful application of high-tech forensic science to avoid wrongful convictions.
In a study with implications for an array of forensic examinations that rely on “vast databases and efficient algorithms,” researchers found the odds of a false match significantly increase when examiners make millions of comparisons in a quest to match wires found at a crime scene with the tools allegedly used to cut them.
The rate of mistaken identifications could be as high as one in 10 or more, concluded the researchers, who are affiliated with the Center for Statistics and Applications in Forensic Evidence (CSAFE), based in Ames, Iowa.
“It is somewhat of a counterintuition,” said co-author Susan VanderPlas, an assistant professor of statistics at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln. “You are more likely to find the right match – but you’re also more likely to find the wrong match.”
VanderPlas worked as a research professor at CSAFE before moving to Nebraska in 2020. Co-authors of the study, “Hidden Multiple Comparisons Increase Forensic Error Rates,” were Heike Hoffmann and Alicia Carriquiry, both affiliated with CSAFE and Iowa State University’s Department of Statistics.
Wire cuts and tool marks are used frequently as evidence in robberies, bombings, and other crimes. In the case of wire cuts, tiny striations on the cut ends of a wire may be matched to one of many available tools in a toolbox or garage. Comparing the evidence to more tools increases the chances that similar striations may be found on unrelated tools, resulting in a false accusation and conviction.
Wire-cutting evidence has been at issue in at least two cases that garnered national attention, including one where the accused was linked to a bombing based on a small piece of wire, a tiny fraction of an inch in diameter, that was matched to a tool found among the suspect’s belongings.
“Wire-cutting evidence is used in court and, based on our findings, it shouldn’t be – at least not without presenting additional information about how many comparisons were made,” VanderPlas said.
Wire cutting evidence is evaluated by comparing the striations found on the cut end of a piece of wire against the cutting blades of tools suspected to have been used in the crime. In a manual test, the examiner slides the end of the wire along the path created along another piece of material cut by the same tool to see where the pattern of striations match.
An automated process uses a comparison microscope and pattern-matching algorithms, to find possible matches pixel by pixel.
This can result in thousands upon thousands of individual comparisons, depending upon the length of the cutting blade, diameter of the wire, and even the number of tools checked.
For example, VanderPlas said she and her husband tallied the various tin snips, wire cutters, pliers and similar tools stored in their garage and came up with a total of 7 meters in blade length.
Examiners may not even be aware of the number of comparisons they are making as they search for a matching pattern, because those comparisons are hidden in the algorithms.
“This often-ignored issue increases the false discovery rate, and can contribute to the erosion of public trust in the justice system through conviction of innocent individuals,” the study authors wrote.
Forensic examiners typically testify based upon subjective rules about how much similarity is required to make an identification, the study explained. The researchers could not obtain error rate studies for wire-cut examinations and used published error rates for ballistics examinations to estimate possible false discovery rates for wire-cut examinations.
Before wire-cut examinations are used as evidence in court, the researchers recommended that:
Examiners report the overall length or area of materials used in the examination process, including blade length and wire diameter. This would enable examination-wide error rates to be calculated.
Studies be conducted to assess both false discovery and false elimination error rates when examiners are making difficult comparisons. Studies should link the length and area of comparison to error rates.
The number of items searched, comparisons made and results returned should be reported when a database is used at any stage of the forensic evidence evaluation process.
The VanderPlas article joins other reports calling for improvements in forensic science in America. The National Academies Press, publisher of the PNAS journal and other publications of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine, also published the landmark 2009 report “Strengthening Forensic Science in the United States: A Path Forward.”
END
Wire-cut forensic examinations currently too unreliable for court, new study says
Analysis has implications for other forensic examinations that rely on large databases and algorithms for comparisons
2024-06-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
SNMMI elects Jean-Luc C. Urbain, MD, Ph.D., FASNC, as President-Elect at 2024 Annual Meeting
2024-06-10
Toronto, Ontario—Jean-Luc C. Urbain, MD, PhD, FASNC, professor of Radiology/Nuclear Medicine and Medicine, has been named president-elect of the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI). SNMMI introduced a new slate of officers during its 2024 Annual Meeting, held June 8-11 in Toronto.
“As SNMMI president-elect, I plan to focus on bringing and integrating radiopharmaceutical theranostics into the clinic to benefit as many patients as possible. This will require an emphasis ...
UNC-Chapel Hill researchers create skin-inspired sensory robots to provide medical treatment
2024-06-10
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill scientists have created innovative soft robots equipped with electronic skins and artificial muscles, allowing them to sense their surroundings and adapt their movements in real-time, according to the paper, “Skin-Inspired, Sensory Robots for Electronic Implants,” in Nature Communications.
In their research, funded by the National Science Foundation and the National Institutes of Health, the robots are designed to mimic the way muscles and skin work together in animals, making them more effective and safer to use inside the body. The e-skin integrates various sensing materials, such as silver nanowires ...
