(Press-News.org)
While animals in drylands hone their natural senses to find vegetation, humans have developed “external eyes” to track these vital resources.
Scientists from the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) Agricultural Research Service (ARS) have created an advanced method that integrates high-frequency near-surface camera data with broader satellite imagery to better monitor and assess dryland ecosystems. Their approach could aid in taking timely action to prevent land degradation, contributing to improved environmental management and conservation strategies.
Their results were published in the Journal of Remote Sensing on July 8.
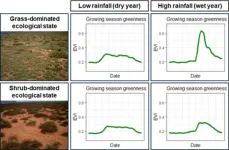
Drylands, including arid, semi-arid and dry sub-humid areas, account for over 40% of the Earth’s land surface and are vital for supporting diverse wildlife, crop production and carbon regulation. These areas, however, are prone to abrupt ecological state changes, such as shifts from grass-dominated to shrub-dominated landscapes, driven by climate change and unsustainable land use.
Drylands pose significant challenges for ecological monitoring due to their sparse vegetation cover, high spatial variability, and year-to-year fluctuations in vegetation growth. Traditional methods often fall short in accurately classifying and detecting changes in ecological states. To address this, the USDA-ARS researchers melded space and ground approaches to eagle-eye these ecosystems.
“We wanted to understand whether we could use images collected remotely from near-surface cameras or satellites to measure differences in dryland vegetation greenness over time and in response to rainfall,” said Emily R. Myers, a SCINet postdoctoral fellow with the USDA-ARS and lead author of this study.
The researchers’ goal was to use these differences to distinguish between different dryland ecological states. The team combined daily data from near-surface cameras (PhenoCam) with satellite imagery (Harmonized Landsat 8 and Sentinel-2, or HLS) at a desert grassland site in southwest New Mexico, analyzing data from 12 different locations over multiple years between 2014 and 2022.
“Measurements from near-surface cameras and satellites were able to distinguish between different dryland vegetation responses to rainfall,” said Dawn M. Browning, a senior research ecologist at the USDA-ARS and co-lead author of the study.
Their findings showed that grass-dominated states were the most affected by rainfall, with rapid spikes in greenness and productivity during wet growing seasons. Shrub-dominated states were less affected by growing season rainfall.
The distinct phenological responses of grass-dominated states can serve as indicators of grass productivity and ecological state change in drylands.
“These differences in greenness responses may help us map and monitor dryland states and productivity using remotely sensed imagery,” Myers said.
By refining remote sensing techniques, the researchers hope to identify and monitor more effectively dryland areas with significant grass cover. This insight could guide management strategies for maintaining grass cover and preventing shrub encroachment in these increasingly vulnerable ecosystems.
“We would like to explore more ways to characterize the growing season, with a particular focus on measurements that are sensitive to the rapid increases in greenness that are indicative of grassy productivity,” Browning said.
END
Data published today in the New England Journal of Medicine Catalyst reported that MedPearl, a Providence-developed clinician-built clinical decision platform, improves primary care clinician productivity, decreases time waste on administrative tasks and improves the quality of referrals sent to specialists.
The paper details operational outcomes from MedPearl’s use among more than 4,000 active monthly clinician users and shows statistically significant improvement in total productivity, after-hours time spent in the EMR and incremental margin per referral ...
East Hanover, NJ – August 21, 2024 – Kessler Foundation researchers have published a new clinical study investigating the effects of robotic postural stand training combined with spinal cord epidural stimulation (Stand-scES) on trunk control in individuals with high-level spinal cord injury (SCI). The open access article, “Effects of Robotic Postural Stand Training with Epidural Stimulation on Sitting Postural Control in Individuals with Spinal Cord Injury: A Pilot Study” (doi.org/10.3390/jcm13154309) was published in the Journal of Clinical ...
