(Press-News.org) Two for two! A duo of interacting galaxies commemorates the second science anniversary of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, which takes constant observations, including images and highly detailed data known as spectra. Its operations have led to a “parade” of discoveries by astronomers around the world.
“Since President Biden and Vice President Harris unveiled the first image from the James Webb Space Telescope two years ago, Webb has continued to unlock the mysteries of the universe,” said NASA Administrator Bill Nelson. “With remarkable images from the corners of the cosmos, going back nearly to the beginning of time, Webb’s capabilities are shedding new light on our celestial surroundings and inspiring future generations of scientists, astronomers, and explorers.”
Also take a moment to scan the background. Webb’s image is overflowing with distant galaxies. Some take spiral and oval shapes, like those threaded throughout the Penguin’s “tail feathers,” while others scattered throughout are shapeless dots. This is a testament to the sensitivity and resolution of the telescope’s infrared instruments. (Compare Webb’s view to the 2018 observation that combines infrared light from NASA’s retired Spitzer Space Telescope and near-infrared and visible light from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope.) Even though these observations only took a few hours, Webb revealed far more distant, redder, and dustier galaxies than previous telescopes – one more reason to expect Webb to continue to expand our understanding of everything in the universe.
Want more? Take a tour to the image, “fly through” it in a visualization, and compare Webb’s image to the Hubble Space Telescope’s.
Arp 142 lies 326 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Hydra.
“In just two years, Webb has transformed our view of the universe, enabling the kind of world-class science that drove NASA to make this mission a reality,” said Mark Clampin, director of the Astrophysics Division at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “Webb is providing insights into longstanding mysteries about the early universe and ushering in a new era of studying distant worlds, while returning images that inspire people around the world and posing exciting new questions to answer. It has never been more possible to explore every facet of the universe.”
The telescope’s specialization in capturing infrared light — which is beyond what our own eyes can detect — shows these galaxies, collectively known as Arp 142, locked in a slow cosmic dance. Webb’s observations, which combine near- and mid-infrared light from Webb’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) and MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument), respectively, clearly show that they are joined by a haze represented in blue that is a mix of stars and gas, a result of their mingling.
Their ongoing interaction was set in motion between 25 and 75 million years ago, when the Penguin (individually cataloged as NGC 2936) and the Egg (NGC 2937) completed their first pass. They will go on to shimmy and sway, completing several additional loops before merging into a single galaxy hundreds of millions of years from now.
Let’s Dance!
Before their first approach, the Penguin held the shape of a spiral. Today, its galactic center gleams like an eye, its unwound arms now shaping a beak, head, backbone, and fanned-out tail.
Like all spiral galaxies, the Penguin is still very rich in gas and dust. The galaxies’ “dance” gravitationally pulled on the Penguin’s thinner areas of gas and dust, causing them to crash in waves and form stars. Look for those areas in two places: what looks like a fish in its “beak” and the “feathers” in its “tail.”
Surrounding these newer stars is smoke-like material that includes carbon-containing molecules, known as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, which Webb is exceptional at detecting. Dust, seen as fainter, deeper orange arcs also swoops from its beak to tail feathers.
In contrast, the Egg’s compact shape remains largely unchanged. As an elliptical galaxy, it is filled with aging stars, and has a lot less gas and dust that can be pulled away to form new stars. If both were spiral galaxies, each would end the first “twist” with new star formation and twirling curls, known as tidal tails.
Another reason for the Egg’s undisturbed appearance: These galaxies have approximately the same mass or heft, which is why the smaller-looking elliptical wasn’t consumed or distorted by the Penguin.
It is estimated that the Penguin and the Egg are about 100,000 light-years apart — quite close in astronomical terms. For context, the Milky Way galaxy and our nearest neighbor, the Andromeda Galaxy, are about 2.5 million light-years apart. They too will interact, but not for about 4 billion years.
Now, look to the top right to spot a galaxy that is not at this party. This edge-on galaxy, cataloged PGC 1237172, is 100 million light-years closer to Earth. It’s also quite young, teeming with new, blue stars.
Want one more party trick? Switch to Webb’s mid-infrared-only image to see PGC 1237172 practically disappear. Mid-infrared light largely captures cooler, older stars and an incredible amount of dust. Since the galaxy’s stellar population is so young, it “vanishes” in mid-infrared light.
The James Webb Space Telescope is the world’s premier space science observatory. Webb is solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and CSA (Canadian Space Agency).
END
Vivid portrait of interacting galaxies marks Webb’s second anniversary
2024-07-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UMass Amherst awarded $2.1 million to advance the science of engagement in community-academic research partnerships
2024-07-12
University of Massachusetts Amherst researcher Thomas Mackie has received a $2.1 million funding award from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) to advance the meaningful engagement of communities that are affected by mental health disparities and underrepresented in research partnerships.
The study, entitled “Improving Research Partnership With Engagement Mapping: A Pilot Study to Advance Engagement Science” and co-led by Karen Tabb, a University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign researcher, is designed to empower community partners to have a greater role ...
