(Press-News.org) An analysis of comments on Chinese social media platform Sina Weibo reveals trends in the public response to measures implemented to support China’s three-child policy, highlighting concerns about women’s rights and employment. Lijuan Peng of Zhejiang Gongshang University in Hangzhou, China, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on July 24, 2024.
For decades, China’s one-child policy restricted most families to having just one child. In 2021, to combat a falling birthrate, China introduced its three-child policy, allowing couples to have up to three children. To help encourage childbirth, China has introduced supportive measures alongside, such as housing subsidies and maternity insurance.
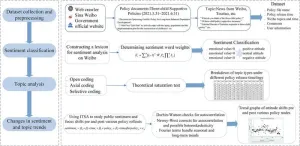
Social media offers a unique window into the public response to new national policies, but few studies have analyzed the three-child policy through such a lens. To deepen understanding of the response to China’s three-child supportive measures, Peng and colleagues analyzed comments posted on Sina Weibo after the release of information about such measures between May 2021 and June 2022. They drew on various statistical and computational tools, including neural network analysis, to identify hot topics and areas of concern.
The analysis revealed short-term, positive attitudes among Weibo users in response to some supportive measures, including those relating to housing subsidies, maternity insurance, and financial incentives. However, users showed persistent negative responses to extensions of maternity leave, primarily due to concerns about women’s future employment opportunities and marital rights.
The researchers found that Sina Weibo discussions about the three-child policy were primarily centered around protection of women’s rights, including post-childbirth legal rights and access to adequate physical and mental healthcare. Other hot topics included the financial difficulty of raising multiple children and concerns about housing and childcare services. The study also highlighted a strong desire for children among many infertile or single women that has gone unfulfilled because of the limitations of the personal medical insurance system.
These findings could help inform China’s future efforts to raise birthrates. Meanwhile, further research could address some of the limitations of this analysis, such as by accounting for social media users’ demographics.
The authors add: “This study reveals the public’s evolving focus, cognition, and emotional response to the three-child supportive policy through Weibo analysis, providing insights for future policy releases.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0306698
Citation: Peng L, Chen T, Yang J, Cong G (2024) Changes in online public opinions associated with various three-child supportive policies in China: Observational study using social media data over time. PLoS ONE 19(7): e0306698. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0306698
Author Countries: China, USA
Funding: This research is supported by Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. LY22G010004), as well as Zhejiang Gongshang University “digital +” discipline construction key project (Grant No. SZJ2022B019). In addition, the funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Weibo posts illuminate public response to China’s three-child policy measures
Measures such as housing subsidies are praised, but extended maternity leave elicits concern
2024-07-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Our ability to recognize music might not diminish with age, with older concert attendees identifying themes in music as well as younger participants
2024-07-24
Our ability to recognize music might not diminish with age, with older concert attendees identifying themes in music as well as younger participants
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0305969
Article Title: Age and familiarity effects on musical memory
Author Countries: Canada, UK
Funding: The author(s) disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: this work was supported by BRZ’s Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada grant. The funders had no role ...
The COVID-19 pandemic slowed progress towards health-related Sustainable Development Goals and increased inequalities
2024-07-24
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly widened existing economic and health disparities between wealthy and low-income countries and slowed progress toward health-related Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), according to a new study published July 24, 2024, in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Wanessa Miranda of Federal University of Minas Gerais, Brazil, and colleagues.
The global SDGs were established in 2015 as a wide and integrated agenda with themes ranging from eradicating poverty and promoting well-being to addressing socioeconomic ...
Even people who harbor positive sentiments toward immigrants imagine immigrants' faces as less trustworthy and less competent than US citizens' faces
2024-07-24
Even people who harbor positive sentiments toward immigrants imagine immigrants' faces as less trustworthy and less competent than US citizens' faces
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0306872
Article Title: Intergroup evaluative bias in facial representations of immigrants and citizens in the United States
Author Countries: USA
Funding: This work was facilitated by the National Science Foundation Division of Behavioral and Cognitive Sciences, grant #1764097 awarded to ART and grant #2215236 awarded to ...
Southern Ocean absorbing more CO2 than previously thought, study finds
2024-07-24
New research led by the University of East Anglia (UEA) and Plymouth Marine Laboratory (PML) has found that the Southern Ocean absorbs more carbon dioxide (CO2) than previously thought.
Using direct measurements of CO2 exchange, or fluxes, between the air and sea, the scientists found the ocean around Antarctica absorbs 25% more CO2 than previous indirect estimates based on shipboard data have suggested.
The Southern Ocean plays a major role in absorbing CO2 emitted by human activities, a process vital for controlling the Earth's climate. However, there are big uncertainties ...
Saharan dust regulates hurricane rainfall
2024-07-24
Giant plumes of Sahara Desert dust that gust across the Atlantic can suppress hurricane formation over the ocean and affect weather in North America.
But thick dust plumes can also lead to heavier rainfall – and potentially more destruction – from landfalling storms, according to a July 24 study in Science Advances. The research shows a previously unknown relationship between hurricane rainfall and Saharan dust plumes.
