(Press-News.org) Late-life depression, typically defined as depression with onset in individuals over 60 years of age, can affect up to a third or more of people older than 60 and can be debilitating. But, like other neurological conditions, an individual’s risk may be influenced by lifestyle choices. Researchers from Mass General Brigham previously developed and validated the Brain Care Score (BCS) for helping patients and clinicians identify lifestyle changes that may reduce their risk of dementia and stroke. Now, with collaborators at Yale University, they have shown that a higher BCS is also associated with a lower risk of late-life depression. Findings, published in Frontiers in Psychiatry, provide further evidence of shared biological risk factors for stroke, dementia and depression and highlight the potential of the BCS to help patients make lifestyle changes to better care for their brain health.
“The Brain Care Score is a simple tool designed to help anyone in the world answer the question, ‘What can I do to take better care of my brain?’” said author Jonathan Rosand MD, MSc, co-founder of the McCance Center for Brain Health at Massachusetts General Hospital and the lead developer of the Brain Care Score. “This paper provides compelling evidence that raising your BCS is not only likely to make your brain healthier and more resistant to diseases like dementia and stroke, but that it also offers the hope of protection from depression.”
The new study represents a collaboration among researchers at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Massachusetts General Hospital, founding members of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system.
“Dementia, stroke, and depression are leading causes of human suffering as we age,” said corresponding author Christopher D. Anderson, MD, MSc, chief of stroke and cerebrovascular diseases in the Department of Neurology at BWH. “This study highlights an extraordinary opportunity to prevent these conditions from developing in the first place.”
The Brain Care Score was developed by researchers at the McCance Center and their collaborators to help patients and clinicians prevent the onset of brain disease by focusing on modifiable risk factors. These include four physical risk factors (blood pressure, hemoglobin A1c, cholesterol and body mass index), five lifestyle elements (nutrition, alcohol intake, smoking, physical activity and sleep) and three social/emotional elements (stress, relationships and life purpose). A higher score on the 21-point scale is indicative of a lower risk of brain disease.
The research team, utilizing data from over 350,000 participants in the U.K. Biobank (UKB) study, demonstrated that a five-point increase in baseline BCS was associated with a 33 percent lower risk of late-life depression and a 27 percent lower composite risk of late-life depression, stroke and dementia over a median follow-up period of 13 years.
The UKB, which the researchers previously utilized to develop and validate the BCS, includes over a decade of systematically collected health information from participants throughout the U.K., who were 40-69 years old during the study’s enrollment period from 2006-2010. Additionally, the researchers verified their findings in a separate dataset of nearly 200,000 individuals from the UKB, whose primary care records were also accessible to the researchers. Under-diagnosis and under-documentation of depression is a known challenge to epidemiological research, but the inclusion of primary care records can reduce the likelihood of missing diagnoses.
When stratifying results by age, the researchers were surprised to find a substantial association between baseline BCS and risk of depression in those under 50 years of age. While the investigators expected that older individuals may experience neurodegenerative and inflammatory processes that can contribute to late-life depression, stroke and dementia, the neurobiological changes that lead to depression in younger individuals are less apparent. Going forward, the researchers are pursuing additional work to understand the relationship between BCS scores and risk of depression in the young.
“There is still much to be learned about what pathways contribute to late-life depression, dementia and stroke,” said first author Sanjula Singh, MD, PhD, MSc, of the McCance Center for Brain Health at Department of Neurology of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School. “Our results emphasize the importance of a holistic view of the brain to further understand underlying connections between different brain diseases.”
The investigators are pursuing ongoing research to determine whether individuals who increase their BSC over time by five points or more have a reduced risk of stroke and dementia in the future, compared to those without substantial score increases.
“Increasingly, data suggest that the risk for a variety of non-communicable diseases is to some extent mediated by modifiable lifestyle changes, should they be undertaken early enough,” said Gregory Fricchione, MD, associate chief of psychiatry at Massachusetts General Hospital. “This research is provocative and hopeful in its implications for tackling prevalent illnesses like depression, which itself is a risk factor for many other diseases. This research reminds us of the interlocking of the nervous system with psychosocial and immunological stress, along with the opportunity to reduce vulnerabilities to downstream damage to the brain through improvements in the factors outlined in the BCS.”
Authorship: Additional Mass General Brigham authors include Zeina Chemali (MGH), Leidys Gutierrez-Martinez (MGH), Livia Parodi (BWH, MGH), Ernst Mayerhofer (BWH, MGH), Jasper Senff (MGH), Courtney Nunley (MGH), Amy Newhouse (MGH), An Ouyang (MGH), M. Brandon Westover (MGH), Rudolph E. Tanzi (MGH), Bart Brouwers (MGH), Nirupama Yechoor (MGH), Christopher D. Anderson (BWH, MGH). Additional authors include Cyprien A. Rivier, Keren Papier, Santiago Clocchiatti-Tuozzo, Ronald M. Lazar, Aleksandra Pikula, Sarah Ibrahim, Virginia Howard, George Howard, Thomas Littlejohns, Kevin N. Sheth, Guido J. Falcone.
Disclosures: Rosand receives sponsored research support from the U.S. National Institutes of Health and the American Heart Association and receives payments for expert testimony and consulting fees from the National Football League. A complete list of disclosures is included in the paper.
Funding: Funding provided by the Lavine Brain Health Innovation Fund and the McCance Center for Brain Health. A complete list of additional research support is included in the article.