With gene editing, mice with a form of inherited deafness can hear again
2024-07-12
Researchers have used gene editing to restore hearing in adult mice with a type of inherited hearing loss. They showed that shutting down a damaged copy of a gene called a microRNA (miRNA) enabled the animals to regain hearing. The approach by a research team supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), reported in Science Translational Medicine, may eventually lead to potential treatments for inherited hearing loss in people.
Zheng-Yi Chen, DPhil., and his colleagues at Mass Eye and Ear in Boston and other institutions studied a rare form of genetic deafness called autosomal dominant deafness-50 (DFNA50). ...
Sant Pau researchers discover a new gene that causes ALS
2024-07-12
Sant Pau researchers discover a new gene that causes ALS
Researchers from the Neuromuscular Diseases Group and the Dementia Neurobiology Group of the Sant Pau Research Institute (IR Sant Pau) and the Memory Unit of the Sant Pau Hospital, led by neurologist Dr. Ricard Rojas-García, have identified a new mutation in the ARPP21 gene that could be the cause of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), a devastating neurodegenerative disease.
Specifically, it is a shared mutation (c.1586C>T; p.Pro529Leu) in the ARPP21 gene that ...
Synthetic biology reveals the secrets of life without oxygen
2024-07-12
Long before photosynthesis brought free oxygen into the world, the earth was already populated by numerous organisms. Oxygen was life-threatening for them and therefore they developed completely different metabolic pathways to those we know from plants, animals and humans. Anaerobic bacteria have survived the ages in special, oxygen-free niches, some of them very close to us: as an essential part of the intestinal microbiome, where they are of enormous importance for the well-being of the organism. However, certain anaerobes can ...
UC3M student startup, Solaris Vita, awarded in Europe's largest entrepreneurship competition
2024-07-12
Solaris Vita, a startup created by students at Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M), has won second place in the "Innovation of the Year" category at Gen-E 2024, the largest European youth entrepreneurship competition, organized by Junior Achievement Europe. This is the first time that a Spanish university team has won this award.
The promoters of Solaris Vita, Miguel Iglesias (Industrial Engineering graduate from UC3M) and Yann Guichard (Economics student at the University), competed ...
How plant cold specialists can adapt to the environment
2024-07-12
Plant cold specialists like the spoonworts have adapted well to the cold climates of the Ice Ages. As cold and warm periods alternated, they developed a number of species that also resulted in a proliferation of the genome. Evolutionary biologists from the universities of Heidelberg, Nottingham, and Prague studied the influence this genome duplication has on the adaptive potential of plants. The results show that polyploids – species with more than two sets of chromosomes – can have an accumulation of structural mutations with signals for a possible local ...
Biomarkers reveal how patients with glaucoma may respond to treatment
2024-07-12
Markers in the blood that predict whether glaucoma patients are at higher risk of continued loss of vision following conventional treatment have been identified by researchers at UCL and Moorfields Eye Hospital.
Over 700,000 people in the UK have glaucoma and it is the leading cause of irreversible blindness worldwide. The condition occurs when the cells in the eye that help you see (called retinal ganglion cells) start to die.
The main risk factors for glaucoma are high eye pressure and older age.
Currently, all licenced treatments are designed to lower pressure in the eye – also known as intraocular pressure. However, some patients ...
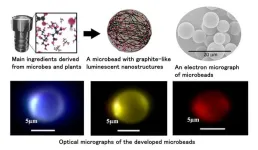
Microbeads with adaptable fluorescent colors from visible light to near-infrared
2024-07-12
1. A research team at NIMS has successfully developed an environmentally friendly, microspherical fluorescent material primarily made from citric acid. These microbeads emit various colors of light depending on the illuminating light and the size of the beads, which suggests a wide range of applications. Furthermore, the use of plant-derived materials allows for low-cost and energy-efficient synthesis.
2. Conventional luminescent devices commonly utilized thin films of compound semiconductors containing metals or sintered inorganic materials with rare earth elements. However, in a circular economy, there ...
Neighborhood disadvantage and prostate tumor RNA expression of stress-related genes
2024-07-12
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study, the expression of several stress-related genes in prostate tumors was higher among men residing in disadvantaged neighborhoods. This study is one of the first to suggest associations of neighborhood disadvantage with prostate tumor RNA expression. Additional research is needed in larger studies to replicate findings and further investigate interrelationships of neighborhood factors, tumor biology, and aggressive prostate cancer to inform interventions to reduce disparities.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, ...
Screen media use and mental health of children and adolescents
2024-07-12
About The Study: This secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial found that a short-term reduction in leisure-time screen media use within families positively affected psychological symptoms of children and adolescents, particularly by mitigating internalizing behavioral issues and enhancing prosocial behavior. More research is needed to confirm whether these effects are sustainable in the long term.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jesper Schmidt-Persson, Ph.D., email jesp@kp.dk.
To ...