Researchers use 3D visualization to predict, prevent hurricane damage
2024-06-10
Beginning annually on June 1, hurricane season poses a major threat to Texas coastal communities, causing both physical and financial damage to the areas they hit. This damage can be staggering; when Hurricane Harvey hit in 2017, it cost Galveston $132.73 billion in damages. Texas A&M University researchers have collaborated to understand the impacts of storm surge floods before they occur to potentially reduce the level of damage. Their study was published in “Urban Informatics.”
The researchers have implemented 3D visualization technology to identify the potential outcomes of hurricane flooding ...
Kepplinger, Vidyashankar to receive funding for conference
2024-06-10
David Kepplinger, Assistant Professor, Statistics, and Anand Vidyashankar, Professor, Statistics, are set to receive funding from the National Science Foundation for: “Conference: Building a robust community: Joint International Conference on Robust Statistics and Conference on Data Science, Statistics, and Data Science.”
Kepplinger and Vidyashankar will receive $20,993 from NSF for this award. Funding will begin in July 2024 and will end in late June 2025.
The funding will support 15–20 students and early-career researchers to participate in the joint International Conference on Robust Statistics (ICORS) and the Conference ...
Novel radiotracer produces high quality images of “Alzheimer’s disease of the heart”
2024-06-10
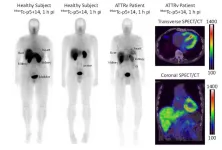
Toronto, Ontario—A newly developed radiotracer can generate high quality and readily interpretable images of cardiac amyloidosis, a condition referred to as the “Alzheimer’s disease of the heart.” As the first amyloid-specific and pan-amyloid binding radiotracer designed for planar and SPECT/CT imaging, 99mTc-p5+14 could play an important role in early detection and treatment of cardiac amyloidosis. This research was presented at the 2024 Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Annual Meeting.
Systemic amyloidosis is an incurable disease in which abnormal amounts of ...
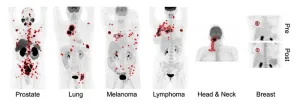
New AI tool accurately detects six different cancer types on whole-body PET/CT scans
2024-06-10
Toronto, Ontario—A novel AI approach can accurately detect six different types of cancer on whole-body PET/CT scans, according to research presented at the 2024 Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Annual Meeting. By automatically quantifying tumor burden, the new tool can be useful for assessing patient risk, predicting treatment response, and estimating survival.
“Automatic detection and characterization of cancer are important clinical needs to enable early treatment,” said Kevin H. ...
Galactic bloodlines: Many nearby star clusters originate from only three "families"
2024-06-10
An international team of astronomers led by the University of Vienna has deciphered the formation history of young star clusters, some of which we can see with the naked eye at night. The team, led by Cameren Swiggum and João Alves from the University of Vienna and Robert Benjamin from the University of Wisconsin-Whitewater, reports that most nearby young star clusters belong to only three families, which originate from very massive star-forming regions. This research also provides new insights into the effects of supernovae (violent explosions at the end of the life ...
New City of Hope study shows liver surgery to remove cancer can now be a safe, outpatient procedure
2024-06-10
LOS ANGELES — A new study guided by a renowned surgeon at City of Hope®, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, demonstrates that robotic liver surgery can be a safe, outpatient procedure. In fact, 8% of the patients sampled in the analysis were discharged to go home on the same day.
“We have made so much progress in liver cancer. We can now deliver more cures and use less invasive treatment options. This study is proof that for the right patients and with the right tools — meaning robotic surgery — we can get people through a liver operation quicker and toward recovery and normal ...
For type 1 diabetes distress, focus first on managing emotions
2024-06-10
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Media Contact: Jess Berthold (628) 399-0432
Jess.Berthold@ucsf.edu
Subscribe to UCSF News
For Type 1 Diabetes Distress, Focus First on Managing Emotions
Virtual, emotion-centered program cuts distress in half after one year, while also improving patients’ glucose control.
The most effective way to reduce the distress that comes with having diabetes – and improve glucose control – is to focus on managing the emotional strain of living with the condition, a new study of adults that was led by researchers at UC San Francisco has found.
Diabetes distress, or DD, refers to ...
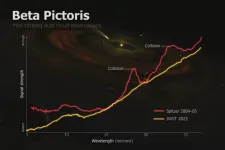
Webb telescope reveals asteroid collision in neighboring star system
2024-06-10
Astronomers have captured what appears to be a snapshot of a massive collision of giant asteroids in Beta Pictoris, a neighboring star system known for its early age and tumultuous planet-forming activity.
The observations spotlight the volatile processes that shape star systems like our own, offering a unique glimpse into the primordial stages of planetary formation.
“Beta Pictoris is at an age when planet formation in the terrestrial planet zone is still ongoing through giant asteroid collisions, so what we could be seeing here is basically how rocky planets and other bodies are forming in real time,” said Christine Chen, a Johns Hopkins University astronomer ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Wire-cut forensic examinations currently too unreliable for court, new study saysAnalysis has implications for other forensic examinations that rely on large databases and algorithms for comparisons