(Press-News.org) Data published today in the New England Journal of Medicine Catalyst reported that MedPearl, a Providence-developed clinician-built clinical decision platform, improves primary care clinician productivity, decreases time waste on administrative tasks and improves the quality of referrals sent to specialists.
The paper details operational outcomes from MedPearl’s use among more than 4,000 active monthly clinician users and shows statistically significant improvement in total productivity, after-hours time spent in the EMR and incremental margin per referral among top users.
“The data shows that human-centered design tools can help ease the burden on clinicians and ensure that only patients who require a specialist are ultimately referred,” said Eve Cunningham, M.D., founder of MedPearl and chief of virtual care and digital health at Providence, one of the nation’s largest health systems. “At Providence, clinicians spent two years developing the MedPearl platform, a comprehensive library of actionable clinical guidance carefully mapped to patient data relevant to a clinical context – bringing knowledge and patient data together on a single screen. Today, our front-line primary care clinicians can access patient management and referral information for over 730 conditions, thereby super-charging clinical decision making.”
Seventy-two percent of clinician users said the platform improved their clinical management and workups, according to the study. Following system-wide integration, MedPearl achieved a 95% success rate in matching queries to relevant guides, and maintains a high user retention rate, with about 75% of users returning month-to-month.
Founded by Cunningham and made possible by the combined research and development efforts of hundreds of clinicians and engineers at Providence, MedPearl is healthcare’s first intelligent clinical decision engine, created to provide immediate and actionable medical knowledge at the point of care. Leveraging artificial intelligence and a no-code environment, combined with EMR integration, Providence implemented MedPearl across its eight-state footprint.
About MedPearl
MedPearl is a clinical intelligence engine providing trusted medical knowledge that is easy to access, interactive, and actionable for use at point of care. Built by clinicians, for clinicians, relevant specialized knowledge is personalized at the patient level delivering medical knowledge side by side with patient data from the EMR for better care and more complete patient workups, resulting in improved clinically appropriate access for patients. To learn more about MedPearl, visit medpearl.com
About Providence
Providence is a national, not-for-profit Catholic health system comprising a diverse family of organizations and driven by a belief that health is a human right. With 51 hospitals, more than 1,100 physician clinics, senior services, supportive housing, and many other health and educational services, the health system and its partners employ more than 129,000 caregivers serving communities across seven states – Alaska, California, Montana, New Mexico, Oregon, Texas, and Washington, with system offices in Renton, Wash., and Irvine, Calif. Learn about our vision of health for a better world at Providence.org.
END
New Data: MedPearl clinical decision platform improves specialty referrals, boosts productivity, and reduces clinician time spent in the EMR
Results were published in New England Journal of Medicine Catalyst
2024-08-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Kessler Foundation scientists investigate effects of robotic postural stand training combined with spinal cord epidural stimulation
2024-08-21
East Hanover, NJ – August 21, 2024 – Kessler Foundation researchers have published a new clinical study investigating the effects of robotic postural stand training combined with spinal cord epidural stimulation (Stand-scES) on trunk control in individuals with high-level spinal cord injury (SCI). The open access article, “Effects of Robotic Postural Stand Training with Epidural Stimulation on Sitting Postural Control in Individuals with Spinal Cord Injury: A Pilot Study” (doi.org/10.3390/jcm13154309) was published in the Journal of Clinical ...
New center to improve robot dexterity selected to receive up to $52 million
2024-08-21
PITTSBURGH - Carnegie Mellon University will be a core partner in a new multi-institutional collaboration that has received $26 million from the National Science Foundation to launch an Engineering Research Center (ERC) dedicated to revolutionizing the ability of robots to amplify human labor.
Nine Carnegie Mellon University faculty members, with expertise ranging from Softbotics, engineering, and computer science to psychology, and diversity and inclusion, will help to develop highly dexterous robotic hands, user-friendly interfaces, ...
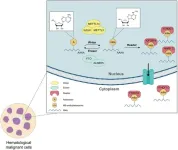
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA modification’s regulatory role in acute and chronic leukemia
2024-08-21
Epigenetics, the modification of chromosomes without altering DNA sequences, serves as a crucial regulatory mechanism for gene expression. Among the various epigenetic marks, N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modifications on RNA have gained significant attention in recent years for their role in various biological processes, including cancer development and progression. This article reviews the latest advances in understanding the role of m6A modifications in leukemia, a heterogeneous group of hematological malignancies.
Role of m6A Modification in Leukemia
m6A Writers and Erasers
m6A modifications ...
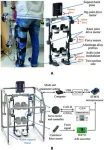
Revolutionary rehab robotics: A new leap in adaptive gait training
2024-08-21
In an era where technology increasingly merges with healthcare to enhance patient outcomes, a groundbreaking study conducted by Fuyang Yu and his colleagues introduces an innovative approach to lower limb rehabilitation. Their research, published in Cyborg Bionic Systems, outlines the development of a lower limb rehabilitation robot designed to significantly improve the safety and effectiveness of gait training through a novel method based on human-robot interaction force measurement.
Rehabilitation robots are ...
Targeted cancer cell therapy may slow endometrial cancer
2024-08-21
There may be a way to slow the growth of endometrial cancer through targeted cancer cell therapy, according to new research from the University of Missouri School of Medicine.
