(Press-News.org) In 2018, Arthur Ashkin won the Nobel Prize in Physics for inventing optical tweezers: laser beams that can be used to manipulate microscopic particles. While useful for many biological applications, optical tweezers require extremely controlled, static conditions to work properly.
“Optical tweezers work by creating a light ‘hotspot’ to trap particles, like a ball falling into a hole. But if there are other objects in the vicinity, this hole is difficult to create and move around,” says Romain Fleury, head of the Laboratory of Wave Engineering in EPFL’s School of Engineering.
Fleury and postdoctoral researchers Bakhtiyar Orazbayev and Matthieu Malléjac have spent the last four years trying to move objects in uncontrolled, dynamic environments using soundwaves. In fact, the team’s method – wave momentum shaping – is entirely indifferent to an object’s environment or even its physical properties. All the information that’s required is the object’s position, and the soundwaves do the rest.
“In our experiments, instead of trapping objects, we gently pushed them around, as you might guide a puck with a hockey stick,” Fleury explains.
The unconventional method, funded by the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) Spark program, has been published in Nature Physics in collaboration with researchers from the University of Bordeaux in France, Nazarbayev University in Kazakhstan, and the Vienna University of Technology in Austria.
Very simple, very promising
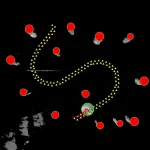
If soundwaves are the hockey stick in Fleury’s analogy, then a floating object like a ping-pong ball is the puck. In the lab’s experiments, the ball was floating on the surface of a large tank of water, and its position was captured by an overhead camera. Audible soundwaves emitted from a speaker array at either end of the tank directed the ball along a pre-determined path, while a second array of microphones ‘listened’ to the feedback, called a scattering matrix, as it bounced off of the moving ball. This scattering matrix, combined with the camera’s positional data, allowed the researchers to calculate in real time the optimal momentum of the soundwaves as they nudged the ball along its path.
“The method is rooted in momentum conservation, which makes it extremely simple and general, and that’s why it’s so promising,” Fleury says.
He adds that wave momentum shaping is inspired by the optical technique of wavefront shaping, which is used to focus scattered light, but this is the first application of the concept to moving an object. What’s more, the team’s method is not limited to moving spherical objects along a path: they also used it to control rotations, and to move more complex floaters like an origami lotus.
Mimicking conditions inside the body
Once the scientists succeeded in guiding a ping-pong ball, they performed additional experiments with both stationary and moving obstacles designed to add inhomogeneity to the system. Successfully navigating the ball around these scattering objects demonstrated that wave momentum shaping could perform well even in dynamic, uncontrolled environments like a human body. Fleury adds that sound is a particularly promising tool for biomedical applications, as it is harmless and noninvasive.
“Some drug delivery methods already use soundwaves to release encapsulated drugs, so this technique is especially attractive for pushing a drug directly toward tumor cells, for example.”
The method could also be a game-changer for biological analysis or tissue engineering applications where manipulating cells by touching them would cause damage or contamination. Fleury also sees 3D printing applications for wave momentum shaping, for example to arrange microscopic particles before solidifying them into an object.
Ultimately, the researchers believe their method could also work using light, but their next goal is to take their sound-based experiments from the macro- to micro-scale. They have already received SNSF funding to do experiments under a microscope, using ultrasonic waves to move cells around.
END
Moving objects precisely with sound
EPFL researchers have succeeded in directing floating objects around an aquatic obstacle course using only soundwaves. Their novel, optics-inspired method holds great promise for biomedical applications such as noninvasive targeted drug delivery.
2024-06-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sustainable electrification: Managing resource demands for future electric vehicles
2024-06-25
With goals to limit CO2 emissions, many countries have set targets to phase out internal combustion vehicles in favor of electric vehicles (EVs). Japan has set a target for 20-30% of all car sales to be battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), and 30-40% of car sales to be hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) by 2030. The USA plans for 50% of new vehicles to be zero-emission by 2030, while Germany wants to have 15 million EVs on the road by 2030. These goals raise concerns about the raw material demand for EVs. Batteries, which account for 50% of all resources consumed in BEV production, require ...
New AI program from BU researchers could predict likelihood of Alzheimer’s disease
2024-06-25
Trying to figure out whether someone has Alzheimer’s disease usually involves a battery of assessments—interviews, brain imaging, blood and cerebrospinal fluid tests. But, by then, it’s probably already too late: memories have started slipping away, long established personality traits have begun subtly shifting. If caught early, new pioneering treatments can slow the disease’s remorseless progression, but there’s no surefire way to predict who will develop the dementia associated with Alzheimer’s.
Now, Boston University researchers say they have designed a promising new artificial ...
Telltale greenhouse gases could signal alien activity
2024-06-25
If aliens modified a planet in their solar system to make it warmer, we’d be able to tell. A new UC Riverside study identifies the artificial greenhouse gases that would be giveaways of a terraformed planet.
A terraformed planet has been artificially made hospitable for life. The gases described in the study would be detectable even at relatively low concentrations in the atmospheres of planets outside our solar system using existing technology. This could include the James Webb Space Telescope, or a future European-led space telescope concept.
And ...
New study unveils formation secrets of tiny rare earth elements
2024-06-25
Researchers from Trinity College Dublin’s School of Natural Sciences have revealed a novel route to the formation of bastnäsite, a crucial mineral for the extraction of rare earth elements (REEs). Their work offers promise in one day making the extraction of these REEs more efficient.
