(Press-News.org) Colorado State University is leading a new interdisciplinary research project into the ways predators and prey in sensitive ecosystems may react to climate change based on their physiology, genetics and relationships to each other.
Led by Professor Chris Funk in the Department of Biology, the project is funded by the National Science Foundation’s Organismal Response to Climate Change program and will focus on interactions between cutthroat trout and tailed frogs in Pacific Northwest streams. This approach is one of the first times researchers have tried to test both the effects of evolution and species interactions to better understand species and ecosystem resilience and vulnerability to climate change.
The CSU team will work on the $1.7 million project with partners over the next four years in the field and lab. Funk said a key goal is to understand how relationships between different species, the coastal versus interior regional climatic variation, and elevation may shape responses to increasing water temperatures due to climate change.
“We are studying the adaptive capacity of these two closely linked species to better understand their ability to acclimate, evolve, or even to move to new locations in the face of changes to water flow or the broader food web,” he said. “This requires an integrated approach that combines expertise in physiology, genomics and ecology, along with skills in modeling and large data sets to understand and share the findings. We need all that expertise to pull this off.”
Cutthroat trout and the tailed frog tadpoles they feed on are an excellent pair to study and compare for this project, said Funk. Both are cold-water specialists known to be sensitive to warming temperatures, and both play key roles in Pacific Northwest stream ecosystems of which they are a part. Funk also noted that the trout – as predators – have lower abundance and a smaller genetic pool compared to the more numerous tailed frogs. As a result, the trout may not be as well adapted to local temperatures, making them more sensitive and vulnerable to climate change.
Field researchers will conduct work at 100 sites – including five different watersheds in Oregon, Washington and Montana – to collect genetic material from trout and frogs. The team will also collect information about their diet, thermal tolerance, and stream temperature and flow.
Interdisciplinary research is key to project’s conservation goals
CSU is joined on the project by researchers from the University of Montana and the University of Idaho. Other contributors include the U.S. Geological Survey and USDA Forest Service, along with the Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife.
Alexandra Fraik is a research scientist with the Forest Service and a key contributor to the project. She specializes in using genomic tools to conduct research that informs managers about threatened and endangered species and their habitat. During the project, Fraik will use population genetic tools to help determine the traits and mechanisms that different species of cutthroat trout and tailed frog have evolved in response to different environmental conditions.
She commented, “I’m excited to work with scientists from a variety of disciplines and backgrounds. It’s a great opportunity for cross collaboration and a way to help integrate cutting-edge science into decision making around managing these species. It could also provide a template for studying co-evolution of other species in changing climates.”
An additional goal of the project is to support conservation activities around these two species and the cold-water ecosystems they inhabit. To that end, the team plans to develop a simplified web-based modeling tool that natural resource managers can use to inform decision making. The final product will pull from data collected on changing environments, food webs and species interactions to generate models showcasing climate change vulnerabilities for a wide range of species.
Funk said that tool could be useful for a variety of situations beyond the Pacific Northwest region.
“This will be a powerful tool for officials considering conservation and management activities for fisheries, as an example. But it could also have broader applications across ecosystems, as the same predator-prey relationships that inform our work are applicable here as well,” he said.
END
NSF funds research on the effects of evolution and food webs in climate change response
Field work in Pacific Northwest will collect genetic material from trout and frogs
2024-08-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Children's Brain Tumor Network hosts 2024 CBTN Summit to transform scientific research and patient care
2024-08-26
What:
The 2024 CBTN Summit hosted by the Children's Brain Tumor Network (CBTN) assembles the brightest minds in Pediatric Brian Tumor research for this annual conference. The event is free but attendees must register in advance.
Register at network.cbtn.org/cbtn-summit
Where:
In person at AWS Headquarters
Amazon WAS16 Aurora, 1770 Crystal Dr, Arlington, VA 22202
Virtual attendance available worldwide.
When:
October 9-11, 2024
Why:
This event is an opportunity ...
Long-term prognosis of patients with myocarditis attributed to COVID-19 mRNA vaccination, SARS-CoV-2 infection, or conventional etiologies
2024-08-26
About The Study: Patients with post–COVID-19 mRNA vaccination myocarditis, contrary to those with post–COVID-19 myocarditis, show a lower frequency of cardiovascular complications than those with conventional myocarditis at 18 months. However, affected patients, mainly healthy young men, may require medical management up to several months after hospital discharge.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Laura Semenzato, MSc (laura.semenzato@assurance-maladie.fr) and Mahmoud Zureik, MD, PhD (Mahmoud.ZUREIK@ansm.sante.fr).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The ...
LZ experiment sets new record in search for dark matter
2024-08-26
Figuring out the nature of dark matter, the invisible substance that makes up most of the mass in our universe, is one of the greatest puzzles in physics. New results from the world’s most sensitive dark matter detector, LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ), have narrowed down possibilities for one of the leading dark matter candidates: weakly interacting massive particles, or WIMPs.
