(Press-News.org) Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) see a realistic path forward to the manufacture of bio-derivable wind blades that can be chemically recycled and the components reused, ending the practice of old blades winding up in landfills at the end of their useful life.
The findings are published in the new issue of the journal Science. The new resin, which is made of materials produced using bio-derivable resources, performs on par with the current industry standard of blades made from a thermoset resin and outperforms certain thermoplastic resins intended to be recyclable.
The researchers built a prototype 9-meter blade to demonstrate the manufacturability of an NREL-developed biomass-derivable resin nicknamed PECAN. The acronym stands for PolyEster Covalently Adaptable Network, and the manufacturing process dovetails with current methods. Under existing technology, wind blades last about 20 years, and afterward they can be mechanically recycled such as shredded for use as concrete filler. PECAN marks a leap forward because of the ability to recycle the blades using mild chemical processes.
The chemical recycling process allows the components of the blades to be recaptured and reused again and again, allowing the remanufacture of the same product, according to Ryan Clarke, a postdoctoral researcher at NREL and first author of the new paper. “It is truly a limitless approach if it’s done right.”
He said the chemical process was able to completely break down the prototype blade in six hours.
The paper, “Manufacture and testing of biomass-derivable thermosets for wind blade recycling,” involved work from investigators at five NREL research hubs, including the National Wind Technology Center and the BOTTLE Consortium. The researchers demonstrated an end-of-life strategy for the PECAN blades and proposed recovery and reuse strategies for each component.
“The PECAN method for developing recyclable wind turbine blades is a critically important step in our efforts to foster a circular economy for energy materials,” said Johney Green, NREL’s associate laboratory director for Mechanical and Thermal Engineering Sciences.
The research into the PECAN resin began with the end. The scientists wanted to make a wind blade that could be recyclable and began experimenting with what feedstock they could use to achieve that goal. The resin they developed using bio-derivable sugars provided a counterpoint to the conventional notion that a blade designed to be recyclable will not perform as well.
“Just because something is bio-derivable or recyclable does not mean it's going to be worse,” said Nic Rorrer, one of the two corresponding authors of the Science paper. He said one concern others have had about these types of materials is that the blade would be subject to greater “creep,” which is when the blade loses its shape and deforms over time. “It really challenges this evolving notion in the field of polymer science, that you can't use recyclable materials because they will underperform or creep too much.”
Composites made from the PECAN resin held their shape, withstood accelerated weatherization validation, and could be made within a timeframe similar to the existing cure cycle for how wind turbine blades are currently manufactured.
While wind blades can measure the length of a football field, the size of the prototype provided proof of the process.
“Nine meters is a scale that we were able to demonstrate all of the same manufacturing processes that would be used at the 60-, 80-, 100-meter blade scale,” said Robynne Murray, the second corresponding author.
The other coauthors, all from NREL, are Erik Rognerud, Allen Puente-Urbina, David Barnes, Paul Murdy, Michael McGraw, Jimmy Newkirk, Ryan Beach, Jacob Wrubel, Levi Hamernik, Katherine Chism, Andrea Baer, and Gregg Beckham.
The U.S. Department of Energy jointly funded the research through its Advanced Materials and Manufacturing Technologies Office and Bioenergy Technologies Office and their support of the BOTTLE Consortium. Additional research and funding will allow the investigators to build larger blades and to explore more bio-derived formulations.
NREL is the U.S. Department of Energy's primary national laboratory for renewable energy and energy efficiency research and development. NREL is operated for DOE by the Alliance for Sustainable Energy LLC.
END
NREL advances method for recyclable wind turbine blades
Resin made from biomass enables chemical recycling at end of useful lifespan
2024-08-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
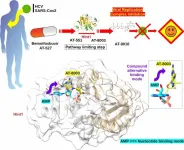
Atomic resolution of the broad-spectrum antiviral drug cascade to facilitate the design of antiviral drugs
2024-08-27
Atomic resolution of the broad-spectrum antiviral drug cascade to facilitate the design of antiviral drugs
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002743
Article Title: The activation cascade of the broad-spectrum antiviral bemnifosbuvir characterized at atomic resolution
Author Countries: France, United States, Germany
Funding: see manuscript END ...
This new technique for studying cell receptors could have sweeping implications for drug development
2024-08-27
One in every three FDA-approved drugs targets a single superfamily of receptors dotting the surfaces of human cells. From beta blockers to antihistamines, these essential, life-saving medications trigger winding biochemical pathways, via these receptors, to ultimately prevent a heart attack, or stop an allergic reaction in its tracks.
But scientists have learned that their story is much more complicated than initially believed—a number of these drugs are in fact targeting a complex composed of one receptor and one associated protein. Now, a ...
Bringing environmental justice to disadvantaged communities
2024-08-27
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Not all communities in the United States face the same risks for environmental problems such as air pollution, noise and wastewater. But how can federal agencies fairly identify which areas deserve the most help?
