(Press-News.org) A researcher at the University of Missouri has developed a program that improves the quality of care and reduces avoidable hospitalizations in nursing homes — saving Missouri nursing homes and Medicare millions of dollars and allowing Missouri nursing homes to invest more in retaining their most skilled staff members. The program is so successful that it’s being recommended for use in all 50 states.
The Quality Improvement Program for Missouri (QIPMO) was created by Marilyn Rantz in 1999 as a partnership between Mizzou’s Sinclair School of Nursing and the Missouri Department of Health and Senior Services.
For the past 25 years, the program has allowed Rantz and her team of experts to meet with the staff and administrators of hundreds of nursing homes throughout Missouri, providing them with strategies to detect illnesses earlier, control the spread of infections and improve all parts of the quality of care they provide.
A new study confirms what Rantz has long known — the QIPMO program works.
The study, which was recently published in the Journal of the American Medical Directors Association, evaluated all 510 Missouri nursing homes that received free services through the QIPMO program from 2020 to 2022. It tracked the number of issues related to various quality measures such as urinary tract infections, high-risk pressure ulcers, antipsychotic use, emergency room visits and hospitalizations, among others.
“The data gets deep into the nitty-gritty details, but the key takeaway is that every single nursing home that received our QIPMO services saw overall improvement,” said Rantz, a Curators’ Distinguished Professor Emerita who has worked in and with the nursing industry for nearly 55 years. “Whether it’s infection control practices, disinfecting procedures in common spaces, education regarding hand-washing or noticing if something seems off with a resident’s behavior, ensuring these evidence-based best practices are being followed around the clock is key. The program has helped improve hundreds — if not thousands — of lives.”
From mid-MO to nationwide
The coronavirus pandemic exposed many issues that U.S. nursing homes have been dealing with for decades, including staffing shortages, underpaid staff and a lack of personalized care. In response, the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine selected Rantz to join a committee of nursing home experts nationwide, recognizing her expertise in improving the quality of care in nursing homes.
In 2022, the committee released a national report providing recommendations to the U.S. Congress and nursing home associations for improving the quality of care in nursing homes throughout the country. Among the recommendations is for quality improvement programs that have a proven track record of success — such as QIPMO — to be emulated in all 50 states nationwide.
“Our work at Mizzou and with the Missouri Department of Health and Senior Services has set the standard in terms of raising the bar for nursing home care statewide,” Rantz said. “Now, it is time to get these best practices implemented across the country.”
“Longitudinal evaluation of a statewide quality improvement program for nursing homes,” was published in the Journal of the American Medical Directors Association.
A living legend
Rantz began her nursing career in 1970. By 1981, she became a nursing home administrator in Wisconsin, leading a staff of more than 400 people and overseeing a 300-bed nursing home.
In her more than 30 years working at Mizzou, Rantz has earned $108 million in total grants, authored or co-authored 250 published research studies and was inducted into the National Academy of Medicine in 2012. She is one of the reasons why Mizzou has seen 10 consecutive years of growth in research expenditures.
In 2020, Rantz was honored as a ‘Living Legend’ by the American Academy of Nursing for her dedicated commitment to improving the quality of care in nursing homes.
END
Leading the way in nursing home care
Mizzou researcher Marilyn Rantz has dedicated her life to improving the quality of care in nursing homes. The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine say her efforts should be emulated nationwide
2024-06-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Exploring early stage Alzheimer’s disease
2024-06-24
Research in nonhuman primates is opening the possibility of testing treatments for the early stages of Alzheimer’s and similar diseases, before extensive brain cell death and dementia set in. A study published June 21 in Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association shows up to a six-month window in which disease progress could be tracked and treatments tested in rhesus macaques.
“This is a very powerful translational model to test interventions that target the tau protein,” said John H. ...
University of Cincinnati study: Signaling pathway in brain helps maintain balance, prevent cognitive deficit
2024-06-24
A new study led by University of Cincinnati researchers sheds new light on the role of a signaling pathway in the brain to maintain health and prevent inflammation and cognitive deficits.
UC’s Agnes (Yu) Luo, PhD, is corresponding author on the research, published June 21 in the journal Nature Communications, and focused on a signaling pathway called TGF-β that plays a number of roles depending on where it is located in the body.
Luo explained that signaling pathways in the body control different cell functions and require two components: a type of molecule called a ligand and a receptor that the ligand binds to and ...
