A new breakthrough in understanding regeneration in a marine worm
2024-07-02
(Press-News.org)
The sea worm Platynereis dumerilii is only a few centimetres long but has a remarkable ability: in just a few days, it can regenerate entire parts of its body after an injury or amputation. By focusing more specifically on the mechanisms at play in the regeneration of this worm’s tail, a research team led by a CNRS scientist1 has observed that gut cells play a role in the regeneration of the intestine as well as other tissues such as muscle and epidermis. Even more surprising, the team found that this ability of gut cells to regenerate other tissue varies according to their location: the closer they are to the posterior end of the worm, the greater the variety of cell types they can rebuild2. This study will appear in Development on 2 July.
Scientists carried out these observations by monitoring the outcome of gut cells and proliferative cells that form close to the amputated end of the worm. This was tracked using different markers in particular by fluorescent beads ingested by the worms. Annelids, or ‘segmented worms’, which have only been studied in the last 20 years, are an ideal model for the study of regeneration, a process that is widespread in animals but still mysterious for scientists.
The research team will continue this work to determine whether cell types, other than gut cells, can play a role in regenerating a variety of cell types.
Notes
1 - Working at the Institut Jacques Monod (CNRS/Université Paris Cité). Scientists at Inserm and Université Paris Cité also contributed to this research.
2 - Only cells involved in the nervous system and growth zone of the worm (a ring of stem cells involved in the continuous growth of the animal until it reaches sexual maturity) cannot, it appears, be generated by gut cells found in the posterior end of the worm.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-07-02
Genoa (Italy)/Grenoble (France) – 2nd July, 2024 - The correct functioning of cells relies heavily on the ability to finely control gene expression, a complex process by which the information contained in DNA is copied into RNA to eventually give rise to all the proteins and most of the regulatory molecules in the cell. If DNA can be imagined as a dense technical manual, gene expression is the method by which the cell extracts useful information from it.
Researchers at the Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT) in Genoa and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in ...
2024-07-02
Like most primates, humans are remarkably touchy-feely. Starved of touch, we release more of the stress hormone cortisol, which causes the immune system to be down-regulated and the heart rate and blood pressure to go up. On the other hand, touch causes the brain to be flooded by natural opioids, the ‘bonding hormone’ oxytocin, and the ‘feel-good’ neurotransmitters dopamine and serotonin.
It is generally assumed that our sense of touch worsens with age, just like our vision and sense of hearing. However, new results are good news for those who wished they could stave off age-related decline forever: they show for the first time that a deterioration ...
2024-07-02
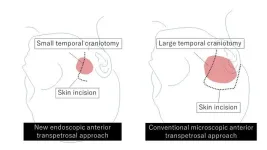
Tumors arising in the base of the skull are among the most difficult to remove in neurosurgery. The current treatment method is to perform surgical removal by what is known as the microscopic anterior transpetrosal approach (ATPA). Seeking to lessen the risk of damage and postoperative complications, as the skull base is densely packed with nerves, blood vessels, and other tissues, not to mention the brain stem, an Osaka Metropolitan University medical research team is taking a new approach.
Led by Dr. Hiroki Morisako, a lecturer in ...
2024-07-02
Transgender, nonbinary, and gender-diverse people face barriers to accessing surgery and to the health system in general, describe authors in two new research papers published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
In many areas of life, people who identify as transgender, nonbinary, and gender diverse experience discrimination even where there are laws to protect transgender human rights. Health systems also pose barriers for transgender, nonbinary, and gender-diverse people, who are more likely to delay obtaining ...
2024-07-02
Extreme weather events such as hurricanes and storms have increased in both frequency and severity in recent years.
With that has come heightened public interest, resulting in often dramatic footage being live-streamed on platforms such as YouTube, TikTok and Discord.
Now, a new study conducted at the University of Plymouth has for the first time analysed what might be motivating people to watch these streams – in some instances for up to 12 hours at a time.
The research centred around the live-streaming ...
2024-07-02
A new study of coral reefs in Papua New Guinea shows ocean acidification simplifies coral structure, making crucial habitat less appealing to certain fish species.
While much media attention has focused on heat stress-induced coral bleaching, this finding, by a University of Adelaide research team led by Professor Ivan Nagelkerken, adds nuance to concerns about how global warming affects coral reefs.
Ocean acidification is caused by an increase in the level of carbon dioxide in oceanwater, leading to a reduction in pH. This makes calcium carbonate less available in the ocean, which corals use to build and repair their skeleton.
Professor Nagelkerken and ...
2024-07-02
Athletes and sporting teams have frequently used the Olympics and other sporting events to make political statements through boycotts and protests. Ahead of the Paris Olympics kicking off this month and amidst the current UEFA (Union of European Football Associations) European Football Championship (Euro 2024), researchers are asking – should sport be a platform for promoting social justice issues?
The 2024 Paris Olympics, like the Euro 2024 soccer tournament, will be watched by billions of people and command media attention around the globe. ...
2024-07-02
A research team of Professor Yoontae Lee and Jiho Park, a PhD candidate, from the Department of Life Sciences at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) recently discovered that a particular protein promotes the development of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The study was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS), one of the world's most-cited multidisciplinary scientific journal.
B cells, components of the body's ...
2024-07-02
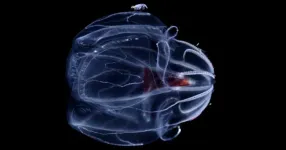
A multi-institutional team that includes researchers from the University of Delaware, University of California San Diego and Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute (MBARI), among others, published a paper in Science on Thursday, June 27, that provides new insight on how deep-sea “comb jellies” called ctenophores adapt and survive at extreme pressures.
It turns out that part of the adaptation involves lipids, fatty chemical compounds found in the membrane of all living cells that perform essential functions, including storing energy, sending signals and controlling what passes through ...
2024-07-02
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) tells staff leaving for industry jobs that, despite restrictions on post-employment lobbying, they are still permitted to influence the agency, reveals an investigation by The BMJ today.
Internal emails, obtained under a freedom of information request, show how two FDA officials who worked on covid-19 vaccine approvals were proactively informed by FDA ethics staff about their ability to indirectly lobby the agency as they left for jobs with Moderna.
The record shows that since 2000 every FDA commissioner, the agency’s highest position, has gone on to work ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A new breakthrough in understanding regeneration in a marine worm