(Press-News.org) Michelle Mendoza, PhD, researcher at Huntsman Cancer Institute and associate professor of oncological sciences at the University of Utah (the U) and Jeffrey Weiss, PhD, professor of biomedical engineering and faculty member in the Scientific Computing and Imaging Institute at the U, are the recipients of a $2.6 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to research how tension in lung tissue affects the growth and distribution of tumors. This innovative approach could uncover new mechanisms for understanding how lung cancer develops.
“There are a lot of people looking at the stiffness of breast tissue or other material properties and other types of cancers, but not so much in the lung. And it's interesting, because the lung is always undergoing stretch as we breathe in and out. There's not a lot of tissues that have that characteristic,” says Mendoza.
The study examines the role of mechanobiology—an emerging field that explores how cells respond to mechanical signals—in the progression of early benign lesions to lung adenocarcinoma. According to the American Cancer Society, adenocarcinoma is the most common subtype of non-small cell lung cancer.
The researchers simulated how the presence of a solid tumor fills and affects alveolar sacs, where lungs and blood exchange oxygen for carbon dioxide, using computational models developed in Weiss’s lab.
They observed that the connective tissues making up the walls of the sacs are sensitive to strain—which may produce a cellular response that allows the tumor to grow.
“It's a new hypothesis about something that's contributing to the early tumor cells progressing to malignancy, which other people haven't looked at,” says Mendoza. “And it would be a really interesting discovery if it's contributing to tumor development—because strain could be affected by things in our environment that cause lung damage or scarring.”
The NIH grant allows Mendoza and Weiss to conduct their research experimentally by testing the effects directly in tissue and also develop more advanced computer models.
Weiss has worked in biomechanics for decades, particularly in musculoskeletal science and cardiovascular mechanics.
“It’s gratifying for me that at this point in my career, I can still do different and new things that are interesting to me,” says Weiss. “I’m pleased to see that the tools that I’ve developed over my career are useful in this context, as well.”
The $2.6 million grant will be distributed over the next five years. Mendoza and Weiss hope the study will lead to further explorations of mechanobiology, as well as the development of neoadjuvant therapies to reduce lung cancer mortality.
About Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah
Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah (the U) is the National Cancer Institute-designated Comprehensive Cancer Center for Utah, Idaho, Montana, Nevada, and Wyoming. With a legacy of innovative cancer research, groundbreaking discoveries, and world-class patient care, we are transforming the way cancer is understood, prevented, diagnosed, treated, and survived. Huntsman Cancer Institute focuses on delivering a cancer-free frontier to all communities in the area we serve. We have more than 300 open clinical trials and 250 research teams studying cancer at any given time. More genes for inherited cancers have been discovered at Huntsman Cancer Institute than at any other cancer center. Our scientists are world-renowned for understanding how cancer begins and using that knowledge to develop innovative approaches to treat each patient’s unique disease. Huntsman Cancer Institute was founded by Jon M. and Karen Huntsman.
END
Mendoza, Weiss receive $2.6 million grant to study biomechanics of lung tumors
2024-07-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study shows how narcissistic CEOs influence the board of directors to take more risk
2024-07-15
Narcissistic CEOs that also serve as chair of the board are adept at controlling how their boards of directors focus their attention, giving the CEO the ability to get their way. A new study published in the Strategic Management Journal found that by driving board discussions about risk-taking to hold a positive tone, narcissistic CEOs can allocate more resources toward risk-taking strategies. The findings deepen our understanding of how CEO behavior and personality types can drive risk management strategies.
The research team — Christopher S. Tuggle of the University of Central Arkansas, Cameron J. Borgholthaus of the University of Wyoming, Peter D. Harms of the University of Alabama, ...
Study shows timely transition from pediatric to adult care is critical for young adults with sickle cell disease
2024-07-15
Sickle cell disease is the most common inherited red blood cell disorder in the United States and can lead to health problems including organ dysfunction, acute chest syndrome and strokes over a patient’s lifespan. According to a new study, individuals living with sickle cell disease who experience a delay of more than six months after transferring from pediatric to adult care are twice as likely to be hospitalized compared to those who transition in less than two months.
In the study, Kristen ...
University of Cincinnati study: Long-term stroke survival improving, but racial disparities remain
2024-07-15
Overall rates of long-term survival following stroke are improving, but Black individuals experience worse long-term outcomes compared to white individuals, according to University of Cincinnati research published online July 15 in Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
UC’s David Robinson, MD, corresponding author on the research, said prior studies had examined short-term stroke outcomes of 30 or 60 days, but this time the team looked at survival rates five years past a person’s stroke.
