(Press-News.org) About The Study: Researchers found corresponding increases in hypertension prevalence as neighborhood disadvantage and the percentage of Black patients residing in a neighborhood increased in this cross-sectional study. A higher burden of midlife hypertension was identified in Black adults compared with other racial and ethnic groups that persisted across levels of socioeconomic disadvantage. This study also found that living in socioeconomically disadvantaged neighborhoods was associated with higher hypertension rates among people of all racial and ethnic backgrounds. Using spatial analysis techniques to identify neighborhoods in need, future research might investigate structural interventions to address place-based hypertension disparities.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jarrod E. Dalton, PhD, email daltonj@ccf.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.29764)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.29764?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=082324
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Neighborhood-level disparities in hypertension prevalence and treatment among middle-aged adults
JAMA Network Open
2024-08-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Strength training activates cellular waste disposal
2024-08-23
The elimination of damaged cell components is essential for the maintenance of the body’s tissues and organs. An international research team led by the University of Bonn has made significant findings on mechanisms for the clearing of cellular wastes, showing that strength training activates such mechanisms. The findings could form the basis for new therapies for heart failure and nerve diseases, and even afford benefits for manned space missions. A corresponding article has been published in the latest issue of the journal Current Biology. EMBARGOED: Do not publish until 5 pm CEST ...
Water activation induced strong interfacial hydrogen bonding interactions for efficient oxygen reduction reaction
2024-08-23
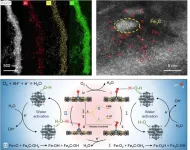
Exploring new energy storage and conversion technologies is crucial for sustainable human development. Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) and metal-air batteries are particularly promising due to their high energy efficiency and environmental friendliness. A key component in these technologies is the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) catalyst. Traditionally, ORR catalysts rely on expensive platinum group metals (PGM), which are cost-prohibitive for widespread use. This has spurred interest in developing non-precious metal alternatives, such as transition metal/nitrogen-doped carbon-based materials (M–N–C). Among these, Fe–N–C ...
Temperature regulates negative supercoils to modulate meiotic crossovers and chromosome organization
2024-08-23
This study is led by Prof. Shunxin Wang (State Key Laboratory of Reproductive Medicine and Offspring Health, Center for Reproductive Medicine, Institute of Women, Children and Reproductive Health, Shandong University) and Prof. Liangran Zhang (Advanced Medical Research Institute, Shandong University). In their study of meiosis in budding yeast, the research team found that yeast senses temperature changes by increasing the level of DNA negative supercoils to increase crossovers and modulate chromosome organization ...
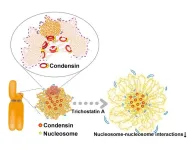
Single nucleosomes tracked in live cells during cell division using super-resolution microscopy
2024-08-23
Individual cells divide through a process called mitosis, during which the cell’s copied DNA is separated between two resulting daughter cells. Despite recent advances in cell biology, the mechanism by which DNA condenses during mitosis is still poorly understood. Researchers recently tracked small stretches of DNA wound around histone proteins, called nucleosomes, to better characterize nucleosome behavior during cell division.
DNA is organized as chromatin, which are dynamic structures comprised of DNA, RNA, and proteins that regulate the accessibility of genes for expression and the overall configuration of genetic material in the cell. Histone proteins, for example, are positively ...
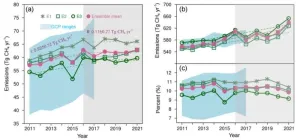
Slow down in China’s methane emission growth
2024-08-23
Methane is a potent greenhouse gas. Since the Industrial Revolution, atmospheric methane concentrations have nearly doubled, with its radiative forcing accounting for one-third of all greenhouse gases. As one of the world's largest methane emitters, China made a clear commitment as early as 2007 to "strive to control the growth rate of methane emissions." The country's 12th, 13th, and 14th Five-Year Plans all proposed measures to control methane emissions. In 2023, China released the "Methane Emission Control Action ...
Socioeconomics shape children’s connection to nature more than where they live
2024-08-23
The income and education levels of a child’s environment determine their relationship to nature, not whether they live in a city or the countryside. This is the finding of a new study conducted by researchers at Lund University, Sweden. The results run counter to the assumption that growing up in the countryside automatically increases our connection to nature, and yet the study also shows that nature close to home increases children’s well-being.
There is a general concern that, with urbanisation, people have lost contact with nature. According to research, less contact ...
The higher the environmental stress, the lower the resistance to global change
2024-08-23
An international study led by Institute of Natural Resources and Agrobiology of Seville (IRNAS-CSIC), of the Spanish National Research Council (CISC), has shown that as the number of global change factors increases, terrestrial ecosystems become more sensitive to the impacts of global change. The results, published in the prestigious journal Nature Geoscience, show that the resistance of our ecosystems to global change decreases significantly as the number of environmental stressors increases, especially when this stress is sustained over time.
This is the conclusion reached by the Biodiversity and Ecosystem Functioning ...
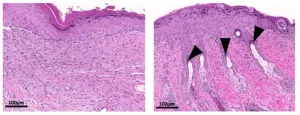
Intestinal parasite could hold key to scar-free wound healing, study suggests
2024-08-23
Researchers at Rutgers University in New Jersey have discovered that a protein produced by parasitic worms in the gut enhances wound healing in mice. The study, to be published August 23 in the journal Life Science Alliance (LSA), reveals that applying the protein to skin wounds speeds up wound closure, improves skin regeneration, and inhibits the formation of scar tissue. Whether the protein can be harnessed to enhance wound healing in human patients remains to be seen.
Skin wounds must be rapidly closed in order to prevent infection, but rapid wound closure can favor the development of scar tissue instead of properly regenerated skin. The balance between scarring ...
Breakthroughs in prostate cancer: New insights into biomarkers and probes
2024-08-23
In a recent comprehensive review published in Cyborg Bionic Systems, researchers led by Keyi Li from the General Hospital of Northern Theater Command in Shenyang, along with international collaborators, detail significant advances in the identification and application of biomarkers for prostate cancer (PCa). This critical insight is pivotal as prostate cancer remains one of the most common malignancies among men globally, emphasizing the urgent need for effective diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
Prostate cancer is characterized by a multitude of molecular aberrations that complicate its early ...
New approach for profiling complex dynamics at the single-molecule level
2024-08-23
A team of researchers led by Professor Sebastian Deindl at Uppsala University has developed a pioneering method that vastly improves the ability to observe and analyse complex biological processes at the single-molecule level. Their work is set to be published in the upcoming issue of the journal Science.
“With our new technique, we can now extend single-molecule biophysics to the genome scale. This advance is expected to significantly deepen our understanding of how nucleic-acid interacting proteins function in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] Neighborhood-level disparities in hypertension prevalence and treatment among middle-aged adultsJAMA Network Open