(Press-News.org) PULLMAN, Wash. – While meant to simulate wood bats, regulation USA Baseball metal bats are more forgiving than wood for young players who might not connect with the ball on a bat’s optimal “sweet spot.”
After testing wood bats and two types of metal bats with youth players, Washington State University researchers found that the exit speed of a hit ball was as much as 5% faster with metal bats over wood. Analyzing the data, they found that the performance of the USA Baseball metal bats at the sweet spot was similar to wood. It was when the hits were on less optimal areas that there was a bigger difference.
“There’s more of a penalty when you’re not on the sweet spot with wood bats than with the other metal bats,” said Lloyd Smith, director of WSU’s Sport Science Laboratory and lead author on the study published in The Journal of Sports Engineering and Technology.
Smith’s team has been working with USA Baseball to develop a new wood-like metal bat standard. This study further investigated the performance of the bats designed to meet that standard with lab and field studies—in comparison to wood bats as well as the metal bats previously used in youth baseball, known as BPF 1.15.
The researchers had 52 players, with an average age of 12, take several swings with each type of bat in a batting cage for a total of more than 1,500 swings. The players, bats and balls all had motion sensors attached to measure speed of the swing as well as the balls’ exit speed.
As expected, baseballs hit with the BPF 1.15 metal bats had higher exit speeds than the wood bats, since these metal bats were discontinued in youth leagues because of their performance advantage. For the USA Baseball standard bats, the exit speeds were closer to that of wood but were still on average higher. The data analysis revealed that the difference was in hits that were outside the highest performance spot on the bat.
Metal bats were adopted in amateur baseball leagues back in the 1970s in part because wood bats break and can be costly over time. Soon players noticed the hollow metal bats conferred an advantage from their “trampoline effect” –an advantage that grew as companies competed to make a better bat. Seeing potential hazards and changes to the game from these metal bats, league officials tried to reign this in starting in the 1990s, ultimately restricting the use of metal bats to those that performed in a similar way to wood.
As this study shows, a small performance advantage remains even with the USA Baseball bat, but it is one that is acceptable to officials. There are also good reasons for leagues and coaches to use them over wood bats, Smith said. Namely, that performance advantage and their lighter weight can mean better batting averages for young players which can help leagues keep kids more excited about the game.
“Wood is still heavy. Part of baseball is hitting the ball far, but the other part is just hitting the ball,” he said. “If you have a heavy bat, you're going to have a harder time making contact because it’s harder to control.”
Notably, despite the bat performance differences in this study, the skill of the hitters was still the biggest factor in how fast the ball came off the bat. Smith emphasized that if players really want to improve their batting average, the best thing to do is not to improve their bat, but themselves.
“If you’re really trying to hit the ball far, you’re going to get a much bigger payoff by working out and getting stronger, especially if you’re a young kid and growing fast. That’s going to have a much larger effect on how hard you hit the ball, then on what bat you buy,” he said.
END
Metal baseball bats still help Little Leaguers hit a little better
2024-08-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
AI spots cancer and viral infections at nanoscale precision
2024-08-27
Researchers at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG), the University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU), Donostia International Physics Center (DIPC) and the Fundación Biofisica Bizkaia (FBB, located in Biofisika Institute) have developed an artificial intelligence which can differentiate cancer cells from normal cells, as well as detect the very early stages of viral infection inside cells. The findings, published today in a study in the journal Nature Machine Intelligence, pave the way for improved diagnostic techniques and new monitoring strategies for disease.
The tool, AINU (AI of the NUcleus), scans high-resolution images of cells. The ...
AI-based virtual voice assistant successfully bridges care gap for heart patients
2024-08-27
London, United Kingdom – 27 August 2024: Clinical follow-up using virtual voice technology helped identify complications after transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) with a high degree of patient satisfaction, according to research presented at ESC Congress 2024.1
Explaining the rationale for the development of the virtual voice assistant for TAVI patients, study author Dr. Marta Herrero Brocal from the Dr. Balmis General University Hospital of Alicante, Spain said: “Aortic valve stenosis is common, especially in the ageing population.2 It can be treated with surgery ...
Urban noise pollution may impact cardiovascular risk prediction and prognosis after a heart attack
2024-08-27
London, United Kingdom – 27 August 2024: Research from two studies in different European cities1,2 highlights that urban noise pollution has a significant negative impact on heart health, according to data presented at ESC Congress 2024.
