(Press-News.org) The discovery of a new, ancient, predatory reptile dubbed Parvosuchus aurelioi — part of a group of crocodile-like reptiles called pseudosuchians — in Brazil is described in a paper in Scientific Reports. The specimen, which dates to approximately 237 million years ago, during the Middle-Late Triassic, is the first small predatory reptile of its kind to be found in this country.
Prior to the dominance of the dinosaurs, pseudosuchians were a common form of ancient quadruped reptile during the Triassic Period (252 – 201 million years ago), with some species amongst the largest carnivores of the time. Smaller pseudosuchians known as gracilisuchids lived alongside these apex predators and have been found in areas such as China and Argentina.
Now, Rodrigo Müller reports the discovery of a new species of gracilisuchid based on a specimen found in the Santa Maria Formation in Brazil. The partial skeleton dates to approximately 237 million years ago and consists of a complete skull including the lower jaw, 11 dorsal vertebrae, a pelvis, and partially preserved limbs. The author names the new species Parvosuchus aurelioi which derives from ‘parvus’ (small) and ‘suchus’ (crocodile) and honours the amateur palaeontologist Pedro Lucas Porcela Aurélio, who discovered the fossil materials.
The skull measures 14.4 centimetres in length and features long slender jaws with pointed teeth that curved backwards, and several skull openings. The skeleton is lightly built and estimated to be less than one metre long in total length. These features classify P. aurelioi as a gracilisuchid, which makes it the first species from this group to be confirmed in Brazil, according to the author. This finding highlights the diversity among pseudosuchians in the Triassic, he adds.
END
Palaeontology: New, small, ancient crocodile-like reptile described in Brazil
2024-06-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Prenatal maternal psychological distress during the pandemic and newborn brain development
2024-06-20
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that increased maternal mental health symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic are associated with subsequent changes in regional brain growth in newborn offspring.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Nickie Andescavage, M.D., email nniforat@childrensnational.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.17924)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
Healthy lifestyle and the likelihood of becoming a centenarian
2024-06-20
About The Study: In this case-control study of Chinese older adults, adhering to a healthy lifestyle appears to be important even at late ages, suggesting that constructing strategic plans to improve lifestyle behaviors among all older adults may play a key role in promoting healthy aging and longevity.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Xiang Gao, M.D., Ph.D. (xiang_gao@fudan.edu.cn) and Xiaoming Shi, M.D., Ph.D. (shixm@chinacdc.cn).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.17931)
Editor’s Note: Please see ...
New, simple test detects rare fatal genetic heart condition
2024-06-20
A team of international researchers has revealed a new, simple clinical test to detect Calcium Release Deficiency Syndrome (CRDS), a life-threatening genetic arrhythmia that causes dangerously fast heartbeats and can lead to severe complications such as sudden cardiac arrest and death.
The new diagnostic method monitors for changes in electrocardiography (ECG) after a brief period of a fast heartbeat and a pause, which can occur naturally or be induced by artificially pacing the heart.
This research was co-led by Jason Roberts, a scientist at the Population ...
YALE NEWS: Chemotherapy before surgery benefits some patients with pancreatic cancer
2024-06-20
New Haven, Conn. — Patients with pancreatic cancer who received chemotherapy both before and after surgery experienced longer survival rates than would be expected from surgery followed by chemotherapy, according to a new study from researchers at Yale Cancer Center (YCC) and Yale School of Medicine.
The study, published June 20 in JAMA Oncology, included patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), which accounts for 90% of pancreatic cancers. An aggressive cancer with a high mortality rate, PDAC is predicted ...
First conclusive evidence that a terrestrial leech species can jump
2024-06-20
A new study presents video evidence that at least one species of terrestrial leech can jump, behavior that scientists have debated for more than a century. Researchers from the American Museum of Natural History, Fordham University, and City University of New York (CUNY)’s Medgar Evers College published the footage and corresponding analysis today in the journal Biotropica.
“We believe this is the first convincing evidence that leeches can jump and do so with visible energy expenditure,” said lead author Mai Fahmy, a visiting scientist at the Museum and a postdoctoral researcher ...
Creation of a power-generating, gel electret-based device
2024-06-20
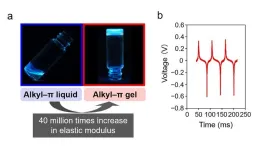
1. A team of researchers from NIMS, Hokkaido University and Meiji Pharmaceutical University has developed a gel electret capable of stably retaining a large electrostatic charge. The team then combined this gel with highly flexible electrodes to create a sensor capable of perceiving low-frequency vibrations (e.g., vibrations generated by human motion) and converting them into output voltage signals. This device may potentially be used as a wearable healthcare sensor.
2. Interest in the development of soft, lightweight, power-generating materials has been growing in recent years for use in soft electronics designed for various purposes, such as ...
How E. coli defends itself against antibiotics
2024-06-20
When E. coli detects damage to its genetic material, it sends out an SOS signal that alters activity inside the cells.
“The bacteria go into full emergency mode,” says PhD candidate Olaug Elisabeth Torheim Bergum at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU).
Imagine that you have a very sore throat. You're sick, your throat hurts, and a visit to the doctor confirms that the pain is due to a bacterial infection. You get a prescription for antibiotics, which quickly sorts out your sore throat. You are pleased that the treatment ...
Mental health leaders to gather for international summit on suicide prevention
2024-06-20
DETROIT (June 20, 2024)— Mental health experts from across the globe will gather to share insights, best practices, and innovations for preventing suicide during the 5th Zero Suicide International Summit June 24-25 in Liverpool, England.
Named for the innovative, evidence-based suicide intervention model developed at Henry Ford Health, the Zero Suicide International Summit is presented by the Detroit-based healthcare system in partnership with Zero Suicide Alliance (ZSA) and The Kevin and Margaret Hines Foundation.
The Zero Suicide model was developed at Henry Ford Health in 2001. Within a year of implementing the ...
Can AI learn like us?
2024-06-20
It reads. It talks. It collates mountains of data and recommends business decisions. Today’s artificial intelligence might seem more human than ever. However, AI still has several critical shortcomings.
“As impressive as ChatGPT and all these current AI technologies are, in terms of interacting with the physical world, they’re still very limited. Even in things they do, like solve math problems and write essays, they take billions and billions of training examples before they can do them well, " explains Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) NeuroAI Scholar Kyle Daruwalla.
Daruwalla ...
Changing climate will make home feel like somewhere else
2024-06-20
Changing climate will make home feel like somewhere else
Interactive app shows how climate change will make places around the world feel like they are closer to the equator
FROSTBURG, MD (June 20, 2024)—The impacts of climate change are being felt all over the world, but how will it impact how your hometown feels? An interactive web application from the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science allows users to search 40,581 places and 5,323 metro areas around the globe to match the expected future climate in each city with the current climate of another location, ...