This year, around 65,000 women are expected to be diagnosed with endometrial cancer, the most common cancer of the female reproductive organs. An increased risk in development for multiple human cancers is associated with mutations in the PTEN protein, which normally regulates cell division and growth. The mutation allows cells to multiply uncontrollably.
Using mice models, Krystina Dunston, research lab manager and NextGen Precision Health researchers Tae Hoon Kim and Jae-Wook Jeong, studied the ...
Hepatic disease: a camu-camu fruit extract to reduce liver fat
2024-08-21
Québec City, August 21, 2024 – A research team from Université Laval has shown the benefits of camu-camu on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, which affects over seven million people in Canada. This exotic fruit reduces liver fat levels.
Over 12 weeks, thirty participants took either camu-camu extract or a placebo at different times in this randomized clinical trial. Participants underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to determine fat levels in the liver. Scientists observed a 7.43% reduction in liver lipids when study participants took camu-camu extract. With the ...
Quenching the intense heat of a fusion plasma may require a well-placed liquid metal evaporator
2024-08-21
Inside the next generation of fusion vessels known as spherical tokamaks, scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) envisioned a hot region with flowing liquid metal that is reminiscent of a subterranean cave. Researchers say evaporating liquid metal could protect the inside of the tokamak from the intense heat of the plasma. It’s an idea that dates back several decades and is tied to one of the Lab’s strengths: working with liquid metals.
“PPPL’s expertise in using liquid metals, ...
The power of face time: Insights from zebra finch courtship
2024-08-21
A new study on songbirds sheds light on the power of social interaction to facilitate learning, insights that potentially apply to human development.
McGill University researchers discovered that zebra finches deprived of early social experiences could still form strong bonds with a partner later in life. Once placed into cohabitation with a male, females that had never heard a mating song before could quickly develop a preference for his melody.
The findings, published in Proceedings of the Royal Society ...
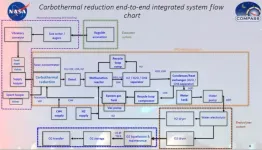
Near-term NASA Mars and lunar in situ propellant production: complexity versus simplicity
2024-08-21
First, lunar ISPP is analyzed from aspects of lunar resources, near-term lunar processes, carbothermal process, polar ice, and reduction of iron oxides. There are basically 4 potential lunar resources: (1) Silicates in regolith containing typically >40% oxygen. (2) Regolith containing FeO for hydrogen reduction. FeO content may vary from 5% to 14%, leading to recoverable oxygen content in the 1 to 3% range. (3) Imbedded atoms in regolith from solar wind (typically parts per million). (4) Water ice in regolith pores in permanently shadowed craters near the poles (unknown percentage but ...
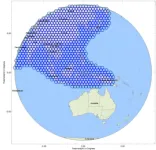
An active multi-beam antenna design method and its application for the future 6G satellite network
2024-08-21
First, the payload requirements and problems faced by traditional multi-beam antenna are described. The user beam of the VHTS payload system mainly uses Ka-band multi-beam antenna for a large range of area coverage, and the number of beams in the coverage area is not less than 500, usually using 7-color frequency reuse scheme(Fig. 2). At present, the spaceborne multi-beam antenna technology applied to high-throughput communication satellites is usually divided into multi-aperture multi-beam antenna and passive multi-feed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Vision sensing for intelligent driving: technical challenges and innovative solutions
To attempt world record, researchers will use their finding that prep phase is most vital to accurate three-point shooting
AI is homogenizing human expression and thought, computer scientists and psychologists say
Severe COVID-19, flu facilitate lung cancer months or years later, new research shows
Housing displacement, employment disruption, and mental health after the 2023 Maui wildfires
GLP-1 receptor agonist use and survival among patients with type 2 diabetes and brain metastases
Solid but fluid: New materials reconfigure their entire crystal structure in response to humidity
New research reveals how development and sex shape the brain
New discovery may improve kidney disease diagnosis in black patients
What changes happen in the aging brain?
Pew awards fellowships to seven scientists advancing marine conservation
Turning cancer’s protein machinery against itself to boost immunity
Current Pharmaceutical Analysis releases Volume 22, Issue 2 with open access research
Researchers capture thermal fluctuations in polymer segments for the first time
16-year study finds major health burden in single‑ventricle heart
Disposable vapes ban could lead young adults to switch to cigarettes, study finds
Adults with concurrent hearing and vision loss report barriers and challenges in navigating complex, everyday environments
Breast cancer stage at diagnosis differs sharply across rural US regions
Concrete sensor manufacturer Wavelogix receives $500,000 grant from National Science Foundation
California communities’ recovery time between wildfire smoke events is shrinking
Augmented reality job coaching boosts performance by 79% for people with disabilities
Medical debt associated with deferring dental, medical, and mental health care
AAI appoints Anand Balasubramani as Chief Scientific Programs Officer
Prior authorization may hinder access to lifesaving heart failure medications
Scholars propose transparency, credit and accountability as key principles in scientific authorship guidelines
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop DDINet for accurate and scalable drug-drug interaction prediction
IEEE researchers achieve 20x signal boost in cerebral blood flow monitoring with next-generation interferometric diffusing wave spectroscopy
IEEE researchers achieve low-power ultrashort mid-IR pulse compression
Deep-sea natural compound targets cancer cells through a dual mechanism
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
[Press-News.org] New Data: MedPearl clinical decision platform improves specialty referrals, boosts productivity, and reduces clinician time spent in the EMRResults were published in New England Journal of Medicine Catalyst