(Press-News.org) Americans’ interest in a potentially harmful “magic mushroom” is soaring, with Google searches skyrocketing 114 percent from 2022 to 2023, according to a new study by researchers at the University of California San Diego Herbert Wertheim School of Public Health and Human Longevity Science. In a paper published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, the scientists suggest that the growing market for Amanita muscaria may be sparked in part by emerging clinical research supporting the safety and efficacy of psilocybin as a treatment for depression.
Like psilocybin mushrooms, Amanita muscaria mushrooms have psychotropic effects. These include a feeling of weightlessness, visual and auditory hypersensitivity, space distortion, unawareness of time, and colored hallucinations. The psychotropic effects are produced by compounds that naturally occur in the mushroom called muscimol and ibotenic acid, its biosynthetic precursor.
However, in addition to being psychotropic, these compounds can also be more toxic than fentanyl, cocaine, and PCP, according to the scientists’ review of estimates from published mouse studies. Nevertheless, gummies and chocolates containing these compounds are being marketed with health-related claims such as mitigation of anxiety, depression, and other conditions, often by vague references to clinical studies related to psilocybin, which is not as toxic and produces different psychotropic effects.
“There is a lot of interest in the therapeutic potential for psilocybin and for good reason. But at the same time, a growing industry may be trying to capitalize on this interest by marketing other mushrooms. For example, some manufacturers are calling Amanita muscaria products ‘magic mushroom gummies’ and not disclosing what mushroom they contain, or not making it clear Amanita muscaria is a different mushroom than psilocybin and has essentially no clinical evidence supporting its use as a therapy,” said Eric Leas, Ph.D., M.P.H., assistant professor in the UC San Diego Herbert Wertheim School of Public Health and Human Longevity Science and senior author on the paper.
Psilocybin and muscimol work in different ways. Psilocybin is an antidepressant that primarily binds to serotonin receptors, activating a neural pathway that mediates happiness and optimism. Amanita muscaria however is a depressant, similar to alcohol and benzodiazepines, which suppress the central nervous system. Leas believes that marketing Amanita muscaria as a psilocybin-type product violates consumers’ right to informed consent.
“There may be some pharmaceutical potential to Amanita muscaria, but muscimol does not have the same effects on the body as psilocybin, so it probably would not have the same treatment applications if it ever went through drug development. For this reason, it is misleading not to clearly distinguish between muscimol and psilocybin. If someone is consenting to a psychedelic experience, they have a right to know what substance they are taking and receive accurate information about its potential health benefits and health risks.”
False marketing may be enabled by lack of federal regulation of Amanita muscaria. Under the 1970 Controlled Substances Act, psilocybin is a Schedule 1 drug, making its manufacture, distribution, import/export, possession and use illegal. In 2017, the FDA designated psilocybin as a “breakthrough therapy” and in 2023 loosened restrictions to allow drug developers and scientists to conduct clinical trials with psilocybin, including some that are taking place at UC San Diego. Nevertheless, it continues to be a Schedule 1 controlled substance, and, therefore its use is disallowed out of the context of clinical trials.
Not so for Amanita muscaria. Although there are several published case studies of hospitalizations and deaths resulting from Amanita muscaria consumption, to date it is not included on a Controlled Substances list (except for the State of Louisiana, where sales are restricted). However, it is often marketed as a dietary supplement, products covered by regulations enforced by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the Federal Trade Commission.
“We have found that many manufacturers use supplement labeling, including ‘Supplement Facts’ panels,” said Leas. “However, there is a process for bringing a supplement to market that involves presenting safety data and filing an application, and we cannot find any evidence that any of these manufacturers have gone through this process, and this makes the current products sold in this manner illegal.
“In my view, if a manufacturer wanted to develop a dietary supplement from Amanita muscaria, the application probably would not be approved because of muscimol and ibotenic acids’ inherent risks,” he added. “But right now it is the ‘Wild West,’ and companies are profiting from delayed enforcement while putting consumers at risk.”
The authors are making several general recommendations. The most restrictive would be to put Amanita muscaria on the Controlled Substances list, where it could first be evaluated for its medical potential and abuse liability before it is widely sold. However, if Amanita muscaria is not placed on a drug schedule, they recommend commonsense precautions, such as setting age restrictions, accurate dosing standards, childproof packaging, and marketing aimed at adults rather than children, all now required for legal sales of recreational cannabis. The authors would also like to see mental health professionals help their patients distinguish between psilocybin and Amanita muscaria.
The authors’ key takeaway is that “companies who are making these products are pushing the limits of our regulations. They are getting away with making a buck until someone tells them they can't. Given the substantial risks associated with using Amanita muscaria products, it is a buyer beware marketplace where consumers are at risk and are not accurately informed. The time for a public health first response is now.”
Co-authors include: Nora Satybaldiyeva, Wayne Kepner, Kevin H. Yang, Raquel M. Harati, Jamie Corroon, and Matthieu Rouffet, of UC San Diego.
The work is supported in part by grant T32IP4684 from the California Tobacco Related Disease Research Program and grant K01DA054303 from the U.S. National Institute on Drug Abuse.
