(Press-News.org) A study conducted through a mobile screening unit in Madrid, Spain from 2017 to 2023 and published in Eurosurveillance found that active hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection decreased from 23% to 6% in that period among people who use drugs (PWUD) that visited the unit. The study found that the use of intravenous drugs was the most significant risk factor for infection among PWUD. It confirmed that HCV screening and treatment programmes targeting this at-risk population are effective and can help achieve the World Health Organization goal of HCV elimination as public health threat by 2030.
Study participants and methods
Participants were recruited in ‘hotspots’ in Madrid where high-risk individuals gathered for dealing and drug consumption. The study included individuals over 18 and with active drug use in the year before being screened.
A mobile screening unit approached these ‘hotspots’’. A nurse collected blood samples from participants for HCV testing, and investigators gathered data on demographic, epidemiology, substance use and sexual risk behaviour.
Results and public health implications
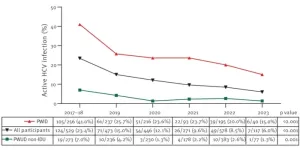
2 349 participants of the initial cohort of 5 270 were actively using drugs. Of these, 2 264 (43%) underwent an HCV antibody test, with 195 (8.6%) participating more than once. Among the group who were tested, 685 (13%) tested positive for anti-HCV antibodies. Of those, 605 participants agreed to undergo HCV-RNA testing, with an active HCV infection detected in 314 (51.9%) individuals.
Participants who reported using drugs and with an active HCV infection were significantly older and were more likely to be of European (Western Europe and Eastern Europe) origin, homeless, consuming cocaine and heroin, injecting drugs, and undergoing opioid substitution treatment than participants who used drugs without an active HCV infection. Significantly, the use of a mobile screening unit led almost 70% of participants who tested positive to start treatment.
The study observed a strong decrease in active HCV infection across the entire population from 23.4% in 2017 to 6% in 2023. However, the prevalence remains 30 and 70 times higher among people who use drugs and people who inject drugs, respectively, than in the general population.
The decrease could be attributed to measures that have helped users of intravenous drugs overcome barriers to testing and treatment, such as better access to testing and care through decentralised approaches, simplified one-step diagnosis, and fewer treatment restrictions. Public health campaigns have also helped raise awareness of the risks related to intravenous drug use.
Additional outputs on hepatitis
Ahead of World Hepatitis Day, Eurosurveillance has also published a study conducted in Australia demonstrating the feasibility and effectiveness of using surveillance systems to improve access to treatment and care of hepatitis C. Additionally, it has published research on the prevalence of chronic hepatitis C infections in Estonia and Romania, with levels shown to be low in both countries, as well as an accompanying editorial highlighting steps needed to achieve the goal of eliminating hepatitis C as public health threat by 2030.
END
World Hepatitis Day 2024: Madrid study shows decrease in active hepatitis C infection among risk groups, indicating effectiveness of public health measures
The study was conducted in a mobile screening unit from 2017-2023 and found that HCV infection decreased from 23% to 6% in that period among PWUDs who visited the unit
2024-07-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
After Trump’s election, women of color had more underweight, premature babies, study finds
2024-07-25
In 2016, President-elect Donald Trump vowed to deport thousands of immigrants. His anti-immigration message vilified foreign-born people living in the U.S. as criminals and rapists. Besides making good on many harsh, immigration-related promises, the years after his election stoked the anxieties of millions of people.
Now, with Trump once again in contention for the White House, a new study from the University of California, Berkeley, reveals the surprising — and potentially lifelong — association between those early Trump years and the health of society's newest citizens.
In ...
Space-trekking muscle tests drugs for microgravity-induced muscle impairment
2024-07-25
A gentle rumble ran under Ngan Huang’s feet as a rocket carrying her research—live, human muscle cells grown on scaffolds fixed on tiny chips—lifted off, climbed, and disappeared into the sky to the International Space Station National Laboratory. These chips would help Huang better understand muscle impairment, often seen in astronauts and older adults, and test drugs to counter the condition.
Now, the results are back. Reporting in a study published July 25 in Stem Cell Reports, Huang’s team showed that space-travelling muscle had metabolic changes that indicate ...
In clinical trial, fecal matter transplant helped half of patients with gastrointestinal cancers overcome resistance to immunotherapy treatment
2024-07-25
Findings from a small, proof-of-concept clinical trial have suggested that fecal microbiota transplants (FMTs) can boost the effectiveness of immunotherapy in a range of gastrointestinal cancers. In the study, published July 25 in the journal Cell Host & Microbe, six of 13 patients who had previously shown resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors benefited from receiving FMTs from donors who had previously responded to treatment. The investigators also identified specific strains of bacteria associated with better or worse responses to FMT and immune checkpoint drugs.