A new consensus study report from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine (NASEM) offer recommendations for developing tools that can help answer that question.
“Our job was to create methods to identify disadvantaged communities that most need federal resources to address environmental justice issues,” said Harvey Miller, ...
Wiener studying learning & metacognition for the perception of time
2024-08-27
Wiener Studying Learning & Metacognition For The Perception Of Time
Martin Wiener, Associate Professor, Psychology, College of Humanities and Social Sciences (CHSS), received funding to study learning and metacognition for the perception of time.
Via this research, Wiener will conduct a series of studies that will inform metacognition and interval timing. He holds that this work will lead to a new domain of study to further understand how humans learn and adapt to temporal intervals.
By understanding how the brain measures and learns intervals of time, we can better understand ...
Dumas receives funding for study of how distinct NMDA receptor signaling domains regulate hippocampal network dynamics
2024-08-27
Dumas Receives Funding For Study Of How Distinct NMDA Receptor Signaling Domains Regulate Hippocampal Network Dynamics
Theodore Dumas, Associate Professor, Psychology, College of Humanities and Social Sciences (CHSS), received funding for the project: “Distinct NMDA receptor signaling domains regulate hippocampal network dynamics.
Dumas and his collaborators hypothesize that in wildtype mice, NMDA receptors regulate hippocampal network oscillatory activity (slow gamma frequency) in the absence of ion conductance (nonionotropic) and that enhancing GluN2B subunit-type nonionotropic signaling will increase slow gamma power and enhance spatial memory retrieval.
The researchers ...
Second genetic sensor for DNA methylation discovered
2024-08-27
DNA methylation is a process in which a methyl group is attached to the cytosine base of the DNA molecule, and a major way that DNA is epigenetically marked. Epigenetic modifications can act as on-off switches to regulate gene expression and help generate diverse cell types without changing the underlying DNA sequence. It is how the body ensures that brain-related genes don’t get turned on in heart cells, for example.
For this reason, maintenance of the DNA methylation pattern is important to ensure the correct and consistent function of each cell type. But this is no easy feat: the DNA methylation pattern can change over time, and this is linked to a variety of diseases. One ...
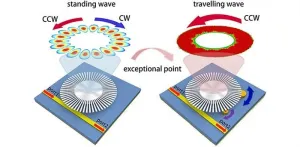
New sensor technology enhances detection of tiny particles
2024-08-27
In recent years, advances in photonics and materials science have led to remarkable developments in sensor technology, pushing the boundaries of what can be detected and measured. Among these innovations, non-Hermitian physics has emerged as a crucial area of research, offering new ways to manipulate light and enhance sensor sensitivity. A recent study published in Advanced Photonics Nexus reports a breakthrough in this field, presenting a new type of sensor that leverages exceptional points (EPs) to achieve unprecedented levels of sensitivity.
This study introduces a highly sensitive and reconfigurable sensor based on a single ...
New technology ‘lights up’ bacteria in wounds for better infection prevention
2024-08-27
LOS ANGELES — Over 6.5 million Americans experience chronic wounds — wounds that do not heal after a few months. Almost all such wounds contain bacteria, which, if not detected and removed, can lead to severe infection and resulting complications, including amputation if a limb is involved.
This is especially true for patients with diabetic foot ulcers (open sores), which affects one-third of people with diabetes. Approximately 20% of those who develop a diabetic foot ulcer will require a lower-extremity amputation, according ...
UCLA receives $120 million from Alya and Gary Michelson for new California Institute for Immunology and Immunotherapy
2024-08-27
UCLA has received a $120 million commitment from surgeon, inventor and philanthropist Dr. Gary Michelson and his wife, Alya, to kick-start the California Institute for Immunology and Immunotherapy, an innovative public-private partnership aimed at spurring breakthrough discoveries that prevent and cure diseases and catalyze economic growth and innovation in Los Angeles.
Michelson, a spine surgeon and prolific inventor who holds nearly 1,000 individual patents, is co-founder and chair of the board of the institute, which will be housed at UCLA’s state-of-the-art research park.
The gift, distributed via ...
Dunick receives funding for Center For Economic Education
2024-08-27
Dunick Receives Funding For Center For Economic Education
Jason Dunick, Associate Chair and Term Associate Professor, Economics, College of Humanities and Social Sciences (CHSS), received $108,692 from Virginia Council on Economic Education for: “Center for Economic Education.”
Dunick will use this funding to support the continuation of the services of the Center for Economic Education. The Center supports K-12 teachers who are teaching economics and personal finance in Virginia.
This grant represents the renewal of a long-standing relationship with the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
[Press-News.org] NREL advances method for recyclable wind turbine bladesResin made from biomass enables chemical recycling at end of useful lifespan