Bank statements reveal clues to excessive spending and cognitive decline
2024-06-24
DETROIT -- Early memory loss has been linked to wealth loss, but research has mostly focused on investments. Four years ago, clinical geropsychologist Peter Lichtenberg, Ph.D., wondered what clues might be found in an older person’s financial decisions to indicate their vulnerability to financial victimization. Lichtenberg is director of the Institute of Gerontology at Wayne State University and a national expert in the financial exploitation of older adults. The results of his curiosity have now been published as “The WALLET Study: Financial ...
Even very small amounts of elements in follicular fluid may impact IVF success rates, according to new study from George Mason University researcher
2024-06-24
Though exposure to “trace” (an extremely small amount) elements has been shown to affect ovarian functions in experimental studies, there has been little research on the impact of trace levels of non-essential elements, such as lead (Pb) and mercury (Hg), on female reproduction. Studies have shown that high levels of these non-essential elements may lead to decreased female fertility and reduce the likelihood of getting pregnant. Taken together, this evidence raises concern about the potential negative impact of exposure ...
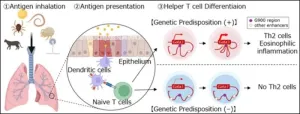
Study elucidates role of “G900” gene enhancers in asthma-associated inflammation
2024-06-24
Asthma patients experience respiratory distress due to allergens like house dust mites or pollen. However, the various triggers for asthma share a common pathway involving the release of proteins called type-2 cytokines by Type-2 helper T (Th2) cells and group-2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s). Both Th2 and ILC2 require high amounts of GATA-binding protein 3 (GATA3) for their maturation.
Specific gene sequences called enhancers are responsible for elevating the expression of GATA3 genes in humans. Studies have found that by controlling the production of GATA3, enhancers influence the development of Th2 and ILC2. The gene region G900, located close to ...
Secrets of drop stains unveiled: New FSU research decodes chemical composition from simple photos
2024-06-24
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. — Imagine zooming in on a dried drop of salt solution — each pattern a unique masterpiece, reminiscent of abstract art, yet no larger than the size of a penny.
New research by scientists in the Florida State University Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry uses the patterns formed by a dried salt solution to train a machine learning algorithm that can identify the chemical composition of different salts. The work will be published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“We are taking chemical fingerprints ...
New computational model of real neurons could lead to better AI
2024-06-24
Nearly all the neural networks that power modern artificial intelligence tools such as ChatGPT are based on a 1960s-era computational model of a living neuron. A new model developed at the Flatiron Institute’s Center for Computational Neuroscience (CCN) suggests that this decades-old approximation doesn’t capture all the computational abilities that real neurons possess and that this older model is potentially holding back AI development.
The new model developed at CCN posits that individual neurons exert more control over their surroundings than previously thought. The updated neuron model could ultimately lead to more powerful artificial neural ...
AI matches protein interaction partners
2024-06-24
Proteins are the building blocks of life, involved in virtually every biological process. Understanding how proteins interact with each other is crucial for deciphering the complexities of cellular functions, and has significant implications for drug development and the treatment of diseases.
However, predicting which proteins bind together has been a challenging aspect of computational biology, primarily due to the vast diversity and complexity of protein structures. But a new study from the group of Anne-Florence Bitbol at EPFL might now change all that.
The team of scientists, ...
Navigating the labyrinth: How AI tackles complex data sampling
2024-06-24
The world of artificial intelligence (AI) has recently seen significant advancements in generative models, a type of machine-learning algorithms that “learn” patterns from set of data in order to generate new, similar sets of data. Generative models are often used for things like drawing images and natural language generation – a famous example are the models used to develop chatGPT.
Generative models have had remarkable success in various applications, from image and video generation to composing music and to language modeling. The problem ...
Hydrothermal vents on seafloors of ‘ocean worlds’ could support life, new study says
2024-06-24
We’ve all seen the surreal footage in nature documentaries showing hydrothermal vents on the frigid ocean floor—bellowing black plumes of super-hot water—and the life forms that cling to them. Now, a new study by UC Santa Cruz researchers suggests that lower-temperature vents, which are common across Earth's seafloor, may help to create life-supporting conditions on "ocean worlds" in our solar system.
Ocean worlds are planets and moons that have—or had in the past—a liquid ocean, often under an icy shell or within their rocky interior. In Earth's solar system, several of Jupiter's and Saturn's moons are ocean worlds, and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
[Press-News.org] Leading the way in nursing home careMizzou researcher Marilyn Rantz has dedicated her life to improving the quality of care in nursing homes. The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine say her efforts should be emulated nationwide