# # #
END
Unregulated sales of a toxic and hallucinogenic mushroom endanger public health
2024-06-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Alarming trends call for action to define the future role of food in nation’s health
2024-06-10
CHICAGO, June 10, 2024 — The cost of nutritious food and the lack of access to it are of significant concern to U.S. consumers. That’s according to a new national poll of public attitudes on food and nutrition conducted by Zogby Analytics on behalf of Research!America and the American Heart Association. Nearly 7 in 10 (68%) respondents recognize healthy eating habits as an important factor in improving a person’s chance for a long and healthy life. Yet more than half (53%) say the United ...
Case studies show how quasi-governmental organizations could strengthen climate adaptation governance
2024-06-10
The politicization of climate issues and the unsynchronized efforts of stakeholders are hindering the effectiveness of climate adaptation governance in the U.S. According to a new study(Link is external) published by Princeton researchers, the design characteristics of quasi-governmental organizations (QGOs) could provide insights on how to depoliticize climate information sources and foster multi-level stakeholder coordination.
Quasi-governmental organizations are entities that have a combination of public and private characteristics, utilizing both for-profit and not-for-profit ...
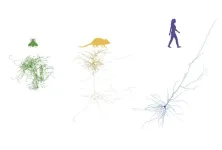
Brain’s structure hangs in ‘a delicate balance’
2024-06-10
When a magnet is heated up, it reaches a critical point where it loses magnetization. Called “criticality,” this point of high complexity is reached when a physical object is transitioning smoothly from one phase into the next.
Now, a new Northwestern University study has discovered that the brain’s structural features reside in the vicinity of a similar critical point — either at or close to a structural phase transition. Surprisingly, these results are consistent across brains from humans, mice and fruit flies, which suggests the finding might be universal.
Although the researchers don’t ...
Protein study could help researchers develop new antibiotics
2024-06-10
A bacterial enzyme called histidine kinase is a promising target for new classes of antibiotics. However, it has been difficult to develop drugs that target this enzyme, because it is a “hydrophobic” protein that loses its structure once removed from its normal location in the cell membrane.
Now, an MIT-led team has found a way to make the enzyme water-soluble, which could make it possible to rapidly screen potential drugs that might interfere with its functions.
The researchers created their new version ...
Two can play that game: juvenile dolphins who play together are more successful as adults
2024-06-10
Juvenile social play predicts adult reproductive success in male bottlenose dolphins, a new study has found.
Fresh findings published today in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences led by researchers from the University of Bristol and University of Western Australia, show that juvenile male dolphins with strong social bonds practice adult-like reproductive behaviours when playing together, and those juvenile males who spend more time practicing will father more offspring as adults. The study provides rare evidence for a link between juvenile social play and reproductive success in a wild animal.
In collaboration with international colleagues, the ...
Wire-cut forensic examinations currently too unreliable for court, new study says
2024-06-10
A research article published June 10 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences highlights the importance of careful application of high-tech forensic science to avoid wrongful convictions.
In a study with implications for an array of forensic examinations that rely on “vast databases and efficient algorithms,” researchers found the odds of a false match significantly increase when examiners make millions of comparisons in a quest to match wires found at a crime scene with the tools allegedly used to cut them.
The rate of mistaken identifications could be as high as one in 10 or more, concluded ...
SNMMI elects Jean-Luc C. Urbain, MD, Ph.D., FASNC, as President-Elect at 2024 Annual Meeting
2024-06-10
Toronto, Ontario—Jean-Luc C. Urbain, MD, PhD, FASNC, professor of Radiology/Nuclear Medicine and Medicine, has been named president-elect of the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI). SNMMI introduced a new slate of officers during its 2024 Annual Meeting, held June 8-11 in Toronto.
“As SNMMI president-elect, I plan to focus on bringing and integrating radiopharmaceutical theranostics into the clinic to benefit as many patients as possible. This will require an emphasis ...
UNC-Chapel Hill researchers create skin-inspired sensory robots to provide medical treatment
2024-06-10
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill scientists have created innovative soft robots equipped with electronic skins and artificial muscles, allowing them to sense their surroundings and adapt their movements in real-time, according to the paper, “Skin-Inspired, Sensory Robots for Electronic Implants,” in Nature Communications.
In their research, funded by the National Science Foundation and the National Institutes of Health, the robots are designed to mimic the way muscles and skin work together in animals, making them more effective and safer to use inside the body. The e-skin integrates various sensing materials, such as silver nanowires ...
Researchers use 3D visualization to predict, prevent hurricane damage
2024-06-10
Beginning annually on June 1, hurricane season poses a major threat to Texas coastal communities, causing both physical and financial damage to the areas they hit. This damage can be staggering; when Hurricane Harvey hit in 2017, it cost Galveston $132.73 billion in damages. Texas A&M University researchers have collaborated to understand the impacts of storm surge floods before they occur to potentially reduce the level of damage. Their study was published in “Urban Informatics.”
The researchers have implemented 3D visualization technology to identify the potential outcomes of hurricane flooding ...
Kepplinger, Vidyashankar to receive funding for conference
2024-06-10
David Kepplinger, Assistant Professor, Statistics, and Anand Vidyashankar, Professor, Statistics, are set to receive funding from the National Science Foundation for: “Conference: Building a robust community: Joint International Conference on Robust Statistics and Conference on Data Science, Statistics, and Data Science.”
Kepplinger and Vidyashankar will receive $20,993 from NSF for this award. Funding will begin in July 2024 and will end in late June 2025.
The funding will support 15–20 students and early-career researchers to participate in the joint International Conference on Robust Statistics (ICORS) and the Conference ...