(Press-News.org) In recent years, advances in photonics and materials science have led to remarkable developments in sensor technology, pushing the boundaries of what can be detected and measured. Among these innovations, non-Hermitian physics has emerged as a crucial area of research, offering new ways to manipulate light and enhance sensor sensitivity. A recent study published in Advanced Photonics Nexus reports a breakthrough in this field, presenting a new type of sensor that leverages exceptional points (EPs) to achieve unprecedented levels of sensitivity.
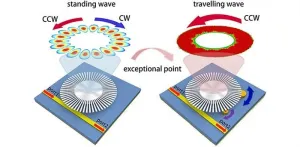
This study introduces a highly sensitive and reconfigurable sensor based on a single spoof localized surface plasmon (LSP) resonator. Exceptional points are unique spectral singularities where eigenvalues and their corresponding eigenvectors converge, significantly boosting the sensitivity of optical sensors. Traditional EP-based sensors, such as whispering gallery mode (WGM) microtoroids, have demonstrated enhanced sensitivity compared to conventional sensors. However, these sensors face limitations: their EPs are fixed after fabrication, which makes precise adjustments challenging, and they often operate within a narrow frequency range, struggling to detect very small particles due to constraints in perturbation strength and excitation efficiency.
The novel sensor design addresses these issues by incorporating spoof LSP resonators, which simulate the behavior of localized surface plasmons and offer greater flexibility. Suspended above a microstrip line and paired with two movable Rayleigh scatterers, this setup allows for dynamic reconfiguration of EP states across a wide frequency range. This adaptability makes the sensor more robust to fabrication imperfections and enhances its capability to detect extremely small particles.
Key features of the new sensor include:
Reconfigurability: Adjustable Rayleigh scatterers enable dynamic formation and reconfiguration of EPs, improving the sensor’s precision and flexibility.
Enhanced perturbation strength: Confining electromagnetic fields to the resonator's surface significantly increases sensitivity to perturbations from surrounding particles.
Multipolar mode excitation: The design supports various plasmonic resonance modes, expanding the sensor's operational bandwidth and detection range.
This advancement represents a significant leap forward in sensor technology, offering exceptional sensitivity for detecting particles as small as 0.001 times the wavelength of light and opening new possibilities for applications in scientific research and industry.
Read the original Gold Open Access article by Y. Zhang, H. Hu, et al., “Reconfigurable exceptional point- based sensing with 0.001λ sensitivity using spoof localized surface plasmons,” Adv. Photon. Nexus 3(5) 056004 (2024), doi 10.1117/1.APN.3.5.056004.
END
New sensor technology enhances detection of tiny particles
Reconfigurable exceptional point-based sensing technology achieves unprecedented sensitivity
2024-08-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New technology ‘lights up’ bacteria in wounds for better infection prevention
2024-08-27
LOS ANGELES — Over 6.5 million Americans experience chronic wounds — wounds that do not heal after a few months. Almost all such wounds contain bacteria, which, if not detected and removed, can lead to severe infection and resulting complications, including amputation if a limb is involved.
This is especially true for patients with diabetic foot ulcers (open sores), which affects one-third of people with diabetes. Approximately 20% of those who develop a diabetic foot ulcer will require a lower-extremity amputation, according ...
UCLA receives $120 million from Alya and Gary Michelson for new California Institute for Immunology and Immunotherapy
2024-08-27
UCLA has received a $120 million commitment from surgeon, inventor and philanthropist Dr. Gary Michelson and his wife, Alya, to kick-start the California Institute for Immunology and Immunotherapy, an innovative public-private partnership aimed at spurring breakthrough discoveries that prevent and cure diseases and catalyze economic growth and innovation in Los Angeles.
Michelson, a spine surgeon and prolific inventor who holds nearly 1,000 individual patents, is co-founder and chair of the board of the institute, which will be housed at UCLA’s state-of-the-art research park.
The gift, distributed via ...
Dunick receives funding for Center For Economic Education
2024-08-27
Dunick Receives Funding For Center For Economic Education
Jason Dunick, Associate Chair and Term Associate Professor, Economics, College of Humanities and Social Sciences (CHSS), received $108,692 from Virginia Council on Economic Education for: “Center for Economic Education.”
Dunick will use this funding to support the continuation of the services of the Center for Economic Education. The Center supports K-12 teachers who are teaching economics and personal finance in Virginia.
This grant represents the renewal of a long-standing relationship with the ...
