(Press-News.org) A team of international researchers has revealed a new, simple clinical test to detect Calcium Release Deficiency Syndrome (CRDS), a life-threatening genetic arrhythmia that causes dangerously fast heartbeats and can lead to severe complications such as sudden cardiac arrest and death.
The new diagnostic method monitors for changes in electrocardiography (ECG) after a brief period of a fast heartbeat and a pause, which can occur naturally or be induced by artificially pacing the heart.
This research was co-led by Jason Roberts, a scientist at the Population Health Research Institute (PHRI), a joint institute of McMaster University and Hamilton Health Sciences, and Wayne Chen, a scientist and professor at the Libin Cardiovascular Institute and Hotchkiss Brain Institute at the University of Calgary's Cumming School of Medicine, and published on June 20, 2024, in JAMA.
While 60,000 cardiac arrests occur annually in Canada, CRDS remains undetectable with standard clinical tests, often resulting in the cardiac arrests being labeled as unexplained. This gap in understanding the underlying cause prevents the delivery of optimal care to survivors and vulnerable family members who may be affected by this genetic condition.
"This novel and simple diagnostic method, which can be performed using an electrocardiogram in a broad range of clinical settings, is hopefully an important step towards improving our evaluation of initially unexplained cardiac arrest (UCA)," said Roberts, co-principal investigator of the study.
Roberts and Chen led this multi-centre case-control study involving 68 study participants from 10 centres in seven countries. The participants were from four categories of heart conditions, including CRDS patients and UCA survivors. Accompanying studies from Chen’s lab revealed findings in genetic mouse models that mirrored those observed in humans. The mouse studies also provided insight into the underlying cellular mechanism responsible for this apparent ECG signature of CRDS.
"CRDS has been linked to many tragic incidents and heartbreaking stories affecting families. There have been numerous cases where patients experienced fainting episodes, but their tests showed no issues, which led doctors to believe the fainting was not due to a dangerous heart condition. A portion of these individuals, often young and otherwise healthy, subsequently suffered sudden cardiac arrests, and some did not survive," said Roberts.
“This raised many questions in the medical community, most of which remained unanswered until Chen and his team established the existence of this rare genetic syndrome in 2021. However, the diagnosis has required specialized laboratory testing available only in research settings, making it inaccessible to most physicians and limiting the ability to care for potentially affected patients and their families.”
The study marks the initial stage of Roberts and Chen's efforts in further exploring a diagnostic approach for CRDS and collecting additional data as part the ongoing PHRI DIAGNOSE CRDS trial. This trial represents a broader, international initiative aimed at strengthening their conclusions. Currently in the recruitment phase, DIAGNOSE CRDS aims to enroll 500 participants from 30 sites across 10 countries.
“We hope this test will help many families worldwide who have faced unexplained cardiac incidents or lost loved ones to them” added Roberts.
The team anticipates this simple pacing test will be incorporated into the routine diagnostic tests for initially unexplained cardiac arrest, providing hope for better outcomes and prevention of future tragedies.
“This is an important discovery because there is an urgent need for a clinical diagnostic test for CRDS,” says Chen. “This will allow us to identify individuals at risk, better understand the prevalence of CRDS and, hopefully, develop treatments for the condition.”
____________________________________________________________________
For an interview with Jason Roberts, please contact him at jason.roberts@phri.ca.
For an interview with Wayne Chen, please contact Kelly Johnston, senior communications specialist at the Cumming School of Medicine at kelly.johnston2@ucalgary.ca.
For further assistance or to obtain a copy of the embargoed study, please reach out to Adam Ward, media relations officer with McMaster University’s Faculty of Health Sciences, at warda17@mcmaster.ca
END
New, simple test detects rare fatal genetic heart condition
2024-06-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
YALE NEWS: Chemotherapy before surgery benefits some patients with pancreatic cancer
2024-06-20
New Haven, Conn. — Patients with pancreatic cancer who received chemotherapy both before and after surgery experienced longer survival rates than would be expected from surgery followed by chemotherapy, according to a new study from researchers at Yale Cancer Center (YCC) and Yale School of Medicine.
The study, published June 20 in JAMA Oncology, included patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), which accounts for 90% of pancreatic cancers. An aggressive cancer with a high mortality rate, PDAC is predicted ...
First conclusive evidence that a terrestrial leech species can jump
2024-06-20
A new study presents video evidence that at least one species of terrestrial leech can jump, behavior that scientists have debated for more than a century. Researchers from the American Museum of Natural History, Fordham University, and City University of New York (CUNY)’s Medgar Evers College published the footage and corresponding analysis today in the journal Biotropica.
“We believe this is the first convincing evidence that leeches can jump and do so with visible energy expenditure,” said lead author Mai Fahmy, a visiting scientist at the Museum and a postdoctoral researcher ...
