(Press-News.org) Why are RMDs an issue for Europe?
RMDs, often dubbed 'the invisible diseases', affect approximately 120 million Europeans, constituting one in five individuals across the continent. Despite their prevalence, there remains a significant lack of awareness among policymakers and the general public, leading to their frequent neglect in political and financial agendas. However, the impact of RMDs is far-reaching, contributing to physical disability, chronic health conditions, and substantial economic burdens, amounting to an estimated 240 billion Euros annually.
Furthermore, RMDs not only pose a direct threat to individual health but also contribute to the development of high-mortality Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and mental health disorders. Alarmingly, RMDs represent over 50% of Years Lived with Disabilities (YLDs) in Europe and are responsible for approximately 38% of all occupational diseases.
A comprehensive RMD strategy addressing quality of care, research, and social policy
Recognising the gravity of this situation, EULAR calls upon the European Union and national governments to develop comprehensive RMD strategies. The EULAR 2024 - 2029 European Manifesto has already garnered support from multiple MEPs, who recognise the urgent need for action in addressing the challenges posed by RMDs, particularly in quality of care, research, and social policy.
The strategies developed should encompass various areas, including improving prevention, early diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation interventions for RMDs. EULAR advocates for prioritising RMDs within the EU's 'Healthier Together – NCD Initiative' and national NCD plans, as well as addressing the chronic shortage of rheumatologists and healthcare professionals specialised in rheumatology in order to improve standards of quality of care.
As RMDs can affect people of all ages throughout their lifespan, EULAR emphasises the importance of social policies aimed at mitigating the burden of RMDs on health-related quality of life, education, and employment. This includes recognising RMDs as a leading cause of disability, promoting inclusive and flexible education and workplaces, and increasing funding for improved mobility and accessibility measures.
In order to advance not just rheumatology, but the medical field as a whole, EULAR calls for the establishment of an ambitious research agenda targeting the causes, treatment, and multidisciplinary care models for RMDs. This includes launching a dedicated 'Inflammation, non-communicable diseases, and comorbidities' European Partnership under Horizon Europe and strengthening support for RMD-related European Reference Networks (ERNs).
Together, EULAR, its member organisations, and its partners are committed to driving forward a European response that prioritises the health and well-being of all citizens.
About EULAR
EULAR is the European umbrella organisation representing scientific societies, health professional associations and organisations for people with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs). EULAR aims to reduce the impact of RMDs on individuals and society, as well as improve RMD treatments, prevention, and rehabilitation. To this end, EULAR fosters excellence in rheumatology education and research, promotes the translation of research advances into daily care, and advocates for the recognition of the needs of those living with RMDs by EU institutions.
Contact
EULAR Communications, communications@eular.org
Notes to Editors
EULAR Recommendations
EULAR School of Rheumatology
EULAR Press Releases
END
Putting rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) at the forefront of the next European Union healthcare agenda
EULAR calls for a comprehensive European response to RMDs
2024-06-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Tackling issues in childhood arthritis
2024-06-14
Community awareness that children and young people get arthritis is low.1 This is associated with delays in diagnosis, worse clinical outcomes, and adverse societal factors such as stigma and isolation. Raising awareness of childhood arthritis is crucial in combatting these issues to improve the lives of those living with JIA. An abstract plenary session at the 2024 EULAR congress shared work from Juvenile Arthritis Research – a patient organisation in the UK that is involved in a variety of projects to raise awareness and support JIA patients and their families. These include a variety ...
Predictors for organ damage
2024-06-14
cSLE is a rare multisystem disorder with significant associated morbidity, but evidence-based guidelines are sparse, and as such management is often based on clinical expertise.2 The EULAR/ACR-2019 criteria have shown sensitivity in cSLE patients, which could allow earlier recognition of patients with single or major organ involvement,3 but identifying specific predictors in this vulnerable group is vital for preventing long-lasting damage.
The new work, presented at the 2024 EULAR congress, aimed ...
Osteoarthritis: associations and comorbidities
2024-06-14
In the 2023 update of their recommendations for osteoarthritis management, EULAR – The European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology – recognise osteoarthritis as a severe disease, and one with important implications for both the individual and society.3 However, most people with osteoarthritis do not receive optimal management,4,5 and this represents an important unmet need – especially when considering additional systemic comorbidities. To explore this further, ComOA6 has combined case-control and cohort studies for over 3 million people in primary care in the UK, Netherlands, Sweden, and Spain. The analyses – shared at ...
High-precision measurements challenge our understanding of Cepheids
2024-06-14
“Classical Cepheids” are a type of pulsating star that rhythmically brightens and dims over time. These pulsations help astronomers measure vast distances across space, which makes Cepheids crucial “standard candles” that help us understand the size and scale of our universe.
Despite their importance, studying Cepheids is challenging. Their pulsations and potential interactions with companion stars create complex patterns that are difficult to measure accurately. Different instruments and methods used over the years have led to inconsistent data, ...
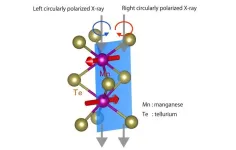
New approach to identifying altermagnetic materials
2024-06-14
Magnetic materials have traditionally been classified as either ferromagnetic, like the decorative magnets on iron refrigerator doors that are seemingly always magnetic, or antiferromagnetic, like two bar magnets placed end-to-end with opposite poles facing each other, canceling each other out so that the material has no net magnetism. However, there appears to be a third class of magnetic materials exhibiting what in 2022 was dubbed altermagnetism.