“This research highlights the complex interplay between beneficial ...
Royal Ontario Museum scientist identifies Great Salt Lake as a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions
2024-07-25
Newly announced research by Royal Ontario Museum (ROM) examining greenhouse gas emissions from the drying lake bed of Great Salt Lake, Utah, calculates that 4.1 million tons of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases were released in 2020. This research suggests that drying lake beds are an overlooked but potentially significant source of greenhouse gases, which may further increase due to climate change. These results were announced in the paper, “A desiccating saline lake bed is a significant source of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions,” published in the journal One Earth.
“Human-caused ...
Provision of stroke care services by community disadvantage status
2024-07-25
About The Study: Hospitals in communities with the greatest level of socioeconomic disadvantage had the lowest likelihood of becoming stroke certified while hospitals in the most advantaged communities had the highest likelihood in this cohort study. These findings suggest that there is a need to support hospitals in disadvantaged communities to obtain stroke certification as a way to reduce stroke disparities.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Renee Y. Hsia, M.D., M.Sc., email renee.hsia@ucsf.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
Bilateral mastectomy and breast cancer mortality
2024-07-25
About The Study: This cohort study indicates that the risk of dying of breast cancer increases substantially after experiencing a contralateral breast cancer. Women with breast cancer treated with bilateral mastectomy had a greatly diminished risk of contralateral breast cancer; however, they experienced similar mortality rates as patients treated with lumpectomy or unilateral mastectomy.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Steven A. Narod, M.D., email steven.narod@wchospital.ca.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2024.2212)
Editor’s ...
Antisense oligonucleotide treatment shows promise in treating Parkinson's disease progression
2024-07-25
TMDU researchers demonstrate proof of concept of antisense nucleic acid therapy to prevent the spread of α-synuclein pathologies in synucleinopathies.
Tokyo, Japan – Parkinson’s disease (PD), as well as many other neurodegenerative disorders, has shown a link between the abnormal aggregation of a protein called α-synuclein (aSyn) and neuronal death. These aggregates, known as Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites depending on their subcellular localization, can spread by continuously causing normal endogenous aSyn to misfold. The complex nature of this aggregation process poses significant challenges ...
Intelligent engineering: AI transforms spatial arrangement of hydropower underground facilities
2024-07-25
Designing the spatial arrangement of underground powerhouses involves numerous complex parameters and boundaries, requiring frequent reference to various cases and specifications. Traditional methods struggle to efficiently retrieve this information, leading to suboptimal designs and extended project timelines. Due to these challenges, there is a pressing need for a more intelligent and efficient approach to streamline the design process, enhance accuracy, and improve project management in hydropower engineering.
Researchers from Tianjin University, in collaboration with PowerChina Kunming Engineering Corporation Limited and other ...
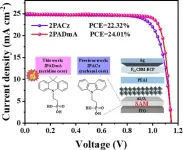
Unlocking new potential in solar tech: dimethyl acridine enhances perovskite solar cells
2024-07-25
Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) are highly regarded for their exceptional performance and straightforward fabrication. However, traditional hole transport layers (HTLs) like Poly (triarylamine) (PTAA), Nickel Oxide (NiOx), and poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly (styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT) have inherent limitations that impede efficiency and stability. These materials often suffer from issues such as hydrophobicity, high reactivity, and acidity, which negatively affect the overall performance of PSCs. Due to these challenges, there is a pressing ...
Harnessing blue energy: advanced nanofluidic membranes boost aquatic energy conversion efficiency
2024-07-25
To achieve carbon neutrality, advancements in energy conversion and storage technologies are essential. Current aqueous energy devices suffer from performance limitations due to the trade-off between permeability and selectivity in permselective membranes. This trade-off hampers the efficiency of energy conversion and storage systems, necessitating the development of membranes that can balance these properties effectively. Due to these challenges, further research is required to explore innovative membrane structures that can enhance the performance of energy conversion and storage devices.
A research team from Tsinghua University has published a study (DOI: 10.26599/EMD.2024.9370041) ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
[Press-News.org] World Hepatitis Day 2024: Madrid study shows decrease in active hepatitis C infection among risk groups, indicating effectiveness of public health measuresThe study was conducted in a mobile screening unit from 2017-2023 and found that HCV infection decreased from 23% to 6% in that period among PWUDs who visited the unit