The study – published today in the journal Nanoscale – uncovers for first time how fluocerite, a rare mineral, quickly forms and transforms into bastnäsite. The occurrence and origin of fluocerite in natural deposits was not fully understood, ...
DOE awards Sandia small business program and local veteran
2024-06-25
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — The Department of Energy has once again awarded Sandia National Laboratories for its work helping small businesses. One of those businesses, owned by a disabled veteran, was also awarded for its extraordinary work.
DOE Mentor of the Year
Sandia’s small business Mentor-Protégé Program has been named as DOE Mentor of the year, an award it has received for three consecutive years.
Now in its fifth year, the program has mentored five protégés from around the country. More than 150 volunteer mentors and support personnel help these small and disadvantaged businesses grow, succeed and navigate doing business ...
Family, friends can be more effective health role models than celebrities
2024-06-25
PULLMAN, Wash. – Your mom might be a better health influencer than Dwayne “The Rock” Johnson.
Adults in a study who said they looked to a person they knew as role model for good health—such as a friend, relative or healthcare provider—rather than a celebrity, had greater motivation to reach their health goals. The women participants were also more likely than men to choose a personal role model rather than a celebrity. And the person most often named was their own mother.
“We know that parents have a huge influence on shaping people’s health trajectories throughout their life just ...
Australia’s giant lizards help save sheep from being eaten alive
2024-06-25
Giant lizards called heath goannas could save Australian sheep farmers millions of dollars a year by keeping blowfly numbers down - and must be prioritised in conservation schemes to boost native wildlife, say researchers.
A study led by the University of Cambridge has found that heath goannas - a species of giant, scavenging lizard - act as natural clean-up crews by clearing maggot-ridden animal carcasses from the landscape.
This reduces the emergence of blowflies, which attack sheep by laying eggs on their backsides that hatch into flesh-eating maggots. The disease, known as ‘fly strike’, costs the Australian sheep farming industry an estimated $280 million a year.
This ...
New tipping point discovered beneath the Antarctic ice sheet
2024-06-25
This process is currently not included in models that predict sea level rise, so the new results could offer a more accurate picture of how the world will change with global warming and how much coastal areas will need to adapt.
Carried out by scientists at the British Antarctic Survey (BAS), the findings are published in the journal Nature Geoscience.
“We have identified the possibility of a new tipping-point in Antarctic ice sheet melting,” says Alex Bradley, an ice dynamics researcher ...
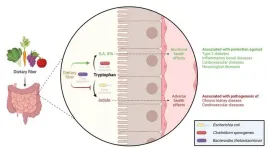
Dietary fibers make our gut bacteria behave healthy
2024-06-25
We get healthy dietary fibres from consuming fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. But why are the fibres so good for us? A team of researchers has discovered that dietary fibres play a crucial role in determining the balance between the production of healthy and harmful substances by influencing the behaviour of bacteria in the colon.
Dietary fibres benefit our health, and scientists from DTU National Food Institute and the Department of Nutrition, Exercise and Sports at the University of Copenhagen have now uncovered an essential part of why this is the case. Different types of bacteria inside our colon compete to utilize an essential amino acid called tryptophan. This competition ...
Study links gut microbiome changes to increased risk of type 2 diabetes
2024-06-25
The largest and most ethnically and geographically comprehensive investigation to date of the gut microbiome of people with type 2 diabetes (T2D), prediabetes, and healthy glucose status has found that specific viruses and genetic variants within bacteria correspond with changes in gut microbiome function and T2D risk. Results of the study—which represents a collaboration across Brigham and Women’s Hospital (a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system), the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, and Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health—are published in Nature Medicine.
"The microbiome is highly variable across different geographic ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
Accounting for soil saturation enhances atmospheric river flood warnings
The research that got sick veterans treatment
Study finds that on-demand wage access boosts savings and financial engagement for low-wage workers
Antarctica has lost 10 times the size of Greater Los Angeles in ice over 30 years
Scared of spiders? The real horror story is a world without them
New study moves nanomedicine one step closer to better and safer drug delivery
Illinois team tests the costs, benefits of agrivoltaics across the Midwest
Highly stable self-rectifying memristor arrays: Enabling reliable neuromorphic computing via multi-state regulation
Composite superionic electrolytes for pressure-less solid-state batteries achieved by continuously perpendicularly aligned 2D pathways
Exploring why some people may prefer alcohol over other rewards
How expectations about artificial sweeteners may affect their taste
Ultrasound AI receives FDA De Novo clearance for delivery date AI technology
Amino acid residue-driven nanoparticle targeting of protein cavities beyond size complementarity
New AI algorithm enables scientific monitoring of "blue tears"
Insufficient sleep among US adolescents across behavioral risk groups
Long COVID and recovery among US adults
Trends in poverty and birth outcomes in the US
Heterogeneity of treatment effects of GLP-1 RAs for weight loss in adults
Within-person association between daily screen use and sleep in youth
Low-dose lithium for mild cognitive impairment
Catheter ablation and oral anticoagulation for secondary stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation
A new theory of brain development
Pilot clinical trial suggests low dose lithium may slow verbal memory decline
[Press-News.org] Moving objects precisely with soundEPFL researchers have succeeded in directing floating objects around an aquatic obstacle course using only soundwaves. Their novel, optics-inspired method holds great promise for biomedical applications such as noninvasive targeted drug delivery.