Creation of a power-generating, gel electret-based device
2024-06-20
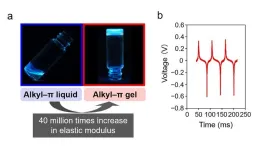
1. A team of researchers from NIMS, Hokkaido University and Meiji Pharmaceutical University has developed a gel electret capable of stably retaining a large electrostatic charge. The team then combined this gel with highly flexible electrodes to create a sensor capable of perceiving low-frequency vibrations (e.g., vibrations generated by human motion) and converting them into output voltage signals. This device may potentially be used as a wearable healthcare sensor.
2. Interest in the development of soft, lightweight, power-generating materials has been growing in recent years for use in soft electronics designed for various purposes, such as ...
How E. coli defends itself against antibiotics
2024-06-20
When E. coli detects damage to its genetic material, it sends out an SOS signal that alters activity inside the cells.
“The bacteria go into full emergency mode,” says PhD candidate Olaug Elisabeth Torheim Bergum at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU).
Imagine that you have a very sore throat. You're sick, your throat hurts, and a visit to the doctor confirms that the pain is due to a bacterial infection. You get a prescription for antibiotics, which quickly sorts out your sore throat. You are pleased that the treatment ...
Mental health leaders to gather for international summit on suicide prevention
2024-06-20
DETROIT (June 20, 2024)— Mental health experts from across the globe will gather to share insights, best practices, and innovations for preventing suicide during the 5th Zero Suicide International Summit June 24-25 in Liverpool, England.
Named for the innovative, evidence-based suicide intervention model developed at Henry Ford Health, the Zero Suicide International Summit is presented by the Detroit-based healthcare system in partnership with Zero Suicide Alliance (ZSA) and The Kevin and Margaret Hines Foundation.
The Zero Suicide model was developed at Henry Ford Health in 2001. Within a year of implementing the ...
Can AI learn like us?
2024-06-20
It reads. It talks. It collates mountains of data and recommends business decisions. Today’s artificial intelligence might seem more human than ever. However, AI still has several critical shortcomings.
“As impressive as ChatGPT and all these current AI technologies are, in terms of interacting with the physical world, they’re still very limited. Even in things they do, like solve math problems and write essays, they take billions and billions of training examples before they can do them well, " explains Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) NeuroAI Scholar Kyle Daruwalla.
Daruwalla ...
Changing climate will make home feel like somewhere else
2024-06-20
Changing climate will make home feel like somewhere else
Interactive app shows how climate change will make places around the world feel like they are closer to the equator
FROSTBURG, MD (June 20, 2024)—The impacts of climate change are being felt all over the world, but how will it impact how your hometown feels? An interactive web application from the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science allows users to search 40,581 places and 5,323 metro areas around the globe to match the expected future climate in each city with the current climate of another location, ...
Newly discovered dinosaur boasts big, blade-like horns
2024-06-20
What do you get when you cross Norse mythology with a 78-million-year-old ancestor to the Triceratops? Answer: Lokiceratops rangiformis, a plant-eating dinosaur with a very fancy set of horns.
The new dinosaur was identified and named by Colorado State University affiliate faculty member Joseph Sertich and University of Utah Professor Mark Loewen. The dinosaur’s name, announced today in the scientific journal PeerJ, translates roughly to “Loki’s horned face that looks like a caribou.”
Loewen and Sertich, co-lead authors of the PeerJ study, dubbed the new species Lokiceratops (lo-Kee-sare-a-tops) ...
Exploring the relationship between civilians and military organizations through an experiment in Japan
2024-06-20
In democracies where civilian control is followed, the power to make crucial decisions, like those of national security, is mainly exercised by elected officials, allowing the citizens who elect them to influence such decisions indirectly. This role can give people a sense of participation in matters of national importance, potentially associated with their political trust. The military, in such cases, advises and helps these elected leaders in serving the nation, rather than assuming leadership itself. A balance between civilians and military organizations is, therefore, crucial for any democracy to thrive, and it is pointed out that civilian control is a requisite of democracy.
Existing ...
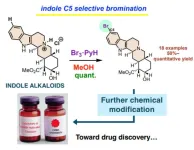
A simple, fast, and versatile method for selective bromination of indole alkaloids
2024-06-20
Indolo[2,3-a]quinolizidine is a common structural motif in various natural products. Its molecular structure contains the indole ring, a functional group in tryptophan. Tryptophan, an essential amino acid, is required for the production and maintenance of our body’s proteins, muscles, enzymes, and neurotransmitters. Many natural products are derived from it. Over 3,000 monoterpene indole alkaloids (MTIAs), which are natural products consisting of indole rings, have been found in plants, and some of them have been used as medicines. For example, vinblastine has been used as an anticancer drug, and reserpine is used to treat high blood pressure.
The ...