(Press-News.org) New methods to shape RNA molecules into circles could lead to more effective and long-lasting therapies, shows a study by researchers at the University of California San Diego. The advance holds promise for a range of diseases, offering a more enduring alternative to existing RNA therapies, which often suffer from short-lived effectiveness in the body.
The work was published Aug. 26 in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
RNA molecules have emerged as powerful tools in modern medicine. They can silence genes through small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) or serve as templates for making therapeutic proteins, as seen with messenger RNAs (mRNAs). Unlike gene editing technologies, which make permanent changes to DNA, RNA therapies offer a temporary but highly targeted approach.
However, one major challenge is RNAs do not last long in the body, which limits their effectiveness. The concept of circular RNAs (cRNAs) have gained traction as a solution to this challenge. Circular RNAs, unlike their linear counterparts, have a closed-loop structure that renders them more resistant to degradation. The problem is that existing methods for creating circular RNAs are complex and inefficient.
To overcome these hurdles, researchers led by Prashant Mali, a professor in the Shu Chien-Gene Lay Department of Bioengineering at UC San Diego, developed two new methods for producing circular RNAs that are simple and scalable. One method occurs inside cells using a naturally occurring protein called RtcB, to splice RNA strands into loops. The other method, in contrast, uses a type of bacterial enzyme known as group II introns to form circular RNAs outside of cells. The researchers also developed simple purification steps that significantly boost the yield of circular RNAs. These advancements mean that circular RNAs can be produced with greater ease and quantities than previously possible.
The circular RNAs were tested in heart muscle cells and neurons. They displayed enhanced stability and biological activity, outperforming traditional linear RNAs in both cell types. These findings suggest that circular RNAs could be beneficial in treating conditions that affect the heart and nervous system.
Next, researchers are working to extend these studies into additional in vivo settings.
END
Closing the RNA loop holds promise for more stable, effective RNA therapies
2024-08-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
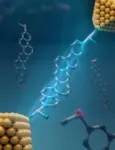
Controlling molecular electronics with rigid, ladder-like molecules
2024-08-26
As electronic devices continue to get smaller and smaller, physical size limitations are beginning to disrupt the trend of doubling transistor density on silicon-based microchips approximately every two years according to Moore’s law. Molecular electronics—the use of single molecules as the building blocks for electronic components—offers a potential pathway for the continued miniaturization of small-scale electronic devices. Devices that utilize molecular electronics require precise control over the flow of electrical current. However, the dynamic nature of these single molecule components affects device performance and impacts ...
Marine science oxygen produced in the deep sea raises questions about extraterrestrial life
2024-08-26
Over 12,000 feet below the surface of the sea, in a region of the Pacific Ocean known as the Clarion-Clipperton Zone (CCZ), million-year-old rocks cover the seafloor. These rocks may seem lifeless, but nestled between the nooks and crannies on their surfaces, tiny sea creatures and microbes make their home, many uniquely adapted to life in the dark.
These deep-sea rocks, called polymetallic nodules, don’t only host a surprising number of sea critters. A team of scientists that includes Boston University experts has discovered they ...
What microscopic fossilized shells tell us about ancient climate change
2024-08-26
At the end of the Paleocene and beginning of the Eocene epochs, between 59 to 51 million years ago, Earth experienced dramatic warming periods, both gradual periods stretching millions of years and sudden warming events known as hyperthermals.
Driving this planetary heat up were massive emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases, but other factors like tectonic activity may have also been at play.
New research led by University of Utah geoscientists pairs sea surface temperatures with levels ...
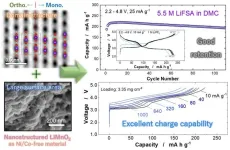
Li-ion batteries show promise as cheap and sustainable alternative to Ni/Co materials
2024-08-26
Lithium-ion (or Li-ion) batteries are heavy hitters when it comes to the world of rechargeable batteries. As electric vehicles become more common in the world, a high-energy, low-cost battery utilizing the abundance of manganese (Mn) can be a sustainable option to become commercially available and utilized in the automobile industry. Currently, batteries used for powering electric vehicles (EVs) are nickel (Ni) and cobalt (Co)-based, which can be expensive and unsustainable for a society with a growing desire for EVs. By switching the positive electrode ...
The Lundquist Institute announces updates to its Board of Directors
2024-08-26
The Lundquist Institute for Biomedical Innovation at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center (TLI) announced updates to its Board of Directors today. TLI welcomes one new distinguished member and thanks the two outgoing members for their invaluable contributions.
“On behalf of the Board, I am delighted that Dr. Bill Dorfman, a global leader in cosmetic dentistry, has joined the TLI Board. Dr. Dorfman's extensive expertise and commitment to philanthropy make him an invaluable addition to our leadership,” said Mitchel Sayare, PhD, TLI Board ...
Research from UTHealth Houston finds parents who recently experienced intimate partner violence had higher potential for parenting stress and child maltreatment
2024-08-26
Parents who recently experienced intimate partner violence reported more parenting stress and higher potential for child maltreatment, and were less likely to use positive parenting strategies, according to UTHealth Houston research published Aug. 26, 2024, in JAMA Pediatrics.
“Our findings demonstrate the collateral damage of domestic violence — that the negative consequences are not limited to the couple and instead have the potential to affect how they parent, and ultimately the health of their children. We must expend every effort to prevent this public health problem,” said Jeff Temple, PhD, ...
Research spotlight: Key regulators of pd-1 in melanoma cells and the immune system’s response
2024-08-26
How would you summarize your study for a lay audience?
Immune checkpoint inhibitors are cancer fighting drugs that help the immune system do its job of detecting and attacking tumor cells. Programmed Cell Death 1 (PD-1) is a common target for this type of drug—it is a protein that sits on the surface of T cells and helps regulate the immune system’s response to neighboring cells, both normal and cancerous. While most research efforts to date have focused on PD-1’s role in T cells, it is also active in many other kinds of cells—including cancer cells as first demonstrated by the Schatton ...
Lighting the way for quantum innovation
2024-08-26
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — Sandia National Laboratories and Arizona State University, two research powerhouses, are collaborating to push the boundaries of quantum technology and transform large-scale optical systems into compact integrated microsystems.
Nils Otterstrom, a Sandia physicist specializing in integrated photonics, is at the forefront of scaling down optical systems to the size of a chip. This innovation offers performance advantages and scalability for an array of applications from advanced computing to secure communications.
“Integrated ...
Spin squeezing for all
2024-08-26
Nothing in science can be achieved or understood without measurement. Today, thanks to advances in quantum sensing, scientists can measure things that were once impossible to even imagine: vibrations of atoms, properties of individual photons, fluctuations associated with gravitational waves.
A quantum mechanical trick called “spin squeezing” is widely recognized to hold promise for supercharging the capabilities of the world’s most precise quantum sensors, but it’s been notoriously difficult to achieve. In new research, Harvard physicists describe how they’ve put spin squeezing ...
NSF funds research on the effects of evolution and food webs in climate change response
2024-08-26
Colorado State University is leading a new interdisciplinary research project into the ways predators and prey in sensitive ecosystems may react to climate change based on their physiology, genetics and relationships to each other.
Led by Professor Chris Funk in the Department of Biology, the project is funded by the National Science Foundation’s Organismal Response to Climate Change program and will focus on interactions between cutthroat trout and tailed frogs in Pacific Northwest streams. This approach is one of the first times researchers have tried to test both the effects of evolution and ...