Paper cited: Singh SD, et al. “A Brain Care Score for Risk of Late-Life Depression and A Composite Outcome of Dementia, Stroke and Late-Life Depression: data from the UK Biobank cohort” Frontiers in Psychiatry DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1373797
###
About Mass General Brigham
Mass General Brigham is an integrated academic health care system, uniting great minds to solve the hardest problems in medicine for our communities and the world. Mass General Brigham connects a full continuum of care across a system of academic medical centers, community and specialty hospitals, a health insurance plan, physician networks, community health centers, home care, and long-term care services. Mass General Brigham is a nonprofit organization committed to patient care, research, teaching, and service to the community. In addition, Mass General Brigham is one of the nation’s leading biomedical research organizations with several Harvard Medical School teaching hospitals. For more information, please visit massgeneralbrigham.org.
END
World leaders must take advantage of a pivotal window of opportunity for forging a much-needed joined-up approach to tackle climate change and biodiversity loss, say scientists from ZSL and York University. Without this, work on tackling either crisis could inadvertently harm progress on the other.
Published today (Tuesday 23 July) in the Journal of Applied Ecology, a paper from international conservation charity ZSL and researchers at York University, Toronto, titled ‘The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework and the Paris Agreement need a joint work programme for climate, nature, and people’ conceptualises how a joint work ...
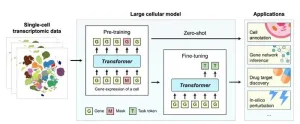
In a landmark move to advance the frontiers of artificial intelligence, the Quantitative Biology (QB) journal has published a comprehensive commentary titled "Current Opinions on Large Cellular Models," highlighting the cutting-edge developments in the field of large cellular models (LCMs). The journal has brought together a consortium of leading scholars from China, the United States, and Canada to delve into the future of AI-driven biological research.
The commentary features influential authors behind some of the most impactful LCMs, such as scBERT, Geneformer, scGPT, scFoundation, and GeneCompass. These AI ...
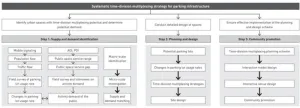
Compact city is an urban planning strategy aimed at promoting environmental, economic, and social sustainability through spatial configurations featured with relatively high density and mixed land use. The continuous growth in car ownership forces cities to construct more static transportation facilities such as parking lots, squeezing the activity spaces of residents and consequently giving rise to a series of efficiency and equity issues. Thus, the conflict between people and vehicles in compact cities is increasingly prominent and urgently ...
The prevalence of kidney disease has been increasing in Japan, with it now affecting one in eight adults, but developing effective treatment remains a challenge. The kidneys are among the most energy-intensive organs in the body. For the kidneys to function, they constantly produce and consume large amounts of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is a chemical that the body uses to store and transport energy. However, ATP dynamics—the changes over time in ATP production and utilization—within the kidney have been poorly understood because of the lack of suitable imaging technologies.
Using a newly developed ATP imaging system, the researchers ...
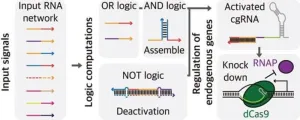
Guides typically assist tourists with directions, but the experience could be greatly enhanced if they offered personalized services tailored to individual interests. Recently, researchers have transformed guide RNAs, which direct enzymes, into a smart RNA capable of controlling networks in response to various signals. This innovative research is gaining significant attention in the academic community.
A research team consisting of Professor Jongmin Kim and PhD candidates Hansol Kang and Dongwon Park from the Department of Life Sciences at POSTECH has developed a multi-signal ...
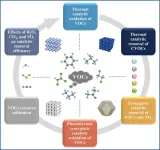
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs), with toxicity and irritability, could cause atmospheric environmental problems such as haze and photochemical smog, seriously threatening the ecological environment and human health. The primary source of VOCs is human production, such as the petrochemical industry, pharmaceutical industry, footwear industry, electronic manufacturing, and cooking fumes. Catalytic oxidation technology can highly effectively remove organic pollutants without secondary pollution, and it is receiving increasing attention in VOC pollution control. In real-world operating conditions, the ...
HONG KONG (21 July 2024) --- The progress of solar energy technology took a step forward recently with the development of a groundbreaking living passivator at City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) that can substantially enhance the stability and efficiency of perovskite solar cells.
This newly developed passivator is a type of corrosion inhibitor that appreciably changes the potential of a metal. The CityUHK technology leverages dynamic covalent bonds that activate on exposure to moisture and heat, enabling it to evolve new passivators in response to environmental factors.
This innovative approach allows for real-time repair and maintenance of perovskite solar cells. ...
New research presented at this year’s Annual Meeting of the European Association for Study of Diabetes (Madrid, Spain, 9-13 September) shows that the risk of developing type 1 diabetes (T1D) decreases markedly in girls after age 10 years, while the risk in boys stays the same.
Furthermore, risk of T1D is significantly higher boys with a single autoantibody than their female counterparts, suggesting the sex could be linked with autoantibody development, indicating the importance of incorporating sex in the assessment ...
Background and Goal: Sulfonylureas are a class of oral medications used to manage blood glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes. These drugs increase insulin production regardless of blood sugar levels. For this reason, the drugs can cause blood sugar to drop too low, leading to hypoglycemia. The goal of this study was to compare how prevalent impaired awareness of hypoglycemia was when patients with type 2 diabetes were treated with either insulin or sulfonylureas for both long and short-term periods.
Study Approach: Researchers collected data from a group of 898 participants with type 2 diabetes enrolled in pharmacies, clinics, ...
Background and Goal: Social determinants of health are the conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age. These conditions include income, education, and access to health care. Knowledge of these factors is essential for primary care clinicians to deliver fair and complete care, plan programs and distribute resources effectively. However, this information is rarely captured consistently in clinical settings. This study identified how an Artificial Intelligence (AI) social determinants of health tool can be designed using a collaborative design strategy with input from primary care team members.
Study Approach: ...