LZ, led by the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), hunts for dark matter from a cavern nearly one mile underground at the Sanford Underground Research Facility in South Dakota. The experiment’s new results explore weaker dark matter interactions ...
Astrophysicists use AI to precisely calculate universe’s ‘settings’
2024-08-26
The standard model of the universe relies on just six numbers. Using a new approach powered by artificial intelligence, researchers at the Flatiron Institute and their colleagues extracted information hidden in the distribution of galaxies to estimate the values of five of these so-called cosmological parameters with incredible precision.
The results were a significant improvement over the values produced by previous methods. Compared to conventional techniques using the same galaxy data, the approach yielded less than half ...
SETI Institute starts first low frequency search for alien technology in distant galaxies
2024-08-26
August 26, 2024, Mountain View, CA -- The SETI Institute, the Berkeley SETI Research Center and the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research announced a groundbreaking study using the Murchison Widefield Array (MWA) in Western Australia. Led by Dr. Chenoa Tremblay of the SETI Institute and Prof. Steven Tingay of Curtin University, this research is the first to search for signs of alien technology in galaxies beyond our own, focusing on low radio frequencies (100 MHz). This innovative study used the MWA’s large field of view (FOV), allowing the team to cover about 2,800 galaxies in one observation, of which 1300 we know the distance to. Usually, the search for extraterrestrial ...
Bicycle rolling-stop laws don’t lead to unsafe behavior by riders or motorists, research shows
2024-08-26
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Laws that let bicyclists treat stop signs as yield signs lead neither riders nor motorists to act unsafely, according to a groundbreaking Oregon State University study.
The project by OSU College of Engineering researchers featured a novel experimental technique – linking separate bicycle and motor vehicle simulators – and the findings are important as more and more states consider bicycle rolling-stop legislation, said David Hurwitz, the study’s leader.
“It required fully connecting two independent simulators, running subjects in pairs simultaneously and having each subject interacting with an avatar of the other in a shared virtual ...
How a retracted paper affected the course of Alzheimer’s research (video)
2024-08-26
WASHINGTON, Aug. 26, 2024 — In June 2024, a landmark Alzheimer's research paper was retracted due to fraud allegations. Did we waste billions of dollars and thousands of hours of scientists’ time? Maybe not. There are now two potentially helpful drugs on the market targeting the subject of the paper: amyloid beta. This video breaks down the amyloid-beta hypothesis, the fraud itself and where we go from here.
Reactions is a video series produced by the American Chemical Society and PBS Digital Studios. Subscribe to Reactions and follow us on X, formerly Twitter @ACSReactions.
The American Chemical ...
Genotype Matters: Tailored screening for germline CHEK2 variants
2024-08-26
“In our study, we postulated that these differences were driven by three common low-risk (LR) missense variants: p.I157T, p.S428F, and p.T476M, all of which have a BC odds ratio of <1.4.”
BUFFALO, NY- August 26, 2024 – A new editorial was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on July 10, 2024, entitled, “Genotype matters: Personalized screening recommendations for germline CHEK2 variants.”
Recognized as a moderate-risk gene, CHEK2—responsible for encoding the CHK2 protein, ...
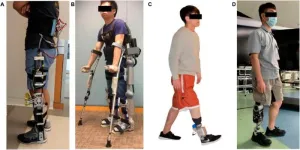
Interlimb and intralimb synergy modeling for lower limb assistive devices: Modeling methods and feature selection
2024-08-26
A research paper by scientists at Hainan University proposed FSS-eq2Seq as a 2-stage strategy for gait synergy modeling in lower limb assistive devices to achieve synergic and user-adaptive trajectories that improve human-machine interactions.
The new research paper, published on Jul. 03 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, indicatedSeq2Seq outperforms LSTM, RNN, and GRU in both interlimb and intralimb synergy modeling. Further, FS significantly improves Seq2Seq’s modeling performance.
The concept of gait synergy provides novel human-machine interfaces and has been applied ...
Darwin’s fear was unjustified: Writing evolutionary history by bridging the gaps
2024-08-26
Fossils are used to reconstruct evolutionary history, but not all animals and plants become fossils and many fossils are destroyed before we can find them (e.g., the rocks that contain the fossils are destroyed by erosion). As a result, the fossil record has gaps and is incomplete, and we’re missing data that we need to reconstruct evolutionary history. Now, a team of sedimentologists and stratigraphers from the Netherlands and the UK examined how this incompleteness influences the reconstruction of evolutionary history. To their surprise, they found that the incompleteness itself is actually not such a big issue. “It’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
[Press-News.org] NSF funds research on the effects of evolution and food webs in climate change responseField work in Pacific Northwest will collect genetic material from trout and frogs