(Press-News.org) By late in the pandemic more than 96% of individuals in the U.S. ages 16 and older had COVID-19 antibodies from infection or vaccination. However, immunity from the virus tends to wane over time. Uptake of the boosters has been quite low, meaning that over time the current high levels of protection will dissipate.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, at-home antigen tests became widely accepted for detecting infection. In a new joint study by the George Washington University, the University of North Carolina, and others, researchers looked into the benefits of using at-home antibody tests to detect immunity and to make decisions about the need for a COVID-19 booster shot - something that may be of particularly relevance for those at high risk for poor outcomes from Covid infection.
In the study, the researchers found that a negative result on an ‘at-home’ antibody test indicates inadequate immunity as reflected in an extensive and sophisticated battery of Covid immune tests performed by highly specialized academic/industry labs at various centers around the country.
“Our research suggests that an antibody test taken at home will allow at-risk individuals to conveniently identify inadequate immunity to COVID-19 - in a world in which population immunity is declining, “ said co-author John Lafleur, professor of emergency management at the George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences. “This can be important information for those who are considering booster vaccination, but question whether or not it is needed. In addition, as with home antigen testing, home antibody tests may be another useful tool in any future viral pandemic.”
The study,“COVID-19 Point-of-Care Tests can Identify Low-Antibody Individuals: In-depth Immunoanalysis of Boosting Benefits in a Healthy Cohort,” was published June 12 in Science Advances.
END
Convenient at-home test identifies at-risk individuals with inadequate immunity to COVID-19
2024-06-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sweetpotato’s sweet revenge
2024-06-12
Sweetpotato black rot is a devastating disease caused by the fungus Ceratocystis fimbriata. Since the late 1800s, black rot of sweetpotato has threatened to destroy as much as 30% of the sweetpotato crop in the United States. In 2015, all sweetpotato-producing states in the United States experienced one of the worst outbreaks recorded in history, with up to 60% losses reported. While fungicides can help manage the disease, they are not a sustainable solution, especially with volatile restrictions on fungicide residues among major export markets. An additional ...
Pacific coast gray whales have gotten 13% shorter in the past 20-30 years, Oregon State study finds
2024-06-12
Gray whales that spend their summers feeding in the shallow waters off the Pacific Northwest coast have undergone a significant decline in body length since around the year 2000, a new Oregon State University study found.
The smaller size could have major consequences for the health and reproductive success of the affected whales, and also raises alarm bells about the state of the food web in which they coexist, researchers say.
“This could be an early warning sign that the abundance of this population is starting to decline, or is not healthy,” said K.C. Bierlich, co-author on the study and an assistant professor at OSU’s ...
Pairing shelter dogs has ‘pawsitive’ results
2024-06-12
Shelter dogs awaiting adoption fare better with a canine companion than when they’re housed alone, according to new research from Virginia Tech.
The study, led by Erica Feuerbacher, associate professor in the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences’ School of Animal Sciences, revealed that companiable dogs housed together showed fewer signs of stress and were adopted more quickly than dogs that were housed by themselves.
Nearly 4 million dogs enter shelters every year, according to the American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals. The study’s findings offer one possible solution for animal shelters ...
Ancient Syrian diets resembled the modern “Mediterranean diet”
2024-06-12
Thousands of years ago, people in ancient Syria likely ate mostly grains, grapes, olives and a small amount of dairy and meat — similar to today’s “Mediterranean diet,” according to a study published June 12 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Benjamin T. Fuller from the University of Leuven, Belgium, Simone Riehl from the University of Tübingen, Germany, and colleagues.
Tell Tweini, an archeological site located near the Syrian coastal city of Jableh, contains relics dating ...
Greek Island was home to Bronze Age purple dye workshop
2024-06-12
The Greek island of Aegina was home to a Late Bronze Age purple dye workshop, according to a study published June 12, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Lydia Berger of Paris Lodron University of Salzburg, Austria and colleagues.
Colored dyes were a significant commodity in the Mediterranean region during the Late Bronze Age, and understanding the production of these dyes is valuable for interpretations of culture and trade at the time. In this study, Berger and colleagues describe the site of a purple dye workshop from the 16th century BC located at Aegina Kolonna in the Saronic Gulf.
The presence of a dye workshop at this site is inferred from three main lines of ...
Housing compatible shelter dogs together could reduce stress and might help them find homes sooner
2024-06-12
Housing compatible shelter dogs together could reduce stress and might help them find homes sooner
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0301137
Article Title: Effects of single- or pair-housing on the welfare of shelter dogs: Behavioral and physiological indicators
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The current research was funded by a grant to ENF from the Waltham Foundation (grant number) www.waltham.com. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to ...
When the TV show Neighbours ended, surveyed fans experienced strong grief, loss, and sometimes a lack of closure - implying that strong "parasocial" relationships link TV viewers and favorite shows
2024-06-12
When the TV show Neighbours ended, surveyed fans experienced strong grief, loss, and sometimes a lack of closure - implying that strong "parasocial" relationships link TV viewers and favorite shows
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0302160
Article Title: When TV neighbours become good friends: Understanding Neighbours fans’ feelings of grief and loss at the end of the series
Author Countries: Australia
Funding: The author received no ...
Some honeybees learn tasks better than others, and gene expression patterns in their brains may be associated with this difference in ability
2024-06-12
Some honeybees learn tasks better than others, and gene expression patterns in their brains may be associated with this difference in ability
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0304563
Article Title: Behavioral and genetic correlates of heterogeneity in learning performance in individual honeybees, Apis mellifera
Author Countries: Germany
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Incorporating “touch” into social media interactions can increase feelings of support and approval
2024-06-12
Including “tactile emoticons” into social media communications can enhance communication, according to a study published June 12, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Alkistis Saramandi and Yee Ki Au from University College London, United Kingdom, and colleagues.
Digital communications rely exclusively on visual and auditory cues (text, emoticons, videos, and music) to convey tone and emotion. Currently lacking from these platforms is touch, which can convey feelings of love and support, impact emotions, and influence behaviors. Technology companies are developing devices to incorporate touch into digital interactions, such as interactive kiss ...
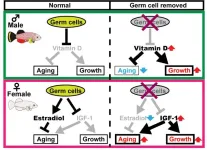
The gender gap in life expectancy: are eggs and sperm partly responsible?
2024-06-12
Osaka, Japan – Women live longer than men. This isn’t unique to humans, either; we see this trend in a wide range of other animals. Biologists have theorized that the discrepancy in life expectancy between sexes might be partly related to reproduction, but how?
In a study published in Science Advances, researchers from Osaka University have discovered for the first time that germ cells, the cells that develop into eggs in females and sperm in males, drive sex-dependent lifespan differences in vertebrate animals.
The researchers ...