“Surprisingly, the leading factor controlling hurricane precipitation is not, as traditionally thought, sea surface temperature or humidity in the atmosphere. Instead, it’s Sahara dust,” said the corresponding ...
Fighting leukemia by targeting its stem cells
2024-07-24
Acute myeloid leukaemia is one of the deadliest cancers. Leukaemic stem cells responsible for the disease are highly resistant to treatment. A team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), University Hospital of Geneva (HUG), and Inserm has made a breakthrough by identifying some of the genetic and energetic characteristics of these stem cells, notably a specific iron utilisation process. This process could be blocked, leading to the death or weakening of these stem cells without affecting healthy cells. These results, published in Science Translational Medicine, pave the way for new therapeutic strategies.
Acute ...
NASA’s Webb images cold exoplanet 12 light-years away
2024-07-24
An international team of astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has directly imaged an exoplanet roughly 12 light-years from Earth. The planet, Epsilon Indi Ab, is one of the coldest exoplanets observed to date.
The planet is several times the mass of Jupiter and orbits the K-type star Epsilon Indi A (Eps Ind A), which is around the age of our Sun, but slightly cooler. The team observed Epsilon Indi Ab using the coronagraph on Webb’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument). Only a few tens of exoplanets have been directly imaged previously by space- and ground-based observatories.
“Our prior observations of this system have been more indirect measurements ...
Prevalence and impact of the KIT M541L variant in patients with mastocytosis
2024-07-24
“This study uniquely examines the prevalence and impact of the KIT M541L variant in both adult and pediatric patients with mastocytosis further stratified by disease variant.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 24, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on July 22, 2024, entitled, “Prevalence and impact of the KIT M541L variant in patients with mastocytosis.”
Activating mutations in KIT, particularly D816V, have been associated with mastocytosis. Additionally, expression of heterozygous KIT M541L has been primarily ...
Experts outline considerations to deploy AI in radiology
2024-07-24
Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools can play a key role in medical imaging if radiologists trust in their design, deploy them with adequate training and establish clear guidelines regarding clinical accountability, according to a recently published Special Report in Radiology: Artificial Intelligence, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
RSNA and the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) Society have led a series of joint panels and seminars focused on the present impact and future directions of AI in radiology. These conversations ...
Johns Hopkins Medicine’s Center for Inherited Disease Research renews 7-year award for up to $98 million
2024-07-24
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
With renewed funding of up to $98.8 million for seven years, Johns Hopkins Medicine scientists will continue to be a worldwide resource for discovering the genes and their variations that contribute to human disease.
Leaders of the Johns Hopkins Center for Inherited Disease Research, established in 1996, received the fourth consecutive renewal for up to $98,880,900 in funds from a consortium of 10 institutes at the National Institutes of Health. The seven-year award is divided between ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Highly stable self-rectifying memristor arrays: Enabling reliable neuromorphic computing via multi-state regulation
Composite superionic electrolytes for pressure-less solid-state batteries achieved by continuously perpendicularly aligned 2D pathways
Exploring why some people may prefer alcohol over other rewards
How expectations about artificial sweeteners may affect their taste
Ultrasound AI receives FDA De Novo clearance for delivery date AI technology
Amino acid residue-driven nanoparticle targeting of protein cavities beyond size complementarity
New AI algorithm enables scientific monitoring of "blue tears"
Insufficient sleep among US adolescents across behavioral risk groups
Long COVID and recovery among US adults
Trends in poverty and birth outcomes in the US
Heterogeneity of treatment effects of GLP-1 RAs for weight loss in adults
Within-person association between daily screen use and sleep in youth
Low-dose lithium for mild cognitive impairment
Catheter ablation and oral anticoagulation for secondary stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation
A new theory of brain development
Pilot clinical trial suggests low dose lithium may slow verbal memory decline
Bioprinting muscle that knows how to align its cells just as in the human body
A hair-thin fiber can read the chemistry of a single drop of body fluid
SwRI develops magnetostrictive probe for safer, more cost-effective storage tank inspections
National report supports measurement innovation to aid commercial fusion energy and enable new plasma technologies
Mount Sinai, Uniformed Services University join forces to predict and prevent diseases before they start
Science of fitting in: Do best friends or popular peers shape teen behavior?
USF study: Gag grouper are overfished in the Gulf; this new tool could help
New study from Jeonbuk National University finds current climate pledges may miss Paris targets
Theoretical principles of band structure manipulation in strongly correlated insulators with spin and charge perturbations
A CNIC study shows that the heart can be protected during chemotherapy without reducing antitumor efficacy
Mayo Clinic study finds single dose of non-prescribed Adderall raises blood pressure and heart rate in healthy young adults
Engineered immune cells show promise against brain metastases in preclinical study
Improved EV battery technology will outmatch degradation from climate change
AI cancer tools risk “shortcut learning” rather than detecting true biology
[Press-News.org] Weibo posts illuminate public response to China’s three-child policy measuresMeasures such as housing subsidies are praised, but extended maternity leave elicits concern