“This was ...
National Institutes of Health grant could mean progress toward improved outcomes for stroke patients
2024-07-15
The Associate Dean of Research at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center’s College of Nursing has received a two-year, $421,188 grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to improve cognitive screening in people who suffer from a devastating type of stroke called aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (aSAH).
Professor Ansley Stanfill, PhD, RN, FAAN, has devoted her program of research to improving outcomes for people who survive strokes. Her latest grant aims to determine if an existing screening tool can be used in a new way to assess patients following aSAH and trigger a ...
SfN establishes James L. Roberts Endowed Fund
2024-07-15
Washington, D.C. – The Society for Neuroscience (SfN) has received $128,000 from the estate of James L. Roberts, PhD. With the funds, SfN Council voted to create a new long-term endowed fund, The James L. Roberts Fund, and will use the income from its investments to create and perpetually fund James L. Roberts Trainee Professional Development Awards (TPDAs) beginning at Neuroscience 2024.
“I knew Jimmy Roberts very well. We basically launched neurobiology at Sinai when we co-directed the Fishberg Research Center for Neurobiology at Mount Sinai from 1989–2002,” said incoming SfN President John Morrison. “Jimmy was an outstanding ...
Unlocking the mystery of preexisting drug resistance: New study sheds light on cancer evolution
2024-07-15
CLEVELAND—The evolution of resistance to diseases, from infectious illnesses to cancers, poses a formidable challenge.
Despite the expectation that resistance-conferring mutations would dwindle in the absence of treatment due to a reduced growth rate, preexisting resistance is pervasive across diseases that evolve—like cancer and pathogens—defying conventional wisdom.
In cancer, it is well known that small numbers of drug-resistant cells likely exist in tumors even before they’re treated. In something of a paradox, before treatment, these mutants have been repeatedly shown to have lower fitness than the surrounding ancestor cells from which they arose. It leads ...
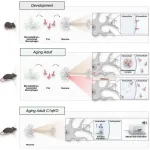
New study reveals critical role of C1q protein in neuronal function and aging
2024-07-15
BOSTON, Mass. (July 15, 2024)—A groundbreaking study conducted at the lab of Beth Stevens, PhD, at Boston Children’s Hospital has revealed that an immune protein impacts neuronal protein synthesis in the aging brain. Previous work from the Stevens lab had uncovered that immune cells in the central nervous system, microglia, help prune synapses in the developing brain by tagging synapses with the immune protein C1q. New research led by Nicole Scott-Hewitt, published in Cell, shows that neurons can also internalize C1q. C1q seems to influence protein production inside neurons by interacting with ribosomal proteins, RNA-binding proteins, and ...
New research demonstrates potential for increasing effectiveness of popular diabetes, weight-loss drugs
2024-07-15
A network of proteins found in the central nervous system could be harnessed to increase the effectiveness and reduce the side effects of popular diabetes and weight-loss drugs, according to new research from the University of Michigan.
The study, appearing today in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, focused on two proteins called melanocortin 3 and melanocortin 4 found primarily on the surface of neurons in the brain that play a central role in regulating feeding behavior and maintaining the body's energy balance.
Melanocortin ...
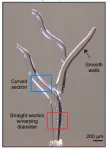
Understanding the 3D ice-printing process to create micro-scale structures
2024-07-15
Advances in 3D printing have enabled many applications across a variety of disciplines, including medicine, manufacturing, and energy. A range of different materials can be used to print both simple foundations and fine details, allowing for the creation of structures with tailored geometries.
However, creating structures with micro-scale, precise internal voids and channels still poses challenges. Scaffolds used in tissue engineering, for example, must contain a three-dimensional complex network of conduits that mimic the human vasculature. With traditional additive manufacturing, where the material is deposited layer ...
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia researchers develop antioxidant strategy to address mitochondrial dysfunction caused by SARS-CoV-2 virus
2024-07-15
Philadelphia, July 15, 2024 – Building upon groundbreaking research demonstrating how the SARS-CoV-2 virus disrupts mitochondrial function in multiple organs, researchers from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) demonstrated that mitochondrially-targeted antioxidants could reduce the effects of the virus while avoiding viral gene mutation resistance, a strategy that may be useful for treating other viruses. The preclinical findings were recently published in the journal Proceedings ...