PITTSBURGH - Carnegie Mellon University will be a core partner in a new multi-institutional collaboration that has received $26 million from the National Science Foundation to launch an Engineering Research Center (ERC) dedicated to revolutionizing the ability of robots to amplify human labor.
Nine Carnegie Mellon University faculty members, with expertise ranging from Softbotics, engineering, and computer science to psychology, and diversity and inclusion, will help to develop highly dexterous robotic hands, user-friendly interfaces, ...
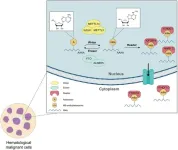
Epigenetics, the modification of chromosomes without altering DNA sequences, serves as a crucial regulatory mechanism for gene expression. Among the various epigenetic marks, N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modifications on RNA have gained significant attention in recent years for their role in various biological processes, including cancer development and progression. This article reviews the latest advances in understanding the role of m6A modifications in leukemia, a heterogeneous group of hematological malignancies.
Role of m6A Modification in Leukemia
m6A Writers and Erasers
m6A modifications ...
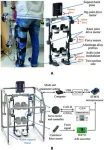
In an era where technology increasingly merges with healthcare to enhance patient outcomes, a groundbreaking study conducted by Fuyang Yu and his colleagues introduces an innovative approach to lower limb rehabilitation. Their research, published in Cyborg Bionic Systems, outlines the development of a lower limb rehabilitation robot designed to significantly improve the safety and effectiveness of gait training through a novel method based on human-robot interaction force measurement.
Rehabilitation robots are ...
There may be a way to slow the growth of endometrial cancer through targeted cancer cell therapy, according to new research from the University of Missouri School of Medicine.
This year, around 65,000 women are expected to be diagnosed with endometrial cancer, the most common cancer of the female reproductive organs. An increased risk in development for multiple human cancers is associated with mutations in the PTEN protein, which normally regulates cell division and growth. The mutation allows cells to multiply uncontrollably.
Using mice models, Krystina Dunston, research lab manager and NextGen Precision Health researchers Tae Hoon Kim and Jae-Wook Jeong, studied the ...
Québec City, August 21, 2024 – A research team from Université Laval has shown the benefits of camu-camu on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, which affects over seven million people in Canada. This exotic fruit reduces liver fat levels.
Over 12 weeks, thirty participants took either camu-camu extract or a placebo at different times in this randomized clinical trial. Participants underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to determine fat levels in the liver. Scientists observed a 7.43% reduction in liver lipids when study participants took camu-camu extract. With the ...
Inside the next generation of fusion vessels known as spherical tokamaks, scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) envisioned a hot region with flowing liquid metal that is reminiscent of a subterranean cave. Researchers say evaporating liquid metal could protect the inside of the tokamak from the intense heat of the plasma. It’s an idea that dates back several decades and is tied to one of the Lab’s strengths: working with liquid metals.
“PPPL’s expertise in using liquid metals, ...
A new study on songbirds sheds light on the power of social interaction to facilitate learning, insights that potentially apply to human development.
McGill University researchers discovered that zebra finches deprived of early social experiences could still form strong bonds with a partner later in life. Once placed into cohabitation with a male, females that had never heard a mating song before could quickly develop a preference for his melody.
The findings, published in Proceedings of the Royal Society ...
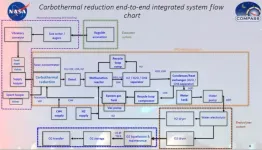
First, lunar ISPP is analyzed from aspects of lunar resources, near-term lunar processes, carbothermal process, polar ice, and reduction of iron oxides. There are basically 4 potential lunar resources: (1) Silicates in regolith containing typically >40% oxygen. (2) Regolith containing FeO for hydrogen reduction. FeO content may vary from 5% to 14%, leading to recoverable oxygen content in the 1 to 3% range. (3) Imbedded atoms in regolith from solar wind (typically parts per million). (4) Water ice in regolith pores in permanently shadowed craters near the poles (unknown percentage but ...