Microscopically, magnetism arises from a collection of tiny magnets associated with electrons, ...
Is magnesium the sleeping potion that enables sandhoppers to survive cold winters?
2024-06-14
Magnesium compounds are a common ingredient of many remedies designed to help people wind down and escape the stresses of modern life.
However, a new study has shown it is not only humans that are using forms of the chemical as a way to help them survive challenging conditions.
In tests conducted on beaches in Cornwall, and in the laboratory at the University of Plymouth, scientists confirmed the findings of previous studies which showed large sandhoppers (Talitrus saltator) increase the levels of magnesium ions in their bodies as temperatures fall. This slows them down so they are less active than they would be during the warmer months.
However, the new study has shown for the first time ...
Report highlights trajectory challenges for women in elite football
2024-06-14
Report highlights trajectory challenges for women in elite football
A new report commissioned by the Fédération Internationale de Football Association (FIFA) and Fédération Internationale des Associations de Footballeurs Professionnels (FIFPRO), undertaken by Edith Cowan University (ECU), surveyed footballers across 12 countries in six confederations. More than 700 players participated in the survey, with 71.5% classifying themselves as professional, with a further ...
How men can better support each other’s mental health
2024-06-14
Men are often urged to talk about their mental health with friends, but what does that involve?
This week, researchers from the Men’s Health Research Program at UBC introduced In Good Company, a website and podcast series aimed at answering precisely that question. The website provides practical advice for men seeking to make new connections, strengthen existing relationships and provide mutual support. The podcast series interviews men’s health experts and psychologists to explore the nuances and benefits of authentic male connection. Both ...
Low-sodium alternatives can lead to major health gains in Indonesia
2024-06-14
Excess sodium intake and a lack of potassium are major contributing factors towards high blood pressure in Indonesia, prompting calls for low-sodium potassium-rich salt substitutes (LSSS) to be readily available to improve health and curb health costs.
New Griffith University research has looked at the impact of switching out current table salt (100 per cent sodium chloride) with a low-sodium alternative in Indonesia.
Lead author Dr Leopold Aminde from the School of Medicine and Dentistry said the World Health Organisation has recommended a population-wide reduction in sodium consumption to tackle the burden of high blood pressure and ...
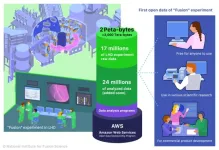
25 years of massive fusion energy experiment data completely open on the “cloud”, to be available to everyone
2024-06-14
Background
High-temperature fusion plasma experiments conducted in the Large Helical Device (LHD) of the National Institute for Fusion Science (NIFS), have renewed the world record for an acquired data amount, 0.92 terabytes (TB) per experiment, in February 2022, by using a full range of state-of-the-art plasma diagnostic devices*1. The International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER), which is currently under construction in France through the international collaboration of seven parties, is expected to generate ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Why conversation is more like a dance than an exchange of words
With Evo 2, AI can model and design the genetic code for all domains of life
Discovery of why only some early tumors survive could help catch and treat cancer at very earliest stages
Study reveals how gut bacteria and diet can reprogram fat to burn more energy
Mayo Clinic researchers link Parkinson's-related protein to faster Alzheimer's progression in women
Trends in metabolic and bariatric surgery use during the GLP-1 receptor agonist era
Loneliness, anxiety symptoms, depressive symptoms, and suicidal ideation in the all of us dataset
A decision-support system to personalize antidepressant treatment in major depressive disorder
Thunderstorms don’t just appear out of thin air - scientists' key finding to improve forecasting
Automated CT scan analysis could fast-track clinical assessments
New UNC Charlotte study reveals how just three molecules can launch gene-silencing condensates, organizing the epigenome and controlling stem cell differentiation
Oldest known bony fish fossils uncover early vertebrate evolution
High‑performance all‑solid‑state magnesium-air rechargeable battery enabled by metal-free nanoporous graphene
Improving data science education using interest‑matched examples and hands‑on data exercises
Sparkling water helps keep minds sharp during long esports sessions
Drone LiDAR surveys of abandoned roads reveal long-term debris supply driving debris-flow hazards
UGA Bioinformatics doctoral student selected for AIBS and SURA public policy fellowship
Gut microbiome connected with heart disease precursor
Nitrous oxide, a product of fertilizer use, may harm some soil bacteria
FAU lands $4.5M US Air Force T-1A Jayhawk flight simulator
SimTac: A physics-based simulator for vision-based tactile sensing with biomorphic structures
Preparing students to deal with ‘reality shock’ in the workplace
Researchers develop beating, 3D-printed heart model for surgical practice
Black soldier fly larvae show promise for safe organic waste removal
People with COPD commonly misuse medications
How periodontitis-linked bacteria accelerate osteoporosis-like bone loss through the gut
Understanding how cells take up and use isolated ‘powerhouses’ to restore energy function
Ten-point plan to deliver climate education unveiled by experts
Team led by UC San Diego researchers selected for prestigious global cancer prize
Study: Reported crop yield gains from breeding may be overstated
[Press-News.org] Putting rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) at the forefront of the next European Union healthcare agendaEULAR calls for a comprehensive European response to RMDs