“The DECIBEL-MI study shows that young patients aged 50 years or less who had a myocardial infarction (MI) had been exposed to higher levels of noise than the general population. The study demonstrates that urban noise could significantly increase the risk of early-onset MI in young people with low traditional risk factors. Including ...
Discovery of a rare genotype causing primary ovarian insufficiency
2024-08-27
Scientists at deCODE genetics and collaborators, have identified a sequence variant in the CCDC201 gene that when inherited from both parents homozygous causes menopause on average nine years earlier.
deCODE genetics, a subsidiary of Amgen, and collaborators from Iceland, Denmark, the UK, and Norway published a study in Nature Genetics today revealing a rare genotype with a significant impact on women's health.
Age at menopause significantly affects fertility and disease risk. This research focused on ...
Menopause potentially linked to adverse cardiovascular health through blood fat profile changes
2024-08-27
London, United Kingdom – 27 Aug 2024: New research presented at the ESC Congress 2024 in London, UK (30 August – 2 September) shows that women in the menopause transition period show changes in their blood cholesterol profiles which could have an adverse impact on their cardiovascular health.
“There is an increase in ‘bad’ low-density type lipoprotein (LDL) particles and a decrease in ‘good’ high-density lipoprotein particles (HDL) that takes place during and after the menopause transition,” says study author Dr Stephanie Moreno, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, USA. “Taken ...
Women in global fisheries industry fall through the safety net
2024-08-27
Millions of women who work in the fisheries industry are being left behind as technologies develop to counter the effects of climate change and economic pressures.
New research led by the University of East Anglia (UEA) looks specifically at post-harvest fisheries and aquaculture, where women constitute 50 per cent of the total workforce. Despite their significant contributions women often remain invisible, are unpaid or underpaid, their work seen as an extension of household work.
The findings, ‘A systematic review of the impact of post-harvest aquatic food ...
In six new rogue worlds, Webb Telescope finds more star birth clues
2024-08-27
The James Webb Space Telescope has spotted six likely rogue worlds—objects with planetlike masses but untethered from any star’s gravity—including the lightest ever identified with a dusty disk around it.
The elusive objects offer new evidence that the same cosmic processes that give birth to stars may also play a common role in making objects only slightly bigger than Jupiter.
“We are probing the very limits of the star forming process,” said lead author Adam Langeveld, an astrophysicist at Johns Hopkins University. “If you have an object that looks like a young Jupiter, is it possible that ...
Star lives and afterlives
2024-08-27
A two-faced star, a star as massive as the Sun but as compact as the Moon, and star ‘corpses’ that engulf entire planets and disrupt planetary orbits. Ilaria Caiazzo, an astrophysicist who has made stunning discoveries, joins the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) as a new assistant professor. Her path led her from philosophy to studying stellar evolution and death while managing her broad interests including movie production.
Ilaria Caiazzo has always had a broad spectrum of interests. Her path to astrophysics started in philosophy and ...
Dungeons and Dragons can help autistic people gain confidence and find their inner hero
2024-08-27
Dungeons and Dragons is a hugely popular roleplaying game enjoyed by millions of people all over the world, both in person and online, every day.
However, new research has found it could be particularly beneficial for people with autism, giving them a safe space to engage in social interactions away from some of the challenges they face in their daily lives.
The study, published in the journal Autism, was led by researchers from the University of Plymouth’s School of Psychology along with colleagues at Edge ...
KKH study: Exclusive breastfeeding leads to greater weight loss in women with high body mass index as compared to women with normal weight
2024-08-27
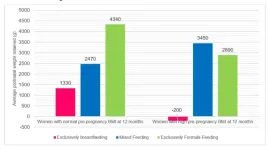
27 August 2024, Singapore – A KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital (KKH) study[1] on breastfeeding practices revealed that among the women who exclusively breastfed, those with high body mass index[2] (BMI) before pregnancy lost more weight than women with a healthy BMI pre-pregnancy.
Women with high BMI who exclusively breastfed, in addition to losing their pregnancy weight, lost an extra 200 grammes on average, 12 months after childbirth. Women with normal BMI who exclusively breastfed lost weight ...