National Institutes of Health awards $2.4 million grant to cross-disciplinary team of researchers to study psychedelics for methamphetamine addiction
2024-08-27
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Media Contacts:
Colleen McDonald
Sr. Consultant, Earned Media
Kara Reed
Director of Development
Lisa Babin
Executive Director of Communications
Medical College of Wisconsin
University of California San Diego
LSU Health Shreveport
414.801.3146 | cmcdonald@mcw.edu
217.390.6629 | k3hendrickson@ucsd.edu
318.675.8769 | lisa.babin@lsuhs.edu
Milwaukee, Wis., August 27, 2024 – John McCorvy, PhD, Assistant Professor in the Department ...
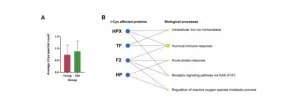
Trioxidized cysteine and aging: Beyond proteinopathic paradigms
2024-08-27
“The results indicated a significant increase in cumulative t-Cys levels and the total number of t-Cys residues in aging and aged mice proteomes compared to young groups.”
BUFFALO, NY- August 27, 2024 – A new research perspective was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 15 on July 25, 2024, entitled, “Trioxidized cysteine and aging: a molecular binomial that extends far beyond classical proteinopathic paradigms.”
Oxidative stress (OS) - characterized by an imbalance between oxidants and antioxidants - leads to the formation ...
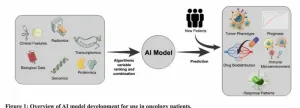
Artificial intelligence: Revolutionizing precision oncology
2024-08-27
“Properly leveraged AI-based techniques could herald a new era of precision medicine guided by non-invasive, imaging-based disease evaluation."
BUFFALO, NY- August 27, 2024 – A new editorial was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on August 26, 2024, entitled, “Artificial intelligence: A transformative tool in precision oncology.”
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing society and healthcare, opening new possibilities for precision medicine. In oncology, immunotherapy (IO) has similarly transformed cancer treatment with novel ...
How much microplastic are you drinking? New UBC tool can tell you in minutes
2024-08-27
Micro- and nanoplastics are in our food, water and the air we breathe. They are showing up in our bodies, from testicles to brain matter.
Now, University of British Columbia researchers have developed a low-cost, portable tool to accurately measure plastic released from everyday sources like disposable cups and water bottles.
The device, paired with an app, uses fluorescent labeling to detect plastic particles ranging from 50 nanometres to 10 microns in size – too small to be detected by the naked eye – and delivers results in minutes.
The method and findings are detailed in ACS Sensors.
“The breakdown of larger plastic pieces into microplastics ...
Race and ethnicity and diagnostic testing for common conditions in the acute care setting
2024-08-27
About The Study: White patients discharged from the emergency department with a nonspecific diagnosis of interest were significantly more likely than Black patients to receive related diagnostic testing in this study. The extent to which this represents diagnostic test overuse in white patients vs undertesting and missed diagnoses in Black patients deserves further study.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Michael I. Ellenbogen, M.D., email mellenb6@jhmi.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.30306)
Editor’s ...
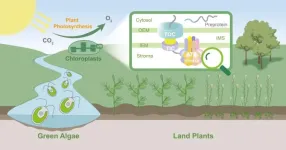
Groundbreaking studies provide key insights into chloroplasts protein import motor
2024-08-27
Two groundbreaking studies published in the journal Cell shed light on the assembly, function and evolutionary diversity of the chloroplast protein import system.
Chloroplasts are fundamental organelles in plant cells that act as the primary site of photosynthesis to sustain life on Earth. Although chloroplasts have their own genome, most of their proteins are encoded in the nucleus and synthesized as preproteins in the cytosol. These preproteins are subsequently transported across the outer and inner envelope membranes of the chloroplasts. The translocon machineries, known as the TOC (translocon at the outer chloroplast membrane) and TIC (translocon at ...
What enables herpes simplex virus to become impervious to drugs?
2024-08-27
All organisms — from fungi to mammals — have the capacity to evolve and adapt to their environments. But viruses are master shapeshifters with an ability to mutate greater than any other organism. As a result, they can evade treatments or acquire resistance to once-effective antiviral medications.
Working with herpes simplex virus (HSV), a new study led by Harvard Medical School researchers sheds light on one of the ways in which the virus becomes resistant to treatment, a problem that could be particularly ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
[Press-News.org] New sensor technology enhances detection of tiny particlesReconfigurable exceptional point-based sensing technology achieves unprecedented sensitivity